New Record for International Trademark Registrations in 2008 but Signs of Slowdown at Year End
Geneva,
March 10, 2009
PR/2009/584
International trademark activity remained robust overall in 2008 with WIPO receiving a record 42,075 applications under the 84-member Madrid system for the international registration of trademarks (“the Madrid system”), representing a 5.3% rate of growth. Filing activity was stronger in the first six months of the year (+6.9% compared to the same period in 2007) than in the second half of 2008 (+3.9%) mirroring a slowdown in global economic conditions.
Applicants from Germany topped the list of top filers for the 16th consecutive year, followed by users in France, the United States of America (USA), the European Community (EC), Switzerland, Italy, Benelux, China, Japan and Austria. China remained the most designated country in international trademark applications followed by the Russian Federation, reflecting sustained interest by foreign companies in trading in those countries.
Mr. Francis Gurry, WIPO Director General, said that the continued growth in the use of the international trademark system underlines the pivotal importance of trademarks to business, particularly within challenging economic times. “Trademarks play a key role in engendering consumer confidence, an important factor for businesses facing the challenges of the current economic slowdown.” Trademarks enable companies to build and maintain their reputation in the market place and to add value to their commercial operations. “Even in economically difficult times, businesses continue to recognize that a trademark is a smart investment in a company’s reputation and long-term sustainability,” Mr. Gurry added.
Regional and National Filing Trends
The 27 countries of the European Union accounted for over half of the international applications received – some 27,242 – in 2008. This figure includes both the international applications filed through the national trademark offices of the countries concerned and those filed through OHIM which rose to 3,600 international applications representing an increase of 6.8 per cent over 2007. Since October 2004, applicants from the EC have the option to file their international applications either through their national trademark office or through the EC’s regional trademark office (OHIM) in Alicante.
Users in Germany filed 6,214 international applications representing 14.8% of the total and a growth rate of 2%. Applicants in France accounted for 10% of the total filing 4,218 international applications representing 7.3% increase on figures for 2007. Businesses in the United States of America (USA) filed the third largest number of applications – 3,684 or 8,8% of the total number showing a slight decrease (-1.5%) over 2007. OHIM ranked fourth with 3,600 international applications marking an increase of 6.8% over 2007. Switzerland moved into 5th position with an 8.6 % growth rate (2,885 international applications), overtaking Italy which fell to 6th position with 2,763 international applications or 3.7% growth.
A number of countries demonstrated significant growth rates in 2008 and improved their rankings. Japan, with 29.9% growth and 1,278 international applications moved up to 9th place from 12th in 2007. The Russian Federation (+33.9%) ranked 11, up two places from 13th in 2007. Spain retained its 14th place with 14.2 % growth and Turkey its 15th position with a 24.1% rate of growth. The Czech Republic, with a growth rate of 12% moved up to 16th from 17th place. Poland with a 41.5% rate of growth moved up 5 places to rank 19. Slovenia enjoyed a rate of growth of 62.6 % to move up seven places to 23rd position. Latvia moved into 31st position with a 48.7% growth rate, followed by Liechtenstein in 32nd position with 14.2% growth; and Singapore in 33rd position with 13.7% growth. Greece saw a growth rate of 46.3% moving up from 39th to 34th; and Lithuania moved into 38th position with a 19.2% growth rate.
Developing countries accounted for 2,133 filings in 2008, representing 5.1% of total filings. The developing country with the highest growth rate in 2008 was Viet Nam with a 51.6% growth rate.
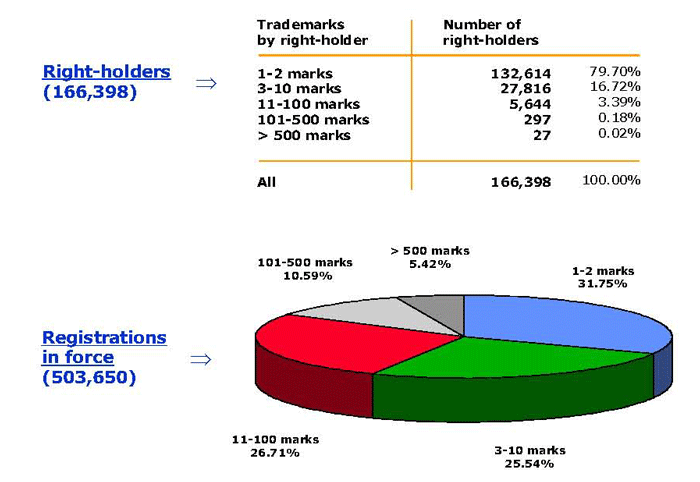
The total number of international registrations in force reached 503,650 (this includes the record figure of 40,985 registrations made in 2008, representing a 6.5 per cent increase on 2007). These registrations belong to 166,398 right holders who are mostly small and medium-sized enterprises.
Top Holders and Top Applicants
With 216 international trademark applications, Lidl from Germany was the largest filer in 2008, followed by Nestlé (Switzerland), Henkel (Germany), Boehringer Ingelheim (Germany), Novartis (Switzerland), Janssen Pharmaceutica (Belgium), BSH Bosch und Siemens (Germany), Zhejiang Medicine Company (China), L’Oréal (France), Deutsche Telekom (Germany), AstraZeneca (Sweden), KRKA (Slovenia), Glaxo Group (UK), Beiersdorf (Germany), MIP Metro (Germany), Hofer Kommanditgesellschaft (Austria), 3 Suisses International (France), ITM Enterprises (France), Egis Gyógyszergyár (Hungary), Actavis Group PTC (Iceland). In 2008, a Chinese firm, Zheijiang Medicine Company, broke into the top 10 ranking for the first time.
Henkel (Germany), with a total of 2,731, holds the largest number of international trademark registrations under the Madrid system. The top twenty holders by the end of 2008 were: Henkel (Germany), Janssen Pharmaceutica (Belgium), Novartis (Switzerland), L’Oréal (France), Nestlé (Switzerland), Unilever (Netherlands), Sanofi-Aventis (France), ITM Enterprises (France), Siemens (Germany), BASF (Germany), Lidl (Germany), Biofarma (France), Richter Gideon (Hungary), Boehringer Ingelheim (Germany), Syngenta (Switzerland), Philips (Netherlands), Kraft Foods (Switzerland), Ecolab (Germany), Merck (Germany) and Deutsche Post Immobilienservice (Germany).
Top Designated Countries
A record 378,894 new designations (made in international registrations or as subsequent designations) of Madrid Union members were notified in 2008, representing a 2.3% increase over 2007. When submitting an international trademark application, applicants must designate those member countries in which they want their mark to be protected. Applicants can also extend the effects of an international registration to other members at a later date by filing a subsequent designation. In this way, the holder of an international registration can expand the geographical scope of the protection of a mark in line with evolving business needs.
For the fourth consecutive year, China was the most designated country. With 17,829 designations, it accounted for 4.7% of the total number of new designations and enjoyed a 6.9% increase in such designations over 2007. The second most designated country was the Russian Federation with 16,768 designations (+8.5%), followed by the USA with 15,715 designations (+7.5%), Switzerland with 14,907 designations (+2.6%), the European Community with 14, 502 (+13.8%) and Japan with 12,748 designations (+3.7%).
The EC continues to be a favorite target market for designations. Having received 14,502 designations in 2008 (+13.8%), the EC confirms its 5th position in the ranking of most designated members of the Madrid Union.
Some of the countries that have moved up in the ranking of most designated countries compared to 2007 are Ukraine (from 8th to 7th place), Singapore (from 14th to 12th place), Belarus (from 19th to 15th place), Serbia (from 21st to 16th place), Montenegro (from 35th to 23rd place) and Viet Nam (from 29th to 24th place).
Profile and Costs of Registrations Recorded in 2008
In 2008, on average, 8 Madrid Union members were designated per registration by applicants seeking international trademark protection under the Madrid system and 59% of the registrations recorded in 2008 contained one to five designations.
In submitting a trademark application, an applicant has to specify the goods or services to which the trademark will be applied in accordance with an international classification system known as the “Nice Classification.” The most popular classes of goods and services in international trademark registrations recorded in 2008 were Class 9 (which covers, e.g., computer hardware and software) representing 8.5% of the total, Class 35 (which covers services such as office functions, advertising and business management) which represented 7.1% of the total, Class 42 (which covers services provided by e.g., scientific, industrial or technological engineers and computer specialists) which represented 5.6% of the total, Class 25 (which covers clothing, footwear and headgear) representing 4.9% of the total and Class 41 (which covers services in the area of education, training, entertainment, sporting and cultural activities) representing 4.5% of the total.
In 2008, applicants paid on average 3,734 Swiss francs for an international registration; for 80% of the registrations the fees paid were less than 5,000 Swiss francs.
The number of trademark renewals went up by 11.4 per cent to reach a total of 19,472. The Madrid system allows for the central administration of an international trademark portfolio, as it provides for procedures which enable trademark holders to record modifications to international registrations (for example, changes of ownership, changes in name or address of the holder or changes in the appointment of the representative of the holder) through the submission of a single request at WIPO. Modifications recorded in 2008 totaled 91,300 representing a 7.1% increase over 2007.
Development of the Madrid System
Membership of the Madrid Union expanded from 81 to 84 members in 2008 with the accession of Ghana, Madagascar and Sao Tome and Principe. An expanding membership and an ever wider geographical spread of the system make it a more attractive option for businesses operating in international markets.
Madrid system operations became fully trilingual (English, French and Spanish) in 2008 meaning that an international application can now be filed in any of these, irrespective of which treaty or treaties governs the application. The Madrid Assembly also commissioned a study on the implications of introducing additional filing languages to the system.
On the legal side, users saw the repeal of the “safeguard clause”. This means that for states bound by both the Madrid Agreement and the Madrid Protocol - the two treaties which govern the Madrid system - only the provisions of the Protocol, the most recent and flexible of the two treaties, will apply. The Madrid Protocol relaxes certain provisions of the Agreement, in order to allow adherence by states and intergovernmental organizations (IGOs) whose trademark registration systems do not match with the provisions of the Agreement, in particular in respect of the fees to be paid by applicants and the applicable time-limits.
An IT modernization program was launched in 2008 which will further enhance the services available under the Madrid system. This will allow WIPO and national/regional trademark offices to improve and expand electronic communication of international applications and notifications under the procedures of the Madrid system, as well as to upgrade the web-based information products and other services available on the WIPO website, such as the ROMARIN database and the WIPO Gazette of International Marks. New features allow users to track their international registrations in designated countries.
Madrid System for the International Registration of Marks
Year Report 2008
Table 1: Major Filing Contracting Parties
Number of applications filed by Contracting Party
Shares within total filings in 2008 and growth rates as compared to 2007
| Contracting Party of Origin | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | Share | Growth | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Germany (DE) | 5,395 | 5,803 | 5,663 | 6,090 | 6,214 | 14.8% | 2.0% |
| 2 | France (FR) | 3,518 | 3,497 | 3,705 | 3,930 | 4,218 | 10.0% | 7.3% |
| 3 | United States of America (US) | 1,737 | 2,849 | 3,148 | 3,741 | 3,684 | 8.8% | -1.5% |
| 4 | European Community (EM) | 354 | 1,852 | 2,445 | 3,371 | 3,600 | 8.6% | 6.8% |
| 5 | Switzerland (CH) | 2,133 | 2,235 | 2,468 | 2,657 | 2,885 | 6.9% | 8.6% |
| 6 | Italy (IT) | 2,499 | 2,340 | 2,958 | 2,664 | 2,763 | 6.6% | 3.7% |
| 7 | Benelux (BX) | 2,482 | 2,426 | 2,639 | 2,510 | 2,667 | 6.3% | 6.3% |
| 8 | China (CN) | 1,015 | 1,334 | 1,328 | 1,444 | 1,585 | 3.8% | 9.8% |
| 9 | Japan (JP) | 692 | 893 | 847 | 984 | 1,278 | 3.0% | 29.9% |
| 10 | Austria (AT) | 1,181 | 1,191 | 1,117 | 1,134 | 1,245 | 3.0% | 9.8% |
| 11 | Russian Federation (RU) | 575 | 604 | 622 | 889 | 1,190 | 2.8% | 33.9% |
| 12 | United Kingdom (GB) | 917 | 1,016 | 1,054 | 1,178 | 1,162 | 2.8% | -1.4% |
| 13 | Australia (AU) | 683 | 852 | 1,100 | 1,169 | 1,092 | 2.6% | -6.6% |
| 14 | Spain (ES) | 866 | 854 | 994 | 859 | 981 | 2.3% | 14.2% |
| 15 | Turkey (TR) | 593 | 787 | 733 | 717 | 890 | 2.1% | 24.1% |
| 16 | Czech Republic (CZ) | 615 | 547 | 559 | 541 | 607 | 1.4% | 12.2% |
| 17 | Denmark (DK) | 441 | 510 | 479 | 573 | 565 | 1.3% | -1.4% |
| 18 | Sweden (SE) | 462 | 409 | 400 | 478 | 476 | 1.1% | -0.4% |
| 19 | Poland (PL) | 344 | 334 | 339 | 294 | 416 | 1.0% | 41.5% |
| 20 | Bulgaria (BG) | 334 | 391 | 426 | 431 | 386 | 0.9% | -10.4% |
| 21 | Norway (NO) | 218 | 235 | 312 | 403 | 368 | 0.9% | -8.7% |
| 22 | Portugal (PT) | 175 | 263 | 276 | 355 | 344 | 0.8% | -3.1% |
| 23 | Slovenia (SI) | 201 | 180 | 177 | 182 | 296 | 0.7% | 62.6% |
| 24 | Finland (FI) | 198 | 208 | 239 | 278 | 282 | 0.7% | 1.4% |
| 25 | Serbia (RS) | 86 | 107 | 157 | 275 | 282 | 0.7% | 2.5% |
| 26 | Ukraine (UA) | 78 | 105 | 133 | 195 | 217 | 0.5% | 11.3% |
| 27 | Hungary (HU) | 231 | 152 | 217 | 438 | 214 | 0.5% | -51.1% |
| 28 | Croatia (HR) | 135 | 79 | 150 | 185 | 200 | 0.5% | 8.1% |
| 29 | Slovakia (SK) | 249 | 215 | 241 | 190 | 187 | 0.4% | -1.6% |
| 30 | Republic of Korea (KR) | 127 | 148 | 190 | 330 | 186 | 0.4% | -43.6% |
| 31 | Latvia (LV) | 109 | 81 | 103 | 115 | 171 | 0.4% | 48.7% |
| 32 | Liechtenstein (LI) | 89 | 96 | 129 | 148 | 169 | 0.4% | 14.2% |
| 33 | Singapore (SG) | 93 | 138 | 161 | 146 | 166 | 0.4% | 13.7% |
| 34 | Greece (GR) | 49 | 65 | 81 | 80 | 117 | 0.3% | 46.3% |
| 35 | Iceland (IS) | 33 | 39 | 92 | 110 | 101 | 0.2% | -8.2% |
| 36 | Romania (RO) | 58 | 101 | 97 | 103 | 99 | 0.2% | -3.9% |
| 37 | Estonia (EE) | 75 | 72 | 96 | 101 | 93 | 0.2% | -7.9% |
| 38 | Lithuania (LT) | 63 | 101 | 84 | 78 | 93 | 0.2% | 19.2% |
| 39 | Morocco (MA) | 57 | 66 | 119 | 93 | 73 | 0.2% | -21.5% |
| 40 | Belarus (BY) | 29 | 24 | 23 | 63 | 69 | 0.2% | 9.5% |
| Other countries | 283 | 378 | 370 | 423 | 444 | 1.1% | 5.0% | |
| Total | 29,472 | 33,577 | 36,471 | 39,945 | 42,075 | 100% | 5.3% |
Madrid System for the International Registration of Marks
Year Report 2008
Table 2: Most Designated Contracting Parties (2008)
Number of designations by designated Contracting Party
(Includes designations in new registrations and subsequent designations)
Growth rates as compared to 2007
| Designated Contracting Party | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | Share | Growth | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China (CN) | 9,265 | 13,575 | 15,801 | 16,676 | 17,829 | 4.7% | 6.9% |
| 2 | Russian Federation (RU) | 9,940 | 12,813 | 14,432 | 15,455 | 16,768 | 4.4% | 8.5% |
| 3 | United States of America (US) | 7,109 | 11,863 | 13,994 | 14,618 | 15,715 | 4.1% | 7.5% |
| 4 | Switzerland (CH) | 10,137 | 13,197 | 14,260 | 14,528 | 14,907 | 3.9% | 2.6% |
| 5 | European Community (EM) | 114 | 6,309 | 10,640 | 12,744 | 14,502 | 3.8% | 13.8% |
| 6 | Japan (JP) | 7,071 | 10,104 | 11,844 | 12,296 | 12,748 | 3.4% | 3.7% |
| 7 | Ukraine (UA) | 6,361 | 8,271 | 9,057 | 9,751 | 10,635 | 2.8% | 9.1% |
| 8 | Australia (AU) | 5,617 | 7,989 | 9,115 | 9,848 | 10,529 | 2.8% | 6.9% |
| 9 | Turkey (TR) | 6,272 | 8,602 | 8,958 | 9,377 | 9,844 | 2.6% | 5.0% |
| 10 | Norway (NO) | 6,821 | 8,443 | 9,102 | 9,346 | 9,787 | 2.6% | 4.7% |
| 11 | Republic of Korea (KR) | 4,852 | 7,160 | 8,334 | 8,988 | 9,539 | 2.5% | 6.1% |
| 12 | Singapore (SG) | 4,451 | 6,127 | 6,717 | 7,005 | 7,607 | 2.0% | 8.6% |
| 13 | Croatia (HR) | 5,298 | 6,716 | 6,970 | 7,059 | 7,482 | 2.0% | 6.0% |
| 14 | Germany (DE) | 8,275 | 9,150 | 8,147 | 7,184 | 6,955 | 1.8% | -3.2% |
| 15 | Belarus (BY) | 4,382 | 5,401 | 5,818 | 6,140 | 6,724 | 1.8% | 9.5% |
| 16 | Serbia (RS) | 4,562 | 5,513 | 5,644 | 5,956 | 6,315 | 1.7% | 6.0% |
| 17 | United Kingdom (GB) | 7,720 | 8,288 | 7,482 | 6,502 | 6,204 | 1.6% | -4.6% |
| 18 | Italy (IT) | 7,945 | 8,817 | 7,374 | 6,618 | 6,171 | 1.6% | -6.8% |
| 19 | France (FR) | 8,094 | 8,587 | 7,495 | 6,443 | 6,035 | 1.6% | -6.3% |
| 20 | Spain (ES) | 7,922 | 8,329 | 7,231 | 6,298 | 5,830 | 1.5% | -7.4% |
| 21 | Benelux (BX) | 7,697 | 7,922 | 6,800 | 5,979 | 5,463 | 1.4% | -8.6% |
| 22 | Austria (AT) | 7,487 | 7,638 | 6,564 | 5,928 | 5,208 | 1.4% | -12.1% |
| 23 | Montenegro (ME) | - | - | - | 3,851 | 5,210 | 1.4% | 35.3% |
| 24 | Viet Nam (VN) | 2,254 | 2,639 | 3,074 | 4,381 | 4,966 | 1.3% | 13.4% |
| 25 | The F.Y.R. of Macedonia (MK) | 3,342 | 4,337 | 4,261 | 4,689 | 4,882 | 1.3% | 4.1% |
| 26 | Poland (PL) | 7,598 | 6,825 | 6,092 | 5,553 | 4,815 | 1.3% | -13.3% |
| 27 | Romania (RO) | 6,125 | 7,766 | 8,103 | 5,649 | 4,429 | 1.2% | -21.6% |
| 28 | Morocco (MA) | 3,091 | 3,992 | 4,229 | 4,194 | 4,362 | 1.2% | 4.0% |
| 29 | Republic of Moldova (MD) | 2,836 | 3,500 | 3,793 | 4,274 | 4,346 | 1.1% | 1.7% |
| 30 | Kazakhstan (KZ) | 2,542 | 3,099 | 3,463 | 4,004 | 4,331 | 1.1% | 8.2% |
| 31 | Hungary (HU) | 6,508 | 5,914 | 5,039 | 4,528 | 4,052 | 1.1% | -10.5% |
| 32 | Liechtenstein (LI) | 3249 | 3,885 | 3,898 | 3,713 | 4,050 | 1.1% | 9.1% |
| 33 | Bosnia and Herzegovina (BA) | 3,282 | 3,797 | 3,798 | 3,976 | 4,041 | 1.1% | 1.6% |
| 34 | Czech Republic (CZ) | 6,633 | 6,018 | 5,161 | 4,546 | 4,015 | 1.1% | -11.7% |
| 35 | Georgia (GE) | 2,439 | 2,951 | 3,347 | 3,801 | 3,980 | 1.1% | 4.7% |
| 36 | Azerbaijan (AZ) | 1,956 | 2,231 | 2,329 | 3,143 | 3,801 | 1.0% | 20.9% |
| 37 | Bulgaria (BG) | 5,407 | 6,596 | 6,903 | 4,987 | 3,777 | 1.0% | -24.3% |
| 38 | Portugal (PT) | 5,609 | 5,695 | 4,839 | 4,130 | 3,767 | 1.0% | -8.8% |
| 39 | Monaco (MC) | 2,987 | 3,792 | 3,876 | 3,737 | 3,728 | 1.0% | -0.2% |
| 40 | Albania (AL) | 2137 | 2721 | 2,881 | 3,268 | 3,588 | 0.9% | 9.8% |
| Other Countries | 82,813 | 89,967 | 87,860 | 89,071 | 89,957 | 23.7% | 1.0% | |
| Total | 298,200 | 356,539 | 364,725 | 370,234 | 378,894 | 100% | 2.3% |
Madrid System for the International Registration of Marks
Year Report 2008
Graph 1 – Trademarks in Force in the International Register
On December 31, 2008
- Tel: (+41 22) 338 81 61 / 338 72 24