Detection systems have become essential technologies for ensuring workplace safety within all sectors. These systems rely on a combination of hardware and software to identify, prevent and respond to workplace accidents, thereby minimizing risks to workers and improving operational efficiency.
Patents provide an overview of technological developments, industry priorities and potential future directions. To this end, this section focuses on technologies associated with Detection, as seen from the perspective of patents.
Analysis and the development of a patent dataset involved segmenting the Detection category into seven key technology areas:
Safety software solutions: Comprehensive platforms designed to manage safety protocols, track incidents, and ensure regulatory compliance. These systems enable real-time monitoring and detailed reporting.
Fire detection and prevention systems: Advanced technologies using sensors and alarms to identify fire hazards early, facilitating prompt responses and prevention measures.
Gas detection equipment: Devices that monitor air quality in order to detect hazardous gases, ensuring worker safety, particularly in confined or high-risk areas.
Temperature monitoring systems: Continuous temperature-monitoring solutions to prevent overheating and mitigate risks associated with extreme temperatures.
Noise level monitoring: Systems that measure and manage noise exposure in environments where excessive noise poses health risks such as hearing loss.
Radiation detection equipment: Specialized tools for detecting and monitoring radiation in industries where exposure is a concern, thereby safeguarding worker health.
Location-based safety systems: Technologies leveraging GPS and other location-tracking methods to provide real-time data for quick emergency response and enhanced situational awareness.
This chapter is structured into three main parts:
Global patent landscape: A broad analysis of the global Detection patent landscape is conducted, the dynamics of publication examined, the most innovative regions or countries identified, and the key players driving advancements in the field of Detection technologies profiled.
Focus on international patent families (IPF): Focusing on IPFs allows the detection of the technology trends that companies consider valuable enough to internationalize and seek protection in overseas markets. Such a focus emphasizes those areas in which significant investments are being made, indicating promising channels for innovation and potential market returns.
Benchmark inventions: Lastly, specific patents that illustrate the field particularly well are highlighted. These examples showcase the cutting-edge innovations shaping the future of Detection technologies.
This multi-faceted approach ensures a comprehensive understanding of how Detection technologies are evolving within the OHS domain and provides actionable insights into the technological strategies shaping workplace safety.
Global patenting landscape
Based on the data collected in this study, Detection technologies accounts for a total of 157,183 patent families, equivalent to 35% of the global patent portfolio for OHS technologies. 17,919 of these are classified as international patent families (Figure 5.2).
Patenting activity corresponds to the number of patent families published annually within a specific field. This metric is based on the date of first publication of each patent family, which typically occurs around 18 months after the filing date. Analyzing patenting activity provides valuable information on innovation trends in a particular field. Comparing the evolution of patent filings in a specific field to the overall growth in global patent filings worldwide enables us to assess the dynamism and innovation intensity of innovation in that field. Such a comparison serves to determine whether a field is experiencing rapid development, stagnation or decline, relative to overall technological progress.
According to Figure 5.3, the number of patents in relation to Detection increased steadily from 2014 to 2023 which represents a CAGR of 10.8%. It peaked in 2021 with a significant 17,825 patent families. This rise shows an increased focus on innovation and safety within the sector. The main reasons for this are improvements in technology and an overall digital change in workplaces. New developments in sensors, automation, the IoT, AI, and wearable devices led to many new inventions during this period. These technologies make workplaces safer and provide real-time detection and monitoring abilities, which probably heightened interest. Also, government regulations and more stringent work safety rules may have contributed to this trend impelling the companies to invest in new solutions that adhere to the rules and keep workers safe.
Top jurisdictions
A look into patent families allows us to identify which countries are driving innovation in certain fields. The first filing in a patent family (known as the priority filing), usually called the priority filing, is mostly done in the applicant's home country. This decision is largely driven by legal frameworks and economic reasons; hence, the location of the priority filing (office of first filing) is a strong indicator of active innovation dynamics.
In the OHS Detection category, the filing trend is clearly reflected in the geographical distribution of patent filings, with Asia in the lead (Figure 5.4). China dominates the region, with 115,975 patent families, followed by the Republic of Korea with 8,227 and Japan with 5,476. The Americas, mainly driven by the United States, take second place with 12,900 patent families, or almost 96% of total filings in the region. Europe ranks third, with 4,064 patent families.
The geographical distribution underlines Asia's central role in shaping the landscape of Detection technologies, with China emerging as an undisputed leader in driving technological advances. The rise in Chinese patent filings not only reflects the country's strategic focus on innovation but also consolidates its position as a global hub for cutting-edge development. In contrast, the United States and Europe exhibit a slower patenting activity rate.
The Relative Specialization Index (RSI) is used to compare the published patenting activity of different countries within the same technology area. RSI is a measure of a country's share of patent families in a particular field of technology as a fraction of that country’s share of patent families in all fields of technology. ln other words, RSI has the advantage of providing a comparison between the patenting activity of two countries' relative to the overall patenting activity of those same two countries. When analyzing patent data, normalized RSI is used
Figure 5.5 shows that India and Canada show the strongest and most sustained specialization in Detection technologies, with consistently high focus. China and the United States demonstrate an initially strong engagement, but China's specialization has declined significantly over time, whereas that of the United States has stabilized after some fluctuation. The Republic of Korea has also undergone a gradual decline, reflecting a reduced emphasis. Europe has maintained a moderate focus, whereas Japan has consistently showed minimal specialization, despite a slight recovery in recent times.
Overall, while some countries like India and Canada lead in sustained commitment, the general trend shows a global decline in RSI values, indicating a reduced focus on Detection technologies. This may indicate either that the field is maturing or there has been a shift in innovation priorities toward other emerging technological domains.
Periodic patent growth in this field has varied widely by country. China and India underwent strong early growth, with India maintaining momentum while China's activity declined after 2020. The United States, European countries, and Japan saw a modest increase initially, followed by a decline over recent years. The Republic of Korea has shown moderate steady growth. Overall, the data highlight India's sustained leadership, contrasting with a declining trend in a traditionally strong Europe, Japan, and the United States.
Analysis of global patent family coverage provides strategic clues as to which regions and markets manufacturers consider essential targets for their innovations. Such data highlights where companies see the greatest potential for commercial success and the importance of securing IP rights to maintain a competitive edge in these markets.
In the realm of Detection technologies, China has emerged as a dominant force, boasting an impressive 73,344 patent families (Figure 5.7). This figure underscores China’s leading role in both innovation and market share in this field. Meanwhile the United States, with 13,477 patent families, occupies second spot, reflecting its robust but relatively focused innovation landscape. The Republic of Korea is third, with 7,852 patent families, clearly demonstrating its role as a technological giant in this field. Other regions and countries also play their part in the global innovation landscape, with the EPO playing a significant role, protecting 6,668 patent families, reflecting Europe's collective focus on occupational safety technologies. In terms of number of patent families, Japan (5,720), India (4,858) and Germany (4,627) are also key players, each contributing to the global innovation landscape in a distinct way. These figures not only highlight the geographical distribution of innovation but also underline the global competition and collaboration behind advances in this crucial domain.
These results and numbers reflect the strategic focus of innovators on key global markets, with China asserting itself as the main hub of innovation and commercial activity in the field of workplace safety technologies. The United States follows as a major player, demonstrating its role in promoting high-value advances. Strong patenting activity in regions and countries, such as the Republic of Korea, Europe and Japan highlights the growing international commitment to workplace safety innovation, driven by the increasing importance of industrial safety standards.
Top patent applicants
Examining patent applicants in this area affords a comprehensive overview of those companies and organizations driving innovation and actively seeking to protect their technological advancements. This analysis identifies the key players contributing to the development of Detection solutions and spotlights their commitment to securing IP rights for their inventions.
Among the top 20 patent applicants in the field of OHS Detection technologies (Figure 5.8), SGCC (State Grid Corporation of China) leads with over 2,500 patent families, well ahead of China Southern Power Grid, which comes second with 692 patent families, while well- known multinationals such as Hauwei, Samsung and IBM hold between 200 and 300 patent families each. These applicants cover various sectors, including energy, technology and academia. This distribution underlines the predominance of Chinese entities, particularly within the energy and technology sectors, in the growth of patenting activity in this field.
Analyzing the dynamics of the top applicants' patent publications, Figure 5.9 shows that there have generally been a high level of innovation activity that peaked between 2010 and 2022 and was followed by a potential recent decline in filings.
Between 2014 and 2023, China State Construction Engineering topped the list with a 42.0% CAGR, followed by China Railway Construction at 37.4% and China Southern Power Grid at 23.6%, reflecting robust advancements in Detection technologies. On the other hand, Microsoft experienced the largest decline at –18.7%, followed by Honeywell at –10.2% and Huawei at –5.5%, indicating a reduction in activity in the Detection category. These figures underscore the diverse organizational priorities in Detection technologies over the period.
Major applicants' activity reveals that the increase in patent filings observed since 2005 has mainly been driven by applicants within the electronics and technology sectors, such as Samsung, IBM, Huawei, LG and Robert Bosch. Energy-sector Chinese players appeared after 2007, with an increasingly high filing rate. Interestingly, this wave of company filings in China was preceded by earlier contributions from Chinese universities, such as Beijing University of Technology, Tsinghua University, Zhejiang University and the China University of Mining and Technology, which probably laid the groundwork for innovation in this field.
International patenting landscape
This section emphasizes the value of analyzing International Patent Families (IPFs) to uncover meaningful insights into technological trends.
Analyzing IPFs helps to filter out less impactful or localized inventions, leaving a dataset that reflects substantial investments and a focus on long-term technological and commercial viability. As a result, this approach provides a clearer view of the key trends shaping innovation and reveals the areas where companies are placing their strategic bets for the future.
IPF growth and development
A review of IPF trends in the field of Detection technologies reveals several key trends. Over the last decade, the total number of patents in this field has increased significantly, mainly due to activity in China. However, many such patents are limited to filings in China and do not extend internationally, resulting in their exclusion from the IPF counts.
As a result, the proportion of IPFs representing patents filed in multiple jurisdictions, has remained consistently low. While the IPF ratio was relatively high in the early years of the period studied (e.g. 38% in 2005 and 2006), it has fallen over time, dropping to just 6% in 2023.
This trend reflects the growing gap between total patenting activity and innovations with global impact. Overall, the IPF ratio for all patents in the Detection segment over the last 20 years until 2023 has averaged 12%, underlining the limited international reach of patent filings in this field.
Furthermore, with regards to IPF growth, the figures suggest that while the total number of patents has increased considerably, the growth of IPFs has remained relatively modest. This indicates there there is less emphasis on global patent protection. The stagnation or slower growth of IPFs could be due to several factors, such the costs associated with international filings, which could deter small companies or individual inventors from pursuing IPFs. In addition, many innovations in the Detection category could be specific to regional needs or regulatory environments, thus reducing the perceived need for international coverage.
IPF top jurisdictions
A closer analysis of the countries in which applicants pursue protection through international patent families (IPFs) helps to illustrate the deliberate strategy of innovators to secure IP in the world's major markets, giving priority to those regions with robust technology ecosystems and considerable business potential.
Figure 5.11 shows that the United States holds a dominant position in globally protected patent families for Detection technologies, with a total of 8,374 patent families. The EPO follows closely behind, with 6,084 patent families, reflecting its reach across multiple European jurisdictions. China also has a significant presence in this field, with 5,951 patent families, underlining its important position as an attractive market for these technologies. Germany (3,955), Japan (3,600) and the United Kingdom (2,843) are other notable countries, representing important centers of interest in this sector.
IPF top patent applicants
The OHS category of Detection technologies has the standard characteristics of emerging technology sectors, with Figure 5.12 showing that 79% of applicants are from industry and hold 84% of the IPFs (which indicates that portfolios are fairly small) and a relatively high number of independent inventors (14% of applicants) hold 9% of the IPFs in the field.
Key players in Detection technologies are shown in Figure 5.13. Huawei holds the largest number of patent families (270), followed by Samsung Electronics (254), ZTE (176) and Microsoft (155). Among the top 20 patent applicants, Asian companies are the most represented, with 12 entities from countries such as Japan, China, and the Republic of Korea. Northern America follows with seven applicants, while Europe is represented by Bosch and Siemens. Japan stands out with seven companies listed, indicating a strong national presence. The data reflects a geographically diverse distribution of patent activity, with leading contributions from both corporate and multinational entities.
The dominance of technology giants shows major technology companies leading the way in innovation and holding most of the Detection patents. This suggests that big firms, with their greater resources and strategic focus, are the primary drivers of new advancements in workplace Detection technologies.
IPF main technologies
As shown in Figure 5.14, observations from 2018 to 2023 reveal steady growth in IPF filings, peaking around 2021 for various Detection technologies. Key technology areas gas detection, fire detection, location-based safety systems, and noise level monitoring experienced significant increases during this period, particularly in 2021.
Following the peak, there is a notable decline in patent filings across most technology areas, especially in the technologies location-based systems, noise monitoring and safety software solutions. This is most evident in 2023.
Location-based safety systems emerge as the most prominent areas for patent filings, with the highest number of inventions recorded between 2018 and 2023, accounting 4,505 patent families. Despite the overall drop, certain technology areas, namely temperature monitoring systems and radiation detection equipment, show relatively less fluctuation, maintaining a moderate level of patenting activity even in 2023.
Benchmark inventions in Detection technologies
Main technologies and application fields
To gain a deep understanding of the technological approaches in the OHS Detection category, the dataset of related simple patent families has been segmented into seven main distinct technology areas listed below in descending order according to the number of patents:
Location-based security systems: With a total of 61,872 patents, this technology area boasts the highest number of patent families.
Safety software solutions: Follows closely behind, with 54,239 patents, indicating significant innovation in security-enhancing software solutions.
Temperature monitoring systems: A total of 34,693 patents reflects the importance of temperature monitoring for safety in a variety of applications.
Radiation detection equipment: This technology area includes 16,533 patents, reflecting efforts to develop technologies for detecting harmful levels of radiation.
Gas detection equipment: With 14,116 patents, this technology area focuses on gas detection for safety purposes, for example to prevent exposure to toxic substances or explosions.
Fire detection and prevention systems: Progress in the field of fire safety is reflected in the 10,140 patents published.
Noise-level monitoring: This is the smallest technology area, with 5,935 patents, indicating a niche specializing in noise level monitoring for safety and regulatory compliance purposes.
Figure 5.15 highlights key trends in patent filings from 2014 to 2023 in Detection technologies. A significant growth trajectory is observed across most technology areas, culminating in a peak around 2021. This peak reflects a heightened emphasis on safety-related innovations, potentially driven by regulatory changes, technological advancements, or a heightened awareness of workplace hazards. However, following this surge, a notable decline in patent filings is observable in most technology areas, suggesting market saturation, shifting priorities, or reduced research and development activities post-2021.
Among the technology areas, safety software solutions and location-based safety systems emerge as dominant fields of innovation. Together, these areas account for the highest number of patent filings, with 34,506 and 38,705 patent families respectively between 2014 and 2023. This prominence underscores a growing reliance on digital solutions and real-time tracking technologies for workplace safety enhancement.
Figure 5.16 provides a comprehensive overview of patent filing trends for Detection technologies in different industrial sectors between 2014 and 2023. The findings reveal that the construction and manufacturing sectors remain the main contributors to patent filings, a key indicator of the significant investment in safety technologies within these industries.
The construction sector stands out as the leader in patent filings, with steady growth observed over time period in question. A steady increase in filings could be attributable to the ongoing progress of safety technologies in construction, stimulated by strong industry demand and strict regulations concerning worker safety.
In contrast, the healthcare and agriculture sectors show a more moderate growth in patent filings, with a marked decrease from 2021 onward. The healthcare sector has seen a sharp decline, with filings falling from 1,230 in 2021 to 784 in 2023.
Example patents
The examples that follow have been chosen because considered particularly representative of the field.
Patent WO2021/220108 outlines the innovative features and benefits of the Smart PPE Respirator System, assigned to 3M Innovative Properties. This invention introduces a novel approach to PPE by integrating a breath temperature sensor that monitors exhalation breath temperature, thereby facilitating the calculation of a core body temperature metric. This advancement is designed to enhance worker safety through real-time monitoring and alerts for potential core temperature issues, ultimately improving comfort and minimizing the need for invasive temperature measurement techniques.
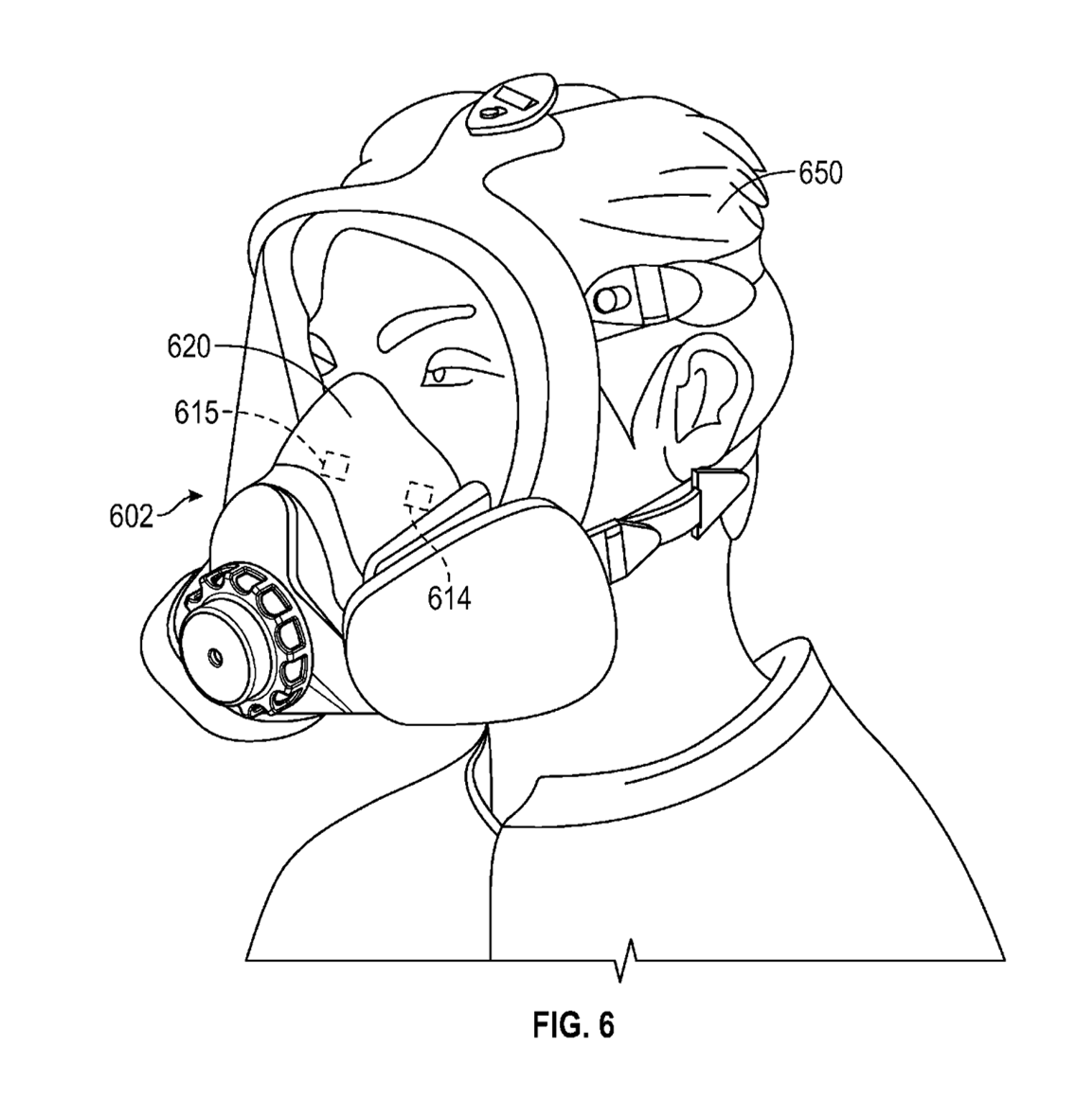
This system is particularly beneficial in various environments where PPE is crucial, including construction sites, healthcare settings, and hazardous work environments. By ensuring the safety and well-being of users, the invention addresses a significant need for effective temperature monitoring in challenging conditions.
Patent JP7573824, assigned to Herutu Electronics, focuses on an innovative apparatus designed to detect the wearing state of PPE, particularly helmets, through the use of contact detection sensors. By enhancing safety measures in hazardous environments, this technology aims to prevent accidents caused by improper equipment usage.
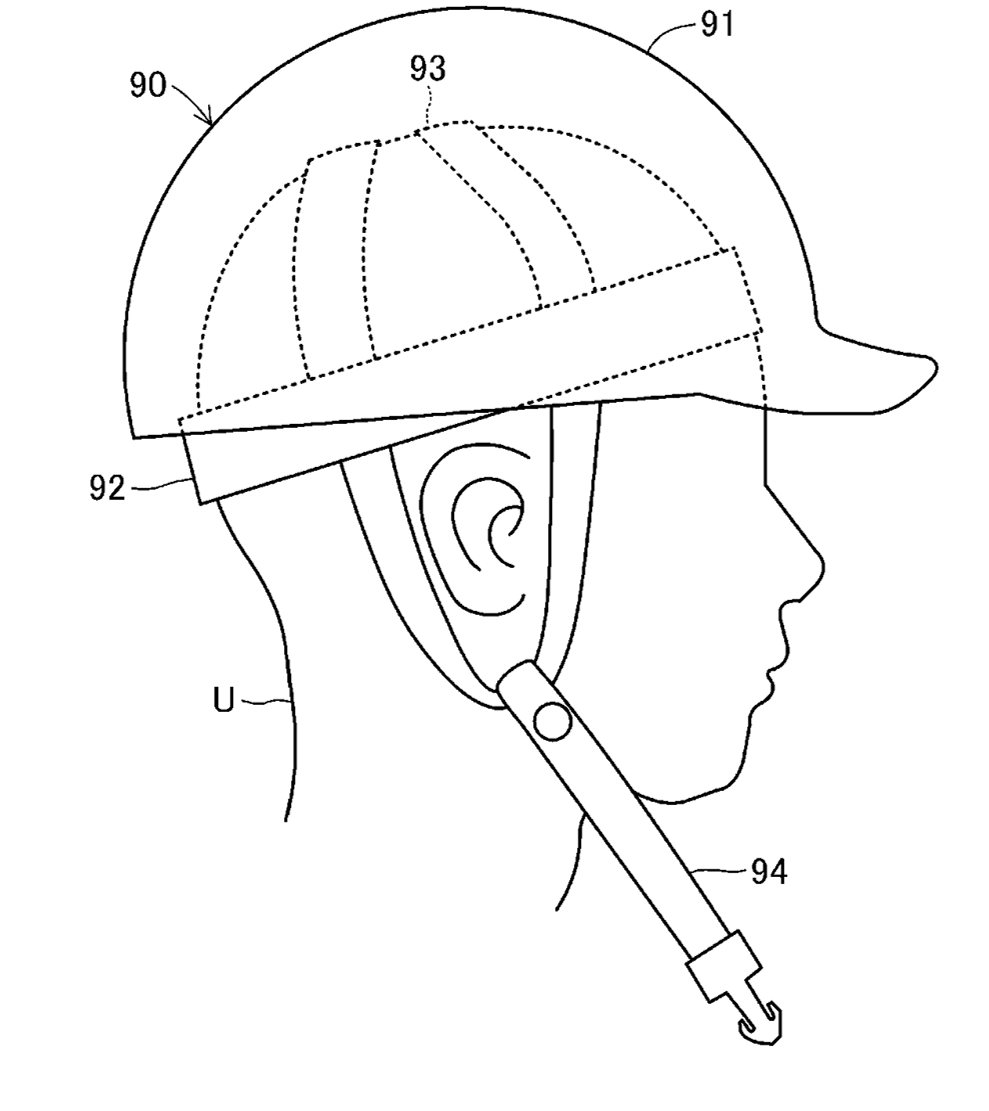
The primary objective of this invention is to establish a dependable method for detecting the wearing state of personal protective equipment, particularly in high-risk environments such as construction sites or factories. The apparatus is designed to ensure that workers are adequately equipped, thereby promoting safety and adherence to safety regulations.
Patent CN105683729 provides an overview of the multi-spectral flame detector developed by MSA Technology. The invention is designed specifically for industrial safety applications in hazardous environments, focusing on the detection of flames and the quantification of radiant energy. The system's advanced features aim to enhance safety measures and response capabilities in industrial settings.
The system is designed to monitor radiant energy, detect flames, quantify radiant heat output, and relay information to utilization devices. This ensures timely alerts and bolsters safety measures in environments where fire risks are prevalent.
Summary of Detection technologies
The analysis of patents related to Detection underscores the dynamic and evolving nature of this crucial OHS category. Over the past decade, there has been a steady increase in innovation, driven by technological advancements in areas such as the IoT, AI, wearable devices, and sensor technologies. These innovations have not only enhanced workplace safety, but also opened avenues for better real-time detection and monitoring.
From a global perspective, the Detection patent landscape reveals strong regional dynamics. China emerges as the dominant player, both in terms of patent volume and innovation intensity, reflecting its strategic focus on workplace safety technologies. The United States, while a significant contributor, displays a relatively more focused and less expansive patenting activity. The Republic of Korea, Japan, and Germany also hold notable positions, contributing to the global ecosystem with their technological strengths.
The segmentation of workplace safety technologies into technology areas such as safety software solutions, location-based safety systems, and advanced detection equipment highlights the diversity of innovation in this category. Location-based systems and safety software have emerged as dominant areas, underlining a growing reliance on digital and real-time solutions to ensure workplace safety. Other technology areas, such as noise and radiation monitoring, although smaller, address critical niche applications and continue to show steady innovation.
The dominance of major technology players, such as Samsung, IBM and Huawei, alongside contributions from academia and smaller innovators, reflects a diverse ecosystem. While large corporations drive broad-based advancements using their substantial resources, universities and independent inventors contribute valuable niche innovations.
