CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
Note(s)
- In section C, the definitions of groups of chemical elements are as follows:
- Alkali metals: Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr
- Alkaline earth metals: Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra
- Lanthanides: elements with atomic numbers 57 to 71 inclusive
- Rare earths: Sc, Y, Lanthanides
- Actinides: elements with atomic numbers 89 to 103 inclusive
- Refractory metals: Ti, V, Cr, Zr, Nb, Mo, Hf, Ta, W
- Halogens: F, Cl, Br, I, At
- Noble gases: He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn
- Platinum group: Os, Ir, Pt, Ru, Rh, Pd
- Noble metals: Ag, Au, Platinum group
- Light metals: alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, Be, Al, Mg
- Heavy metals: metals other than light metals
- Iron group: Fe, Co, Ni
- Non-metals: H, B, C, Si, N, P, O, S, Se, Te, noble gases, halogens
- Metals: elements other than non-metals
- Transition elements: elements with atomic numbers 21 to 30 inclusive, 39 to 48 inclusive, 57 to 80 inclusive, 89 upwards
- Section C covers :
- pure chemistry, which covers inorganic compounds, organic compounds, macromolecular compounds, and their methods of preparation;
- applied chemistry, which covers compositions containing the above compounds, such as: glass, ceramics, fertilisers, plastics compositions, paints, products of the petroleum industry. It also covers certain compositions on account of their having particular properties rendering them suitable for certain purposes, as in the case of explosives, dyestuffs, adhesives, lubricants, and detergents;
- certain marginal industries, such as the manufacture of coke and of solid or gaseous fuels, the production and refining of oils, fats and waxes, the fermentation industry (e.g., brewing and wine-making), the sugar industry;
- certain operations or treatments, which are either purely mechanical, e.g., the mechanical treatment of leather and skins, or partly mechanical, e.g., the treatment of water or the prevention of corrosion in general;
- metallurgy, ferrous or non-ferrous alloys.
- In all sections of the IPC, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, the Periodic System of chemical elements referred to is the one with 8 groups as represented in the table below. For example, group C07F 3/00 "Compounds containing elements of the 2nd Group of the Periodic System" refers to the elements of columns IIa and IIb.
- In the case of operations, treatments, products or articles having both a chemical and a non-chemical part or aspect, the general rule is that the chemical part or aspect is covered by section C.
- In some of these cases, the chemical part or aspect brings with it a non-chemical one, even though purely mechanical, because this latter aspect either is essential to the operation or treatment or constitutes an important element thereof. It has seemed, in fact, more logical not to dissociate the different parts or aspects of a coherent whole. This is the case for applied chemistry and for the industries, operations and treatments mentioned in Notes (1)(c), (d) and (e). For example, furnaces peculiar to the manufacture of glass are covered by class C03 and not by class F27.
- There are, however, some exceptions in which the mechanical (or non-chemical) aspect carries with it the chemical aspect, for example:
- Certain extractive processes, in subclass A61K;
- The chemical purification of air, in subclass A61L;
- Chemical methods of fire-fighting, in subclass A62D;
- Chemical processes and apparatus, in class B01;
- Impregnation of wood, in subclass B27K;
- Chemical methods of analysis or testing, in subclass G01N;
- Photographic materials and processes, in class G03, and, generally, the chemical treatment of textiles and the production of cellulose or paper, in section D.
- In still other cases, the pure chemical aspect is covered by section C and the applied chemical aspect by another section, such as A, B or F, e.g., the use of a substance or composition for:
- When the chemical and mechanical aspects are so closely interlocked that a neat and simple division is not possible, or when certain mechanical processes follow as a natural or logical continuation of a chemical treatment, section C may cover, in addition to the chemical aspect, a part only of the mechanical aspect, e.g., after-treatment of artificial stone, covered by class C04. In this latter case, a note or a reference is usually given to make the position clear, even if sometimes the division is rather arbitrary.
CHEMISTRY
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY [2]
Note(s)
- In this class, the following term is used with the meaning indicated:
- "preparation" covers purification, separation, stabilisation or use of additives, unless a separate place is provided therefor.
- Biocidal, pest repellant, pest attractant or plant growth regulatory activity of compounds or preparations is further classified in subclass A01P.
- In subclasses C07C-C07K and within each of theses subclasses, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, and with the exception referred to below, a compound is classified in the last appropriate place. For example, 2-butyl-pyridine, which contains an acyclic chain and a heterocyclic ring, is classified only as a heterocyclic compound, in subclass C07D. In general, and in the absence of an indication to the contrary (such as groups C07C 59/58, C07C 59/70), the terms "acyclic" and "aliphatic" are used to describe compounds in which there is no ring; and, if a ring were present, the compound would be taken by the "last place" rule to a later group for cycloaliphatic or aromatic compounds, if such a group exists. Where a compound or an entire group of compounds exists in tautomeric forms, it is classified as though existing in the form which is classified last in the system, unless the other form is specifically mentioned earlier in the system.
- Chemical compounds and their preparation are classified in the groups for the type of compound prepared. The processes of preparation are also classified in places for the types of reaction employed, if of interest. Examples of such places outside this class are:
- General processes for the preparation of a class of compounds falling into more than one main group are classified in the groups for the processes employed, when such groups exist. The compounds prepared are also classified in the groups for the types of compound prepared, if of interest.
- In this class, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, the compounds containing carboxyl or thiocarboxyl groups are classified as the relevant carboxylic or thiocarboxylic acids, unless the "last place rule" (see Note (3), above) dictates otherwise; a carboxyl group being a carbon atom having three bonds, and no more than three, to hetero atoms, other than nitrogen atoms of nitro or nitroso groups, with at least one multiple bond to the same hetero atom and a thiocarboxyl group being a carboxyl group having at least one bond to a sulfur atom, e.g. amides or nitriles of carboxylic acids, are classified with the corresponding acids.
- Salts of a compound, unless specifically provided for, are classified as that compound, e.g. aniline hydrochloride is classified as containing carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen only (in group C07C 211/46), sodium malonate is classified as malonic acid (in C07C 55/08), and a mercaptide is classified as the mercaptan. Metal chelates are dealt with in the same way. Similarly, metal alcoholates and metal phenates are classified in subclass C07C and not in subclass C07F, the alcoholates in groups C07C 31/28-C07C 31/32 and the phenates as the corresponding phenols in group C07C 39/235 or C07C 39/44. Salts, adducts or complexes formed between two or more organic compounds are classified according to all compounds forming the salts, adducts or complexes.
Note(s)
- In this subclass, the following terms or expressions are used with the meanings indicated:
- "bridged" means the presence of at least one fusion other than ortho, peri or spiro;
- two rings are "condensed" if they share at least one ring member, i.e. "spiro" and "bridged" are considered as condensed;
- "condensed ring system" is a ring system in which all rings are condensed among themselves;
- "number of rings" in a condensed ring system equals the number of scissions necessary to convert the ring system into one acyclic chain;
- "quinones" are compounds derived from compounds containing a six-membered aromatic ring or a system comprising six-membered aromatic rings (which system may be condensed or not condensed) by replacing two or four
 CH groups of the six-membered aromatic rings by
CH groups of the six-membered aromatic rings by  C=O groups, and by removing one or two carbon-to-carbon double bonds, respectively, and rearranging the remaining carbon-to-carbon double bonds to give a ring or ring system with alternating double bonds, including the carbon-to-oxygen bonds; this means that acenaphthenequinone or camphorquinone are not considered as quinones.
C=O groups, and by removing one or two carbon-to-carbon double bonds, respectively, and rearranging the remaining carbon-to-carbon double bonds to give a ring or ring system with alternating double bonds, including the carbon-to-oxygen bonds; this means that acenaphthenequinone or camphorquinone are not considered as quinones.
- Attention is drawn to Note (3) after class C07, which defines the last place priority rule applied in the range of subclasses C07C-C07K and within these subclasses.
- Therapeutic activity of compounds is further classified in subclass A61P.
- When classifying in this subclass, classification is also made in group B01D 15/08insofar as subject matter of general interest relating to chromatography is concerned.
- In this subclass, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, a process is classified in the last appropriate place.
- In this subclass, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, "quaternary ammonium compounds" are classified with the corresponding "non-quaternised nitrogen compounds".
- For the classification of compounds in groups C07C 1/00-C07C 71/00and C07C 401/00-C07C 409/00:
- a compound is classified considering the molecule as a whole (rule of the "whole molecule approach");
- a compound is considered to be saturated if it does not contain carbon atoms bound to each other by multiple bonds;
- a compound is considered to be unsaturated if it contains carbon atoms bound to each other by multiple bonds, which includes a six-membered aromatic ring,
unless otherwise specified or implicitly derivable from the subdivision, as in group C07C 69/00, e.g. C07C 69/712.
- For the classification of compounds in groups C07C 201/00-C07C 395/00, i.e. after the functional group has been determined according to the "last place rule", a compound is classified according to the following principles:
- compounds are classified in accordance with the nature of the carbon atom to which the functional group is attached;
- a carbon skeleton is a carbon atom, other than a carbon atom of a carboxyl group, or a chain of carbon atoms bound to each other; a carbon skeleton is considered to be terminated by every bond to an element other than carbon or to a carbon atom of a carboxyl group;
- when the molecule contains several functional groups, only functional groups linked to the same carbon skeleton as the one first determined are considered;
- a carbon skeleton is considered to be saturated if it does not contain carbon atoms bound to each other by multiple bonds;
- a carbon skeleton is considered to be unsaturated if it contains carbon atoms bound to each other by multiple bonds, which includes a six-membered aromatic ring.
| Subclass index | |
|---|---|
| COMPOUNDS CONTAINING CARBON AND HYDROGEN ONLY | |
| Preparation | 1/00, 2/00, 4/00, 5/00, 6/00 |
| Purification, separation, stabilisation | 7/00 |
| Compounds | |
| aliphatic | 9/00, 11/00 |
| cycloaliphatic, aromatic | 13/00, 15/00 |
| COMPOUNDS CONTAINING CARBON AND HALOGENS, WITH OR WITHOUT HYDROGEN | |
| Preparation | 17/00 |
| Compounds | |
| aliphatic | 19/00, 21/00 |
| cycloaliphatic, aromatic | 22/00, 23/00, 25/00 |
| COMPOUNDS CONTAINING CARBON AND OXYGEN, WITH OR WITHOUT HYDROGEN OR HALOGENS | |
| Preparation | |
| simultaneous production of more than one class of oxygen- containing compounds | 27/00 |
| of alcohols; of phenols | 29/00, 37/00 |
| of ethers or acetals; of oxo compounds | 41/00, 45/00 |
| of quinones | 46/00 |
| of carboxylic acids, their salts or anhydrides | 51/00 |
| of esters of carboxylic acids | 67/00 |
| of esters of carbonic or haloformic acids | 68/00 |
| Compounds | |
| with OH group(s): aliphatically bound | 31/00, 33/00 |
| cycloaliphatically bound | 35/00 |
| with OH group(s) aromatically bound | 39/00 |
| Ethers, acetals, orthoesters; aldehydes; ketones | 43/00, 47/00, 49/00 |
| Quinones | 50/00 |
| carboxylic acids | |
| acyclic | 53/00, 55/00, 57/00, 59/00 |
| cyclic | 61/00, 62/00, 63/00, 65/00, 66/00 |
| Esters | 69/00, 71/00 |
| COMPOUNDS CONTAINING CARBON AND NITROGEN, WITH OR WITHOUT HYDROGEN, HALOGENS, OR OXYGEN | |
| Preparation | |
| of amines | 209/00 |
| of hydroxy amines, aminoethers, or aminoesters | 213/00 |
| of aminoaldehydes, aminoketones, aminoquinones | 221/00 |
| of aminocarboxylic acids | 227/00 |
| of amides of carboxylic acids | 231/00 |
| of nitriles of carboxylic acids | 253/00 |
| of derivatives of hydrazine | 241/00 |
| of compounds containing carbon- to-nitrogen double bonds, e.g. imines, hydrazones, isocyanates | 249/00, 263/00 |
| of derivatives of carbamic acids | 269/00 |
| of urea or derivatives | 273/00 |
| of guanidines or derivatives | 277/00 |
| of nitro or nitroso compounds, or esters of nitric or nitrous acids | 201/00 |
| Compounds | |
| having nitrogen bound to carbon or to carbon and hydrogen | |
| Amines | 211/00 |
| Hydroxy amines; Aminoethers; Aminoesters | 215/00, 217/00, 219/00 |
| Aminoaldehydes, aminoketones, aminoquinones | 223/00, 225/00 |
| Amino carboxylic acids | 229/00 |
| Amides of carboxylic acids | 233/00, 235/00, 237/00 |
| Compounds containing one or more carbon-to-nitrogen double bonds, e.g. imines | 251/00 |
| Nitriles of carboxylic acids | 255/00 |
| Amidines, imino-ethers | 257/00 |
| Hydroxamic acids | 259/00 |
| Derivatives of cyanic or isocyanic acid | 261/00, 265/00 |
| Carbodiimides | 267/00 |
| Carbamic acids | 271/00 |
| Ureas | 275/00 |
| Guanidines | 279/00 |
| having nitrogen bound to halogens | 239/00 |
| having nitrogen bound to oxygen | |
| Nitro or nitroso compounds | 205/00, 207/00 |
| Nitrites or nitrates | 203/00 |
| Hydroxylamines | 239/00 |
| Oximes | 251/00 |
| having nitrogen bound to another nitrogen | |
| Hydrazines, hydrazides | 243/00 |
| Semicarbazates, semicarbazides | 281/00 |
| Azo compounds, diazo compounds | 245/00 |
| Hydrazones, hydrazidines | 251/00, 257/00 |
| Semicarbazones | 281/00 |
| N-nitro or N-nitroso compounds | 243/00 |
| containing chains of three nitrogen atoms bound together | |
| Triazenes | 245/00 |
| Azides | 247/00 |
| Other compounds containing nitrogen | 291/00 |
| COMPOUNDS CONTAINING CARBON, TOGETHER WITH SULFUR, SELENIUM, OR TELLURIUM, WITH OR WITHOUT HYDROGEN, HALOGENS, OXYGEN, OR NITROGEN | |
| Preparation | |
| of derivatives of sulfuric or sulfonic acids | 303/00 |
| of mercaptans, thiophenols, sulfides, or polysulfides | 319/00 |
| of sulfones or sulfoxides | 315/00 |
| Compounds | |
| having sulfur bound to oxygen | |
| Esters of sulfurous or sulfuric acids | 301/00, 305/00 |
| Sulfonic acids or derivatives | 309/00 |
| Sulfenic or sulfinic acids or derivatives | 313/00 |
| Sulfones, sulfoxides | 317/00 |
| having sulfur bound to carbon | |
| Mercaptans, thiophenols, sulfides or polysulfides | 321/00, 323/00 |
| Thioaldehydes, thioketones | 325/00 |
| Thiocarboxylic acids or derivatives | 327/00 |
| Thiocarbonic acids or derivatives | 329/00 |
| Thiocyanates, isothiocyanates | 331/00 |
| Thiocarbamic acids or derivatives | 333/00 |
| Thioureas | 335/00 |
| Thiosemicarbazides or thiosemicarbazones | 337/00 |
| having sulfur bound to nitrogen | |
| Sulfonamides | 311/00 |
| Sulfenamides, sulfinamides, sulfenylcarbamates or sulfenylureas | 313/00 |
| Amides of sulfuric acids | 307/00 |
| Other compounds containing sulfur | 381/00 |
| Compounds containing selenium | 391/00 |
| Compounds containing tellurium | 395/00 |
| IRRADIATION PRODUCTS OF CHOLESTEROL | 401/00 |
| DERIVATIVES OF CYCLOHEXANE OR OF A CYCLOHEXENE HAVING AN UNSATURATED SIDE-CHAIN WITH AT LEAST FOUR CARBON ATOMS | 403/00 |
| PROSTAGLANDINS OR DERIVATIVES | 405/00 |
| PEROXIDES; PEROXYACIDS | |
| Preparation | 407/00 |
| Compounds | 409/00 |
Hydrocarbons [3]
Preparation of hydrocarbons from one or more compounds, none of them being a hydrocarbon
•
•
•
from carbon monoxide with hydrogen
•
•
•
in the presence of organic compounds, e.g. hydrocarbons
•
•
•
Isosyntheses
•
•
from carbon monoxide with water vapour
•
•
from carbon dioxide with hydrogen
•
starting from organic compounds containing only oxygen atoms as hetero atoms
•
•
from carbonyl compounds [5]
•
•
•
by splitting of esters [5]
•
•
by reduction
•
•
by elimination of water
•
•
by splitting of cyclic ethers [3]
•
starting from organic compounds containing only halogen atoms as hetero atoms
•
•
by ring closure
•
•
by splitting-off the elements of hydrogen halide from a single molecule
•
starting from compounds containing hetero atoms other than, or in addition to, oxygen or halogen [3]
•
•
reacting phosphines with aldehydes or ketones, e.g. Wittig reaction [3]
•
by splitting of esters (C07C 1/213, C07C 1/30 take precedence) [5]
Preparation of hydrocarbons from hydrocarbons containing a smaller number of carbon atoms [3]
•
by addition between unsaturated hydrocarbons [3]
•
•
by oligomerisation of well-defined unsaturated hydrocarbons without ring formation [3]
•
•
•
of alkenes, i.e. acyclic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond [3]
•
•
•
•
Catalytic processes [3]
•
•
•
•
•
with metal oxides [3]
•
•
•
•
•
with crystalline alumino-silicates, e.g. molecular sieves [3]
•
•
•
•
•
with inorganic acids; with salts or anhydrides of acids [3]
•
•
•
•
•
•
Acids of sulfur; Salts thereof; Sulfur oxides [3]
•
•
•
•
•
•
Acids of phosphorus; Salts thereof; Phosphorus oxides [3]
•
•
•
•
•
•
Acids of halogen; Salts thereof [3]
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Metal halides; Complexes thereof with organic compounds [3]
•
•
•
•
•
with metals [3]
•
•
•
•
•
with hydrides or organic compounds (C07C 2/22 takes precedence) [3]
•
•
•
•
•
•
with ion-exchange resins [3]
•
•
•
•
•
•
containing a metal-to-carbon bond; Metal hydrides [3]
•
•
•
•
•
•
as complexes, e.g. acetyl-acetonates [3]
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Metal-hydrocarbon complexes [3]
•
•
•
•
•
•
as phosphines, arsines, stilbines or bismuthines [3]
•
•
•
of dienes or alkynes [3]
•
•
•
•
of conjugated dienes [3]
•
•
homo- or co-oligomerisation with ring formation, not being a Diels-Alder conversion [3]
•
•
•
of conjugated dienes only [3]
•
•
•
•
Catalytic processes [3]
•
•
•
of only hydrocarbons containing a carbon-to-carbon triple bond [3]
•
•
Diels-Alder conversion [3]
•
•
•
Catalytic processes [3]
•
by addition of unsaturated hydrocarbons to saturated hydrocarbons, or to hydrocarbons containing a six-membered aromatic ring with no unsaturation outside the aromatic ring [3]
•
•
Addition to acyclic hydrocarbons [3]
•
•
•
Catalytic processes [3]
•
•
•
•
with halides [3]
•
•
•
•
with acids [3]
•
•
Addition to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [3]
•
•
•
Catalytic processes [3]
•
•
•
•
with halides [3]
•
•
•
•
with acids [3]
•
•
Addition to a non-aromatic carbon atom of hydrocarbons containing a six-membered aromatic ring [3]
•
by addition with simultaneous hydrogenation [3]
•
by condensation of hydrocarbons with partial elimination of hydrogen [3]
•
•
Processes with partial combustion [3]
•
•
Processes with the aid of electrical means [3]
•
•
oxidative coupling [3]
•
•
•
catalytic [3]
•
by condensation between a hydrocarbon and a non-hydrocarbon [3]
•
•
Growth and elimination reactions [3]
Preparation of hydrocarbons from hydrocarbons containing a larger number of carbon atoms [3]
•
by cracking a single hydrocarbon or a mixture of individually defined hydrocarbons or a normally gaseous hydrocarbon fraction [3]
•
•
Thermal processes [3]
•
•
Catalytic processes [3]
•
by splitting-off an aliphatic or cycloaliphatic part from the molecule [3]
•
•
from acyclic hydrocarbons [3]
•
•
from hydrocarbons containing a six-membered aromatic ring, e.g. propyltoluene to vinyltoluene [3]
•
•
•
splitting taking place at an aromatic-aliphatic bond [3]
•
•
•
•
Thermal processes [3]
•
•
•
•
Catalytic processes [3]
•
•
•
•
Hydrogen being formed in situ, e.g. from steam [3]
•
by depolymerisation to the original monomer, e.g. dicyclopentadiene to cyclopentadiene [3]
•
by splitting polyarylsubstituted aliphatic compounds at an aliphatic-aliphatic bond, e.g. 1,4-diphenylbutane to styrene [3]
•
by splitting polyaryl compounds at a bond between uncondensed six-membered aromatic rings, e.g. biphenyl to benzene [3]
Preparation of hydrocarbons from hydrocarbons containing the same number of carbon atoms
•
by hydrogenation
•
•
of non-aromatic carbon-to-carbon double bonds [3]
•
•
•
Partial hydrogenation [3]
•
•
of carbon-to-carbon triple bonds
•
•
•
to carbon-to-carbon double bonds [3]
•
•
of aromatic six-membered rings
•
•
•
Partial hydrogenation [3]
•
•
with simultaneous isomerisation [3]
•
by isomerisation (with simultaneous hydrogenation C07C 5/13)
•
•
Rearrangement of carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds [3]
•
•
•
Migration of carbon-to-carbon double bonds [3]
•
•
Rearrangement of carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon skeleton [3]
•
•
•
changing the number of carbon atoms in a ring while maintaining the number of rings [3]
•
•
•
changing the number of rings [3]
•
by dehydrogenation with formation of free hydrogen [2]
•
•
Formation of non-aromatic carbon-to-carbon double bonds only [3]
•
•
•
Catalytic processes [3]
•
•
Formation of carbon-to-carbon triple bonds only [3]
•
•
Formation of an aromatic six-membered ring from an existing six-membered ring, e.g. dehydrogenation of ethylcyclohexane to ethylbenzene [3]
•
•
with simultaneous isomerisation [3]
•
•
•
of cyclic compounds containing no six-membered ring to compounds containing a six-membered aromatic ring [3]
•
•
•
with cyclisation to an aromatic six-membered ring, e.g. dehydrogenation of n-hexane to benzene [3]
•
•
•
•
Catalytic processes [3]
•
by dehydrogenation with a hydrogen acceptor [2]
•
Note(s)
- In this group:
- the catalyst is considered as forming part of the acceptor system in case of simultaneous catalyst reduction;
- compounds added for binding the reduced acceptor system are not considered as belonging to the acceptor system.
- The acceptor system is classified according to the supplying substances in case of in situ formation of the acceptor system or of in situ regeneration of the reduced acceptor system.
•
•
with a halogen or a halogen-containing compound as an acceptor [2]
•
•
with sulfur or a sulfur-containing compound as an acceptor [2]
•
•
with oxygen as an acceptor [2]
•
•
with an organic compound as an acceptor [2]
•
•
•
with a hydrocarbon as an acceptor, e.g. hydrocarbon disproportionation, i.e. 2 CnHp→ CnHp+q + CnHp-q [2]
•
•
•
•
•
containing only oxygen and either halogens or halogen-containing compounds [3]
Preparation of hydrocarbons from hydrocarbons containing a different number of carbon atoms by redistribution reactions [3]
•
Metathesis reactions at an unsaturated carbon-to-carbon bond [3]
•
•
at a carbon-to-carbon double bond [3]
•
•
•
at a cyclic carbon-to-carbon double bond [3]
•
by conversion at a saturated carbon-to-carbon bond [3]
•
•
in hydrocarbons containing no six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
of exclusively hydrocarbons containing a six-membered aromatic ring [3]
Purification, separation or stabilisation of hydrocarbons; Use of additives [5]
•
by distillation [3]
•
•
with the aid of auxiliary compounds [3]
•
•
•
by azeotropic distillation
•
•
•
by extractive distillation
•
by fractional condensation [3]
•
by extraction, i.e. purification or separation of liquid hydrocarbons with the aid of liquids [3]
•
by absorption, i.e. purification or separation of gaseous hydrocarbons with the aid of liquids [3]
•
by adsorption, i.e. purification or separation of hydrocarbons with the aid of solids, e.g. with ion-exchangers [3]
•
•
by molecular-sieve technique [3]
•
by gas-chromatography [3]
•
by crystallisation; Purification or separation of the crystals [3]
•
using membranes, e.g. selective permeation [3]
•
by treatment giving rise to a chemical modification of at least one compound [3]
•
•
by forming adducts or complexes [3]
•
•
•
with solutions of copper salts [3]
•
•
by hydrogenation [3]
•
•
•
for removal of compounds containing a triple carbon-to-carbon bond [3]
•
•
with acids or sulfur oxides [3]
•
•
•
Sulfuric acid or oleum [7]
•
•
with the aid of organo-metallic compounds [3]
•
•
by selective oligomerisation or selective polymerisation of at least one compound of the mixture [3]
•
Use of additives, e.g. for stabilisation [3]
Acyclic saturated hydrocarbons
•
with one to four carbon atoms [5]
•
•
Methane (production by treatment of sewage C02F 11/04) [5]
•
•
Ethane
•
•
Propane
•
•
with four carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
Iso-butane
•
with five to fifteen carbon atoms
•
•
Straight-chain hydrocarbons [3]
•
•
Branched-chain hydrocarbons
•
•
•
with five carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
2,2,4-Trimethylpentane [3]
•
with more than fifteen carbon atoms
Acyclic unsaturated hydrocarbons
•
Alkenes
•
•
Ethene
•
•
Propene
•
•
with four carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
Isobutene [3]
•
•
with five carbon atoms [5]
•
•
with six carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
Methylpentenes [3]
•
Alkadienes
•
•
Allene
•
•
with four carbon atoms
•
•
•
1,3-Butadiene [3]
•
•
with five carbon atoms [3]
•
•
•
Isoprene [3]
•
•
•
1,3-Pentadiene [3]
•
Alkatrienes; Alkatetraenes; Other alkapolyenes [3]
•
containing carbon-to-carbon triple bonds
•
•
Acetylene (production of acetylene gas by wet methods C10H) [5]
•
containing carbon-to-carbon double bonds and carbon-to-carbon triple bonds
•
•
Butenyne
Cyclic hydrocarbons containing rings other than, or in addition to, six-membered aromatic rings
•
Monocyclic hydrocarbons or acyclic hydrocarbon derivatives thereof
•
•
with a three-membered ring
•
•
with a four-membered ring
•
•
with a five-membered ring
•
•
•
with a cyclopentane ring
•
•
•
•
substituted by unsaturated hydrocarbon groups [2]
•
•
•
with a cyclopentene ring
•
•
•
with a cyclopentadiene ring [3]
•
•
with a six-membered ring
•
•
•
with a cyclohexane ring
•
•
•
•
substituted by unsaturated hydrocarbon groups [2]
•
•
•
with a cyclohexene ring
•
•
•
•
Menthadienes [2]
•
•
•
with a cyclohexadiene ring [3]
•
•
with a seven-membered ring
•
•
with an eight-membered ring
•
•
•
with a cyclo-octene or cyclo-octadiene ring [3]
•
•
•
with a cyclo-octatriene or cyclo-octatetraene ring [3]
•
•
with a nine- to eleven-membered ring [3]
•
•
with a twelve-membered ring [3]
•
•
•
the twelve-membered ring being unsaturated [3]
•
•
•
•
with a cyclododecatriene ring [3]
•
Polycyclic hydrocarbons or acyclic hydrocarbon derivatives thereof
•
Note(s)
- Ring systems consisting only of condensed six-membered rings with maximum number of non-cumulative double bonds are classified in group C07C 15/00.
•
•
with condensed rings
•
•
•
with a bicyclo ring system containing four carbon atoms
•
•
•
with a bicyclo ring system containing five carbon atoms
•
•
•
with a bicyclo ring system containing six carbon atoms
•
•
•
with a bicyclo ring system containing seven carbon atoms [3]
•
•
•
•
with a bicycloheptane ring structure [3]
•
•
•
•
with a bicycloheptene ring structure [3]
•
•
•
•
•
substituted by unsaturated acyclic hydrocarbon groups [3]
•
•
•
with a bicyclo ring system containing eight carbon atoms
•
•
•
with a bicyclo ring system containing nine carbon atoms [3]
•
•
•
•
Indenes; Completely or partially hydrogenated indenes [3]
•
•
•
with a bicyclo ring system containing ten carbon atoms [3]
•
•
•
•
Completely or partially hydrogenated naphthalenes [3]
•
•
•
•
•
Decahydronaphthalenes [3]
•
•
•
•
Azulenes; Completely or partially hydrogenated azulenes [3]
•
•
•
with three condensed rings
•
•
•
•
at least one ring not being six-membered, the other rings being at the most six-membered [3]
•
•
•
•
•
Indacenes; Completely or partially hydrogenated indacenes [3]
•
•
•
•
•
Fluorenes; Completely or partially hydrogenated fluorenes [3]
•
•
•
•
with three six-membered rings [3]
•
•
•
•
•
Completely or partially hydrogenated anthracenes [3]
•
•
•
•
•
Completely or partially hydrogenated phenanthrenes [3]
•
•
•
•
with a bridged ring system [3]
•
•
•
•
•
Bridged indenes, e.g. dicyclopentadiene [3]
•
•
•
•
•
Adamantanes [3]
•
•
•
with more than three condensed rings
•
•
•
•
with a bridged ring system [3]
•
•
•
•
the condensed ring system contains only four rings [3]
•
•
•
•
•
with a bridged ring system [3]
•
•
•
with a condensed ring system consisting of at least two mutually uncondensed aromatic ring systems, linked by an annular structure formed by carbon chains on non-adjacent positions of the aromatic ring, e.g. cyclophanes [3]
•
•
•
Spiro hydrocarbons [3]
Cyclic hydrocarbons containing only six-membered aromatic rings as cyclic part [2]
•
Monocyclic hydrocarbons
•
•
Benzene
•
•
Toluene
•
•
C8H10 hydrocarbons [3]
•
•
•
Ethylbenzene [3]
•
•
•
Xylenes [3]
•
•
Isopropylbenzene [3]
•
•
having a saturated side-chain containing at least six carbon atoms, e.g. detergent alkylates [3]
•
•
•
having at least two saturated side-chains, each containing at least six carbon atoms [3]
•
Polycyclic non-condensed hydrocarbons
•
•
all phenyl groups being directly linked [3]
•
•
containing at least two phenyl groups linked by one single acyclic carbon atom
•
•
containing at least one group with formula 

•
Polycyclic condensed hydrocarbons
•
•
containing two rings
•
•
containing three rings [3]
•
•
•
Anthracenes [3]
•
•
•
Phenanthrenes [3]
•
•
containing four rings [3]
•
substituted by unsaturated hydrocarbon radicals [3]
•
•
monocyclic [3]
•
•
•
the hydrocarbon substituent containing a carbon-to-carbon double bond [3]
•
•
•
•
Styrene; Ring-alkylated styrenes [3]
•
•
•
the hydrocarbon substituent containing a carbon-to-carbon triple bond [3]
•
•
polycyclic non-condensed [3]
•
•
•
containing a group with formula  [3]
[3]
 [3]
[3]•
•
•
containing a group with formula  [3]
[3]
 [3]
[3]•
•
polycyclic condensed [3]
•
•
•
containing two rings [3]
•
•
•
containing three rings [3]
•
•
•
containing four rings [3]
Compounds containing carbon and halogens with or without hydrogen
Preparation of halogenated hydrocarbons
•
from carbon or carbides and halogens [6]
•
by addition of halogens [6]
•
•
to unsaturated hydrocarbons [6]
•
•
to unsaturated halogenated hydrocarbons [6]
•
•
combined with replacement of hydrogen atoms by halogens
•
by addition of hydrogen halides [6]
•
•
to unsaturated hydrocarbons [6]
•
•
to unsaturated halogenated hydrocarbons [6]
•
by replacement by halogens [6]
•
•
of hydrogen atoms (combined with addition of halogens to unsaturated hydrocarbons C07C 17/06) [6]
•
•
•
in the ring of aromatic compounds [6]
•
•
•
in the side-chain of aromatic compounds [6]
•
•
with oxygen as auxiliary reagent, e.g. oxychlorination [6]
•
•
•
of hydrocarbons [6]
•
•
•
•
of saturated hydrocarbons [6]
•
•
•
•
of unsaturated hydrocarbons [6]
•
•
•
of halogenated hydrocarbons [6]
•
•
of hydroxyl groups [6]
•
•
of oxygen atoms of carbonyl groups [6]
•
•
of halogen atoms by other halogen atoms [6]
•
•
•
with simultaneous increase of the number of halogen atoms [6]
•
by dehalogenation [6]
•
by splitting-off hydrogen halides from halogenated hydrocarbons [6]
•
by reactions involving an increase in the number of carbon atoms in the skeleton
•
•
by condensation reactions [6]
•
•
•
of hydrocarbons and halogenated hydrocarbons [6]
•
•
•
of only halogenated hydrocarbons [6]
•
•
by addition reactions [6]
•
•
•
of hydrocarbons and halogenated hydrocarbons [6]
•
•
•
of only halogenated hydrocarbons [6]
•
•
•
•
of only one compound [6]
•
•
by a Diels-Alder synthesis
•
•
by introduction of halogenated alkyl groups into ring compounds
•
by reactions not affecting the number of carbon or halogen atoms in the molecules [6]
•
•
by hydrogenation [6]
•
•
by dehydrogenation [6]
•
•
by isomerisation [6]
•
by reactions involving a decrease in the number of carbon atoms [6]
•
•
by elimination of carboxyl groups [6]
•
•
by depolymerisation [6]
•
by disproportionation of halogenated hydrocarbons [6]
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives
•
•
by distillation [6]
•
•
•
with auxiliary compounds [6]
•
•
by adsorption on solids [6]
•
•
by crystallisation; Purification or separation of the crystals [6]
•
•
by treatment giving rise to a chemical modification of at least one compound [6]
•
•
Use of additives, e.g. for stabilisation [6]
Acyclic saturated compounds containing halogen atoms [5]
•
containing chlorine [6]
•
•
Chloromethanes [6]
•
•
•
Chloroform [6]
•
•
•
Carbon tetrachloride [6]
•
•
Chloroethanes [6]
•
•
•
Dichloroethanes [6]
•
•
•
Trichloroethanes [6]
•
•
•
Tetrachloroethanes [6]
•
containing iodine [2]
•
containing bromine [6]
•
containing fluorine
•
•
and chlorine [6]
•
•
•
having two carbon atoms [6]
•
•
and bromine [6]
•
•
and iodine [6]
Acyclic unsaturated compounds containing halogen atoms [5]
•
containing carbon-to-carbon double bonds
•
•
Chloro-alkenes
•
•
•
Vinyl chloride
•
•
•
Allyl chloride; Methallyl chloride [3]
•
•
•
Dichloro-alkenes [3]
•
•
•
•
Vinylidene chloride [3]
•
•
•
•
Dichloro-butenes [3]
•
•
•
Trichloro-ethylene
•
•
•
Tetrachloro-ethylene
•
•
containing bromine
•
•
•
Crotyl bromide
•
•
containing iodine [5]
•
•
containing fluorine
•
•
•
Tetrafluoroethene [5]
•
•
Halogenated dienes [3]
•
•
•
Halogenated butadienes [3]
•
•
•
•
Chloroprene [3]
•
•
Halogenated polyenes with more than two carbon-to-carbon double bonds [3]
•
containing carbon-to-carbon triple bonds
Cyclic compounds containing halogen atoms bound to an acyclic carbon atom [5]
•
having unsaturation in the rings [5]
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
Trichloromethylbenzene [5]
•
•
•
containing fluorine [5]
Compounds containing at least one halogen atom bound to a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring
•
Monocyclic halogenated hydrocarbons
•
•
with a three-membered ring
•
•
with a four-membered ring
•
•
with a five-membered ring
•
•
with a six-membered ring
•
•
•
Hexachlorocyclohexanes
•
•
with a seven-membered ring
•
•
with an eight-membered ring
•
Polycyclic halogenated hydrocarbons
•
•
with condensed rings none of which is aromatic
•
•
•
with a bicyclo ring system containing four carbon atoms
•
•
•
with a bicyclo ring system containing five carbon atoms
•
•
•
with a bicyclo ring system containing six carbon atoms
•
•
•
with a bicyclo ring system containing seven carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
Saturated bicyclo ring system [5]
•
•
•
•
Mono-unsaturated bicyclo ring system [5]
•
•
•
with a bicyclo ring system containing eight carbon atoms
•
•
•
Halogenated completely or partially hydrogenated indenes
•
•
•
Halogenated completely or partially hydrogenated naphthalenes
•
•
•
with three condensed rings
•
•
•
•
Halogenated completely or partially hydrogenated fluorenes
•
•
•
•
Halogenated completely or partially hydrogenated anthracenes
•
•
•
•
Halogenated completely or partially hydrogenated phenanthrenes
•
•
•
with more than 3 condensed rings
Compounds containing at least one halogen atom bound to a six-membered aromatic ring
•
Monocyclic aromatic halogenated hydrocarbons
•
•
Monochloro-benzene [3]
•
•
Dichloro-benzenes [3]
•
•
Trichloro-benzenes [3]
•
•
Hexachloro-benzene [3]
•
•
Halogenated xylenes [3]
•
•
containing fluorine [3]
•
Polycyclic aromatic halogenated hydrocarbons
•
•
Dichloro-diphenyl-trichloro-ethane
•
•
with condensed rings
•
Halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons with unsaturated side chains
•
•
Halogenated styrenes [3]
Compounds containing carbon and oxygen, with or without hydrogen or halogens [2]
Processes involving the simultaneous production of more than one class of oxygen-containing compounds
•
Saponification of organic acid esters
•
by reduction of oxygen-containing compounds (C07C 29/14 takes precedence)
•
•
by hydrogenation of oxides of carbon
•
•
•
with moving catalysts
•
by oxidation of hydrocarbons
•
•
with oxygen
•
•
•
wholly gaseous reactions
•
•
with other oxidising agents
•
by addition of alkynes to aldehydes, ketones, or alkylene oxides
•
by oxo-reaction
•
•
with the use of catalysts which are specific for this process
•
•
with moving catalysts
•
Purification; Separation; Stabilisation
•
•
by distillation
•
•
•
by azeotropic distillation
•
•
•
by extractive distillation
•
•
by extraction
Preparation of compounds having hydroxy or O-metal groups bound to a carbon atom not belonging to a six-membered aromatic ring
•
by addition of hydroxy groups to unsaturated carbon-to-carbon bonds, e.g. with the aid of H2O2 [3]
•
•
by hydration of carbon-to-carbon double bonds
•
•
•
with formation of absorption products in mineral acids and their hydrolysis [3]
•
•
•
•
the acid being sulfuric acid [3]
•
•
•
•
the acid being phosphoric acid [3]
•
by hydrolysis (of esters of organic acids C07C 27/02) [3]
•
•
of ethers, including cyclic ethers, e.g. oxiranes
•
•
of esters of mineral acids [3]
•
•
•
of halides [3]
•
by alcoholysis (of esters of organic acids C07C 27/02) [3]
•
by reduction of an oxygen-containing functional group [3]
•
•
of  C=O containing groups, e.g. —COOH [3]
C=O containing groups, e.g. —COOH [3]
 C=O containing groups, e.g. —COOH [3]
C=O containing groups, e.g. —COOH [3]•
•
•
of a —CHO group [3]
•
•
•
•
with hydrogen or hydrogen-containing gases [5]
•
•
•
of ketones [5]
•
•
•
•
with hydrogen or hydrogen-containing gases [5]
•
•
•
of carboxylic acids or derivatives thereof [5]
•
•
•
•
with hydrogen or hydrogen-containing gases [5]
•
by reduction of oxides of carbon exclusively [3]
•
•
with hydrogen or hydrogen-containing gases [5]
•
•
•
characterised by the reactor used [5]
•
•
•
characterised by the catalyst used [5]
•
•
•
•
containing copper, silver, gold, or compounds thereof [5]
•
•
•
•
containing iron group metals, platinum group metals, or compounds thereof [5]
•
•
•
•
•
containing platinum group metals or compounds thereof [5]
•
•
•
•
•
•
containing rhodium or compounds thereof [5]
•
•
with reducing agents other than hydrogen or hydrogen-containing gases [5]
•
by oxo-reaction combined with reduction
•
by hydrogenation of carbon-to-carbon double or triple bonds [3]
•
•
in six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
in non-condensed rings substituted with hydroxy groups [3]
•
increasing the number of carbon atoms by reactions without formation of hydroxy groups [3]
•
•
by condensation involving hydroxy groups or the mineral ester groups derived therefrom, e.g. Guerbet reaction [3]
•
increasing the number of carbon atoms by reactions with formation of hydroxy groups, which may occur via intermediates being derivatives of hydroxy groups, e.g. O-metal [3]
•
•
by reaction with aldehydes or ketones [3]
•
•
•
with compounds containing carbon-to-metal bonds [3]
•
•
•
with compounds containing triple carbon-to-carbon bonds, e.g. with metal-alkynes [3]
•
increasing the number of carbon atoms by addition reactions, i.e. reactions involving at least one carbon-to-carbon double or triple bond (C07C 29/16 takes precedence) [3]
•
•
by diene-synthesis [3]
•
by oxidation reactions with formation of hydroxy groups [3]
•
•
with molecular oxygen only [3]
•
•
•
in the presence of mineral boron compounds with, when necessary, hydrolysis of the intermediate formed [3]
•
•
•
starting from compounds containing carbon-to-metal bonds and followed by conversion of the O-metal to hydroxy groups [3]
•
by isomerisation [3]
•
by elimination of halogen, e.g. by hydrogenolysis, splitting-off (C07C 29/124 takes precedence) [3]
•
by elimination of hydroxy groups, e.g. by dehydration (C07C 29/34 takes precedence) [3]
•
by introduction of halogen; by substitution of halogen atoms by other halogen atoms [3]
•
by simultaneous introduction of hydroxy groups and halogens [3]
•
•
by addition of hypohalogenous acids, which may be formed in situ, to carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds [3]
•
Preparation of metal-alcoholates (C07C 29/42, C07C 29/54 take precedence) [3]
•
•
by converting hydroxy groups to O-metal groups [3]
•
•
by oxidation of carbon-to-metal bonds [3]
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [3]
•
•
by physical treatment [3]
•
•
•
by condensation or crystallisation [3]
•
•
•
by distillation [3]
•
•
•
•
by azeotropic distillation [3]
•
•
•
•
by extractive distillation [3]
•
•
•
by liquid-liquid treatment [3]
•
•
by treatment giving rise to a chemical modification of at least one compound (chemisorption C07C 29/76) [3]
•
•
•
using hydrogen only [3]
•
•
•
by a consecutive conversion and reconstruction [3]
•
•
Use of additives, e.g. for stabilisation [3]
Saturated compounds having hydroxy or O-metal groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms
•
Monohydroxylic acyclic alcohols
•
•
Methanol
•
•
Ethanol
•
•
containing three carbon atoms
•
•
containing four carbon atoms
•
•
containing five to twenty-two carbon atoms [3]
•
Monohydroxylic alcohols containing saturated rings [3]
•
•
monocyclic [3]
•
•
•
with five- or six-membered rings; Naphthenic alcohols [3]
•
•
polycyclic with condensed ring systems [3]
•
Polyhydroxylic acyclic alcohols
•
•
Dihydroxylic alcohols
•
•
Trihydroxylic alcohols, e.g. glycerol [3]
•
•
Tetrahydroxylic alcohols, e.g. pentaerythritol [3]
•
•
Hexahydroxylic alcohols
•
Polyhydroxylic alcohols containing saturated rings [3]
•
Metal alcoholates
•
•
Alkali-metal or alkaline-earth-metal alcoholates
•
•
Aluminium alcoholates
•
Halogenated alcohols
•
•
the halogen not being fluorine [3]
•
•
containing only fluorine as halogen [3]
•
•
perhalogenated [3]
•
•
Halogenated polyhydroxylic acyclic alcohols [3]
•
•
Halogenated alcohols containing saturated rings [3]
Unsaturated compounds having hydroxy or O-metal groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms
Note(s)
- In this group, in condensed ring systems of six-membered aromatic rings and other rings, the double bond belonging to a benzene ring is not considered as unsaturated for the non-aromatic ring condensed thereon, e.g. the 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro- naphthalene ring is considered to be saturated outside the aromatic ring.
•
Acyclic alcohols with carbon-to-carbon double bonds
•
•
with only one double bond [3]
•
•
•
in beta-position, e.g. allyl alcohol, methallyl alcohol [3]
•
•
•
Alkenediols [3]
•
Acyclic alcohols with carbon-to-carbon triple bonds
•
•
with only one triple bond [3]
•
•
•
Alkynediols [3]
•
•
•
•
Butynediols [3]
•
•
with double and triple bonds [3]
•
Alcohols containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [2]
•
•
containing five-membered rings [3]
•
•
containing six-membered rings [3]
•
•
containing rings with more than six ring members [3]
•
Monohydroxylic alcohols containing only six-membered aromatic rings as cyclic part [3]
•
•
monocyclic [3]
•
•
•
Benzylalcohol; Phenylethyl alcohol [3]
•
•
polycyclic without condensed ring systems [3]
•
Polyhydroxylic alcohols containing only six-membered aromatic rings as cyclic part [3]
•
Alcohols containing only six-membered aromatic rings as cyclic part with unsaturation outside the aromatic rings [3]
•
•
monocyclic [3]
•
•
•
Cinnamyl alcohol [3]
•
Monohydroxylic alcohols containing six-membered aromatic rings and other rings [3]
•
Polyhydroxylic alcohols containing six-membered aromatic rings and other rings [3]
•
Alcohols containing six-membered aromatic rings and other rings and having unsaturation outside the aromatic rings [3]
•
Halogenated unsaturated alcohols [3]
•
•
acyclic [3]
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
containing only six-membered aromatic rings as cyclic part [3]
•
•
•
with unsaturation outside the aromatic rings [3]
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings and other rings [3]
Compounds having at least one hydroxy or O-metal group bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [2]
•
monocyclic
•
•
containing three- or four-membered rings
•
•
containing five-membered rings
•
•
containing six-membered rings
•
•
•
Menthol
•
•
•
with more than one hydroxy group bound to the ring
•
•
•
•
Inositol
•
•
•
with unsaturation only outside the ring [3]
•
•
•
with unsaturation at least in the ring [3]
•
•
containing seven- or eight-membered rings
•
•
containing nine- to twelve-membered rings, e.g. cyclododecanols [3]
•
polycyclic, at least one hydroxy group bound to a non-condensed ring [2]
•
polycyclic, at least one hydroxy group bound to a condensed ring system [2]
•
•
with a hydroxy group on a condensed ring system having two rings [3]
•
•
•
the condensed ring system containing five carbon atoms [3]
•
•
•
•
Bicyclopentadienols [3]
•
•
•
the condensed ring system containing six carbon atoms [3]
•
•
•
the condensed ring system containing seven carbon atoms [3]
•
•
•
•
being a [2.2.1] system [3]
•
•
•
•
•
Borneol; Isoborneol [3]
•
•
•
the condensed ring system containing eight carbon atoms [3]
•
•
•
the condensed ring system being a [4.3.0] system, e.g. indenols [3]
•
•
•
the condensed ring system being a [5.3.0] system, e.g. azulenols [3]
•
•
•
the condensed ring system being a [4.4.0] system, e.g. hydrogenated naphthols [3]
•
•
with a hydroxy group on a condensed ring system having three rings [3]
•
•
•
derived from the fluorene skeleton [3]
•
•
•
derived from the anthracene skeleton [3]
•
•
•
derived from the phenanthrene skeleton [3]
•
•
with a hydroxy group on a condensed ring system having more than three rings
•
O-metal derivatives of the cyclically bound hydroxy groups [3]
•
Halogenated derivatives [3]
•
•
Alcohols with at least two rings [3]
•
•
Alcohols with a condensed ring system [3]
Preparation of compounds having hydroxy or O-metal groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring
•
by replacing functional groups bound to a six-membered aromatic ring by hydroxy groups, e.g. by hydrolysis [3]
•
•
by substitution of halogen [3]
•
•
by substitution of SO3H groups or a derivative thereof [3]
•
•
by substitution of a group bound to the ring by nitrogen [3]
•
•
•
by substitution of a NH2 group [3]
•
•
by substitution of a group bound to the ring by oxygen, e.g. ether group [3]
•
by conversion of non-aromatic six-membered rings or of such rings formed in situ into aromatic six-membered rings, e.g. by dehydrogenation
•
•
with simultaneous reduction of C=O group in that ring [3]
•
by decomposition of hydroperoxides, e.g. cumene hydroperoxide
•
by reactions increasing the number of carbon atoms [3]
•
•
by addition reactions, i.e. reactions involving at least one carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bond [3]
•
•
by condensation involving hydroxy groups of phenols or alcohols or the ether or mineral ester group derived therefrom [3]
•
•
by condensation involving halogen atoms of halogenated compounds
•
•
using aldehydes or ketones
•
by exchange of hydrocarbon groups which may be substituted, from other compounds, e.g. transalkylation [3]
•
by reactions decreasing the number of carbon atoms (C07C 37/01, C07C 37/08, C07C 37/48 take precedence) [3]
•
•
by splitting polyaromatic compounds, e.g. polyphenolalkanes [3]
•
•
•
by hydrolysis of lignin or sulfite waste liquor [3]
•
•
by replacing a carboxyl or aldehyde group by a hydroxy group [3]
•
by oxidation reactions introducing directly a hydroxy group on a CH-group belonging to a six-membered aromatic ring with the aid of molecular oxygen [3]
•
by oxidation reactions introducing directly a hydroxy group on a CH-group belonging to a six-membered aromatic ring with the aid of other oxidants than molecular oxygen or their mixtures with molecular oxygen [3]
•
by introduction of halogen; by substitution of halogen atoms by other halogen atoms [3]
•
Preparation of O-metal compounds with the O-metal group linked to a carbon atom belonging to a six-membered aromatic ring [3]
•
•
by conversion of hydroxy groups to O-metal groups [3]
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [3]
•
•
by physical treatment [3]
•
•
•
by liquid-liquid treatment [3]
•
•
•
by distillation [3]
•
•
•
•
by steam distillation [3]
•
•
•
•
by azeotropic distillation [3]
•
•
•
•
by extractive distillation [3]
•
•
•
by solid-liquid treatment; by chemisorption [3]
•
•
•
by crystallisation [3]
•
•
by treatment giving rise to a chemical modification (by chemisorption C07C 37/82) [3]
•
•
Use of additives, e.g. for stabilisation [3]
Compounds having at least one hydroxy or O-metal group bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring
Note(s)
- In this group, in condensed ring systems of six-membered aromatic rings and other rings, the double bond belonging to the benzene ring is not considered as unsaturated for the non-aromatic ring condensed thereon.
•
monocyclic with no unsaturation outside the aromatic ring
•
•
Phenol
•
•
Alkylated phenols
•
•
•
containing only methyl groups as alkyl groups, e.g. cresols, xylenols [3]
•
•
Dihydroxy benzenes; Alkylated derivatives thereof
•
•
Polyhydroxy benzenes; Alkylated derivatives thereof (C07C 39/08 takes precedence)
•
•
Alkylated hydroxy benzenes containing also acyclically bound hydroxy groups, e.g. saligenol [3]
•
polycyclic with no unsaturation outside the aromatic rings
•
•
with at least one hydroxy group on a condensed ring system containing two rings [3]
•
•
with all hydroxy groups on non-condensed rings [3]
•
•
•
Bis(hydroxy phenyl)alkanes; Tris(hydroxy phenyl)alkanes [3]
•
•
containing other rings in addition to the six-membered aromatic rings [2]
•
monocyclic with unsaturation outside the aromatic ring
•
•
containing carbon-to-carbon double bonds but no carbon-to-carbon triple bonds [3]
•
•
•
Hydroxy styrenes [3]
•
polycyclic, containing only six-membered aromatic rings as cyclic part, with unsaturation outside the rings [3]
•
•
with at least one hydroxy group on a non-condensed ring [3]
•
•
•
containing the  structure, e.g. diethylstilbestrol [3]
structure, e.g. diethylstilbestrol [3]
 structure, e.g. diethylstilbestrol [3]
structure, e.g. diethylstilbestrol [3]•
•
with at least one hydroxy group on a condensed ring system [3]
•
polycyclic, containing six-membered aromatic rings and other rings, with unsaturation outside the aromatic rings [3]
•
Metal derivatives of a hydroxy group bound to a six-membered aromatic ring [3]
•
Halogenated derivatives
•
•
monocyclic monohydroxylic containing halogen bound to ring carbon atoms
•
•
•
all halogen atoms being attached to the ring
•
•
•
•
the halogen being one chlorine atom
•
•
•
•
the halogen being two chlorine atoms
•
•
•
•
the halogen being three chlorine atoms
•
•
•
•
the halogen being four chlorine atoms
•
•
•
•
Pentachlorophenol
•
•
polycyclic non-condensed, containing only six-membered aromatic rings, e.g. halogenated poly-(hydroxy-phenyl)alkanes [3]
•
•
with all hydroxy groups on non-condensed rings and with unsaturation outside the aromatic rings [3]
•
•
with at least one hydroxy group on a condensed ring system containing two rings
•
•
with at least one hydroxy group on a condensed ring system containing more than two rings [3]
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings and other rings [3]
•
•
Metal derivatives of a hydroxy group bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [3]
Preparation of ethers; Preparation of compounds having  groups,
groups,  groups or
groups or  groups [3]
groups [3]
 groups,
groups,  groups or
groups or  groups [3]
groups [3]•
Preparation of ethers [3]
•
•
from oxiranes [3]
•
•
•
by reaction of an oxirane ring with a hydroxy group [3]
•
•
by addition of compounds to unsaturated compounds [3]
•
•
•
by addition of organic compounds only [3]
•
•
•
•
to carbon-to-carbon triple bonds [3]
•
•
by dehydration of compounds containing hydroxy groups [3]
•
•
by exchange of organic parts on the ether-oxygen for other organic parts, e.g. by trans-etherification [3]
•
•
by reaction of esters of mineral or organic acids with hydroxy or O-metal groups [3]
•
•
by reactions not forming ether-oxygen bonds [3]
•
•
•
by hydrogenation of carbon-to-carbon double or triple bonds [3]
•
•
•
by introduction of halogen; by substitution of halogen atoms by other halogen atoms [3]
•
•
•
by elimination of halogen, e.g. elimination of HCl [3]
•
•
•
by introduction of hydroxy or O-metal groups [3]
•
•
•
from acetals, e.g. by dealcoholysis [3]
•
•
•
by increasing the number of carbon atoms, e.g. by oligomerisation [3]
•
•
by isomerisation [3]
•
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [3]
•
•
•
by solid-liquid treatment; by chemisorption [3]
•
•
•
by liquid-liquid treatment [3]
•
•
•
by change of physical state, e.g. by crystallisation [3]
•
•
•
•
by distillation [3]
•
•
•
by treatment giving rise to a chemical modification (by chemisorption C07C 41/36) [3]
•
•
•
Use of additives, e.g. for stabilisation [3]
•
Preparation of compounds having  groups [3]
groups [3]
 groups [3]
groups [3]•
•
by reactions producing  groups [3]
groups [3]
 groups [3]
groups [3]•
•
•
by substitution of halogen only [3]
•
•
•
by addition of compounds to unsaturated carbon-to-carbon bonds [3]
•
•
•
by condensation of aldehydes, paraformaldehyde, or ketones [3]
•
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [3]
•
Preparation of compounds having  groups or
groups or  groups [3]
groups [3]
 groups or
groups or  groups [3]
groups [3]Ethers; Compounds having  groups,
groups,  groups or
groups or  groups
groups
 groups,
groups,  groups or
groups or  groups
groups •
Ethers
•
•
having all ether-oxygen atoms bound to acyclic carbon atoms [3]
•
•
•
Saturated ethers [3]
•
•
•
•
Diethyl ether [3]
•
•
•
•
of polyhydroxy compounds [3]
•
•
•
•
•
Polyethers containing —O—(C—C—O—)n units with 2 ≤ n ≤ 10 [3]
•
•
•
•
containing carbocyclic rings [3]
•
•
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
•
•
containing hydroxy or O-metal groups (C07C 43/11 takes precedence) [3]
•
•
•
Unsaturated ethers [3]
•
•
•
•
containing only non-aromatic carbon-to-carbon double bonds [3]
•
•
•
•
•
Vinyl ethers [3]
•
•
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
•
•
having unsaturation outside the aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings and other rings [3]
•
•
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
•
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
•
•
•
having unsaturation outside the aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
•
containing hydroxy or O-metal groups [3]
•
•
having an ether-oxygen atom bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring
•
•
•
to a carbon atom of a non-condensed ring [3]
•
•
•
Unsaturated ethers [3]
•
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
•
containing hydroxy or O-metal groups [3]
•
•
having an ether-oxygen atom bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring
•
•
•
the aromatic ring being a non-condensed ring [3]
•
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
having unsaturation outside the six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
•
containing hydroxy or O-metal groups [3]
•
•
having an ether-oxygen atom bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring and to a carbon atom of a ring, other than a six-membered aromatic ring [3]
•
•
•
having unsaturation outside the six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
•
containing hydroxy or O-metal groups [3]
•
•
having an ether-oxygen atom bound to carbon atoms both belonging to six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
the aromatic rings being non-condensed [3]
•
•
•
containing other rings [3]
•
•
•
having all ether-oxygen atoms bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
having unsaturation outside the six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
•
containing hydroxy or O-metal groups [3]
•
Compounds having  groups
groups
 groups
groups •
Note(s)
- In this group, the acetal carbon atom is the carbon of the
 group.
group.
•
•
having acetal carbon atoms bound to acyclic carbon atoms [3]
•
•
having acetal carbon atoms as ring members or bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
having acetal carbon atoms bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
containing oxygen atoms singly bound to carbon atoms not being acetal carbon atoms [3]
•
•
having  groups, X being hydrogen or metal [3]
groups, X being hydrogen or metal [3]
 groups, X being hydrogen or metal [3]
groups, X being hydrogen or metal [3]•
Compounds having  groups or
groups or  groups
groups
 groups or
groups or  groups
groups Preparation of compounds having  C=O groups bound only to carbon or hydrogen atoms; Preparation of chelates of such compounds [2]
C=O groups bound only to carbon or hydrogen atoms; Preparation of chelates of such compounds [2]
 C=O groups bound only to carbon or hydrogen atoms; Preparation of chelates of such compounds [2]
C=O groups bound only to carbon or hydrogen atoms; Preparation of chelates of such compounds [2]•
by hydration of carbon-to-carbon triple bonds [3]
•
by oxidation [3]
•
•
of —CHx-moieties [3]
•
•
of hydroxy groups [3]
•
•
with halogen containing compounds, e.g. hypohalogenation [3]
•
•
with compounds containing mercury atoms, which may be regenerated in situ, e.g. by oxygen [3]
•
•
with molecular oxygen [3]
•
•
•
of CHx-moieties [3]
•
•
•
•
in unsaturated compounds [3]
•
•
•
•
•
in propene or isobutene [3]
•
•
•
•
•
in compounds containing six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
of  C—O— functional groups to
C—O— functional groups to  C=O groups [3]
C=O groups [3]
 C—O— functional groups to
C—O— functional groups to  C=O groups [3]
C=O groups [3]•
•
•
•
being a primary hydroxy group [3]
•
•
•
•
being a secondary hydroxy group [3]
•
by oxidation with ozone; by ozonolysis [3]
•
by hydrogenolysis or reduction of carboxylic groups or functional derivatives thereof [3]
•
by hydrolysis [3]
•
•
of  CX2 groups, X being halogen [3]
CX2 groups, X being halogen [3]
 CX2 groups, X being halogen [3]
CX2 groups, X being halogen [3]•
by reduction and hydrolysis of nitriles [3]
•
by condensation [3]
•
•
Friedel-Crafts reactions [3]
•
•
using phosgene [3]
•
•
involving decarboxylation [3]
•
by reaction with carbon monoxide [3]
•
•
by oxo-reactions [3]
•
by pyrolysis, rearrangement or decomposition [3]
•
•
by dehydration and rearrangement involving two hydroxy groups in the same molecule [3]
•
•
of hydroperoxides [3]
•
•
of compounds containing doubly bound oxygen atoms, e.g. esters [3]
•
•
of oligo- or polymeric oxo-compounds [3]
•
from heterocyclic compounds (C07C 45/55 takes precedence) [3]
•
•
with oxygen as the only hetero atom [3]
•
•
•
in three-membered rings [3]
•
•
•
in five-membered rings (from ozonides C07C 45/40) [3]
•
•
•
in six-membered rings [3]
•
by reactions not involving the formation of  C=O groups [3]
C=O groups [3]
 C=O groups [3]
C=O groups [3]•
•
by hydrogenation of carbon-to-carbon double or triple bonds [3]
•
•
by introduction of halogen; by substitution of halogen atoms by other halogen atoms [3]
•
•
by introduction of functional groups containing oxygen only in singly bound form [3]
•
•
by splitting-off hydrogen atoms or functional groups; by hydrogenolysis of functional groups [3]
•
•
•
by dehydration [3]
•
•
by isomerisation; by change of size of the carbon skeleton [3]
•
•
•
by increase in the number of carbon atoms [3]
•
•
•
•
by addition to carbon-to-carbon double or triple bonds [3]
•
•
•
•
by reaction with functional groups containing oxygen only in singly bound form [3]
•
•
•
•
•
being hydroxy groups [3]
•
•
•
•
by reaction of compounds containing  C=O groups with the same or other compounds containing
C=O groups with the same or other compounds containing  C=O groups [3]
C=O groups [3]
 C=O groups with the same or other compounds containing
C=O groups with the same or other compounds containing  C=O groups [3]
C=O groups [3]•
•
•
•
•
combined with hydrogenation [3]
•
•
•
•
•
combined with dehydration [3]
•
•
•
•
•
Reactions with formaldehyde [3]
•
•
•
with the aid of ketenes [3]
•
Preparation of chelates of aldehydes or ketones [3]
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [3]
•
•
by solid-liquid treatment; by chemisorption [3]
•
•
by liquid-liquid treatment [3]
•
•
by change in the physical state, e.g. crystallisation [3]
•
•
•
by distillation [3]
•
•
•
•
by extractive distillation [3]
•
•
•
•
by azeotropic distillation [3]
•
•
by treatment giving rise to a chemical modification [3]
•
•
Use of additives, e.g. for stabilisation [3]
•
Preparation of ketenes or dimeric ketenes [3]
•
•
from ketones [3]
•
•
from carboxylic acids, their anhydrides, esters or halides [3]
•
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [3]
Preparation of quinones [3]
•
by oxidation giving rise to quinoid structures [3]
•
•
of unsubstituted ring carbon atoms in six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
of at least one hydroxy group on a six-membered aromatic ring [3]
•
•
•
with molecular oxygen [3]
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [3]
Compounds having —CHO groups
•
Saturated compounds having —CHO groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms or to hydrogen
•
•
Formaldehyde
•
•
•
Preparation from carbon monoxide [3]
•
•
•
Preparation by depolymerisation [3]
•
•
•
Preparation by oxidation of hydrocarbons [3]
•
•
•
Preparation by oxidation of methanol [3]
•
•
•
•
using noble metals or compounds thereof as catalysts [3]
•
•
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [3]
•
•
Acetaldehyde
•
•
•
Preparation by oxidation [3]
•
•
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [3]
•
•
containing rings [3]
•
•
•
monocyclic [3]
•
•
•
containing condensed ring systems [3]
•
•
containing more than one —CHO group
•
•
•
Glyoxal [3]
•
•
•
containing rings [3]
•
•
containing halogen
•
•
•
Trichloroacetaldehyde
•
•
•
containing rings [3]
•
•
containing hydroxy groups [3]
•
•
•
containing rings [3]
•
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
containing ether groups,  groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]
 groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]•
Unsaturated compounds having —CHO groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms
•
•
with only carbon-to-carbon double bonds as unsaturation [3]
•
•
•
Acrylaldehyde; Methacrylaldehyde [3]
•
•
with only carbon-to-carbon triple bonds as unsaturation [3]
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings, e.g. phenylacetaldehyde [3]
•
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
•
having unsaturation outside the aromatic rings [3]
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings and other rings [3]
•
•
•
having unsaturation outside the aromatic rings [3]
•
•
containing halogen
•
•
containing hydroxy groups [3]
•
•
•
acyclic [3]
•
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
containing ether groups,  groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]
 groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]•
Saturated compounds having —CHO groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings
•
•
with a three- or four-membered ring [3]
•
•
with a five-membered ring
•
•
with a six-membered ring
•
•
with a seven- to twelve-membered ring [3]
•
•
polycyclic
•
•
•
having a —CHO group on a condensed ring system [3]
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
containing hydroxy groups
•
•
containing ether groups,  groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]
 groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]•
Unsaturated compounds having —CHO groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings
•
•
with a three- or four-membered ring [3]
•
•
with a five-membered ring [3]
•
•
with a six-membered ring [3]
•
•
with a seven- to twelve-membered ring [3]
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
•
containing a condensed ring system [3]
•
•
having unsaturation outside the rings [2]
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
containing hydroxy groups
•
•
containing ether groups,  groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]
 groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]•
Compounds having —CHO groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings
•
•
Benzaldehyde
•
•
Alkylated benzaldehydes [3]
•
•
Diformyl-benzenes; Alkylated derivatives thereof [3]
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
having unsaturation outside the six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
containing halogen [2]
•
•
containing hydroxy groups
•
•
•
all hydroxy groups bound to the ring [3]
•
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
containing ether groups,  groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]
 groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]•
•
•
Vanillin
Ketones; Ketenes; Dimeric ketenes; Ketonic chelates
•
Saturated compounds containing keto groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms
•
•
Acetone [3]
•
•
Methyl-ethyl ketone [3]
•
•
containing rings [3]
•
•
•
monocyclic [3]
•
•
•
containing condensed ring systems [3]
•
•
Ketones containing more than one keto group
•
•
•
Acetylacetone, i.e. 2,4-pentanedione
•
•
•
containing rings [3]
•
•
containing halogen
•
•
•
containing rings [3]
•
•
•
containing only fluorine as halogen [3]
•
•
containing hydroxy groups [2]
•
•
•
containing rings [3]
•
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
•
•
containing —CHO groups [3]
•
Unsaturated compounds containing keto groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms
•
•
with only carbon-to-carbon double bonds as unsaturation [3]
•
•
•
Methyl-vinyl ketone [3]
•
•
with only carbon-to-carbon triple bonds as unsaturation [3]
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
•
having unsaturation outside the aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings and other rings [3]
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
•
having unsaturation outside the aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings and other rings [3]
•
•
containing hydroxy groups
•
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
•
having unsaturation outside the aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings and other rings [3]
•
•
containing ether groups,  groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]
 groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]•
•
containing —CHO groups [3]
•
Saturated compounds containing keto groups bound to rings [3]
•
•
to a three- or four-membered ring [3]
•
•
to a five-membered ring [3]
•
•
to a six-membered ring [3]
•
•
to a seven- to twelve-membered ring [3]
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
•
both carbon atoms bound to the keto group belonging to rings [3]
•
•
•
having keto groups bound to condensed ring systems [3]
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
containing hydroxy groups [3]
•
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
containing ether groups,  groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]
 groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]•
•
containing —CHO groups [3]
•
Saturated compounds containing a keto group being part of a ring [3]
•
•
of a three- or four-membered ring [3]
•
•
of a five-membered ring [3]
•
•
of a six-membered ring [3]
•
•
•
Menthones [3]
•
•
of a seven- to twelve-membered ring [3]
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
•
a keto group being part of a condensed ring system [3]
•
•
•
•
having two rings [3]
•
•
•
•
•
the condensed ring system containing seven carbon atoms [3]
•
•
•
•
•
•
Camphor; Fenchone [3]
•
•
•
•
•
the condensed ring system containing eight or nine carbon atoms [3]
•
•
•
•
•
the condensed ring system containing ten carbon atoms [3]
•
•
•
•
having three rings [3]
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
•
a keto group being part of a six-membered ring [3]
•
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
•
•
a keto group being part of a condensed ring system [3]
•
•
•
•
•
having two rings [3]
•
•
•
•
•
having three rings [3]
•
•
containing hydroxy groups [3]
•
•
•
a keto group being part of a three- to five-membered ring [3]
•
•
•
a keto group being part of a six-membered ring [3]
•
•
•
a keto group being part of a seven- to twelve-membered ring [3]
•
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
•
•
a keto group being part of a condensed ring system [3]
•
•
containing ether groups,  groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]
 groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]•
•
containing —CHO groups [3]
•
Unsaturated compounds containing keto groups bound to rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
to a three- or four-membered ring [3]
•
•
to a five-membered ring [3]
•
•
to a six-membered ring [3]
•
•
to a seven- to twelve-membered ring [3]
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
having unsaturation outside the rings [3]
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
containing hydroxy groups [3]
•
•
containing ether groups,  groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]
 groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]•
•
containing —CHO groups [3]
•
Unsaturated compounds containing a keto group being part of a ring [3]
•
•
of a three- or four-membered ring [3]
•
•
of a five-membered ring [3]
•
•
of a six-membered ring [3]
•
•
of a seven- to twelve-membered ring [3]
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
•
a keto group being part of a condensed ring system [3]
•
•
•
•
having two rings [3]
•
•
•
•
•
the condensed ring system containing seven carbon atoms [3]
•
•
•
•
•
the condensed ring system containing eight or nine carbon atoms [3]
•
•
•
•
•
the condensed ring system containing ten carbon atoms [3]
•
•
•
•
having three rings [3]
•
•
having unsaturation outside the ring [3]
•
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
a keto group being part of a condensed ring system [3]
•
•
•
•
having two rings, e.g. tetralones [3]
•
•
•
•
having three rings [3]
•
•
•
having unsaturation outside the aromatic rings [3]
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
containing hydroxy groups [3]
•
•
•
a keto group being part of a three- to five-membered ring [3]
•
•
•
a keto group being part of a six-membered ring [3]
•
•
•
a keto group being part of a seven- to twelve-membered ring [3]
•
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
•
•
a keto group being part of a condensed ring system [3]
•
•
•
•
•
having two rings [3]
•
•
•
•
•
having three rings [3]
•
•
•
having unsaturation outside the rings, e.g. humulones, lupulones [3]
•
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
containing ether groups,  groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]
 groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]•
•
•
a keto group being part of a condensed ring system with two or three rings, at least one ring being a six-membered aromatic ring [3]
•
•
containing —CHO groups [3]
•
Ketones containing a keto group bound to a six-membered aromatic ring (compounds having a keto group being part of a condensed ring system and being bound to a six-membered aromatic ring C07C 49/657-C07C 49/757)
•
•
Acetophenone
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
•
with all keto groups bound to a non-condensed ring [3]
•
•
•
•
Benzophenone [3]
•
•
•
with keto groups bound to a condensed ring system [3]
•
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
having unsaturation outside an aromatic ring [3]
•
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
containing halogen
•
•
•
all halogen atoms bound to the ring [3]
•
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
containing hydroxy groups [3]
•
•
•
all hydroxy groups bound to the ring [3]
•
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
•
having unsaturation outside an aromatic ring [3]
•
•
•
•
containing —CHO groups [3]
•
Ketenes; Dimeric ketenes [3]
•
•
Ketene, i.e. C2H2O [3]
•
Ketonic chelates [3]
Quinones (for quinone methides, see unsaturated ketones with a keto group being part of a ring) [3]
Note(s)
- In this group, quinhydrones are classified according to their quinoid part.
•
with monocyclic quinoid structure [3]
•
•
Benzoquinones, i.e. C6H4O2 [3]
•
•
with unsaturation outside the quinoid structure [3]
•
with polycyclic non-condensed quinoid structure [3]
•
the quinoid structure being part of a condensed ring system containing two rings [3]
•
•
Naphthoquinones, i.e. C10H6O2 [3]
•
•
with unsaturation outside the ring system, e.g. vitamin K1 [3]
•
the quinoid structure being part of a condensed ring system containing three rings [3]
•
•
Anthraquinones, i.e. C14H8O2 [3]
•
•
with unsaturation outside the ring system [3]
•
the quinoid structure being part of a condensed ring system containing four or more rings [3]
•
containing halogen [3]
•
containing groups having oxygen atoms singly bound to carbon atoms [3]
•
•
with monocyclic quinoid structure [3]
•
•
with polycyclic non-condensed quinoid structure [3]
•
•
the quinoid structure being part of a condensed ring system having two rings [3]
•
•
the quinoid structure being part of a condensed ring system having three rings [3]
•
•
the quinoid structure being part of a condensed ring system having four or more rings [3]
•
containing —CHO or non-quinoid keto groups [3]
Preparation of carboxylic acids or their salts, halides, or anhydrides [2]
•
from salts of carboxylic acids
•
from carboxylic acid halides
•
from carboxylic acid amides
•
from nitriles
•
from carboxylic acid anhydrides [3]
•
•
by hydrolysis [3]
•
from carboxylic acid esters or lactones (saponification of carboxylic acid esters C07C 27/02)
•
by hydrolysis of —CX3 groups, X being halogen [3]
•
from or via nitro-substituted organic compounds [3]
•
by reaction with carbon monoxide
•
•
on an oxygen-containing group in organic compounds, e.g. alcohols
•
•
on a carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bond in organic compounds [3]
•
•
with simultaneous oxidation [3]
•
by reaction of organic compounds with carbon dioxide, e.g. Kolbe-Schmitt synthesis [2]
•
by oxidation (C07C 51/145 takes precedence) [3]
•
•
with molecular oxygen [3]
•
•
•
of saturated hydrocarbyl groups [3]
•
•
•
•
of paraffin waxes [3]
•
•
•
of oxygen-containing groups to carboxyl groups [3]
•
•
•
•
of —CHO groups or primary alcohol groups [3]
•
•
•
•
of keto groups or secondary alcohol groups [3]
•
•
•
of unsaturated compounds containing no six-membered aromatic ring [3]
•
•
•
of compounds containing six-membered aromatic rings without ring-splitting [3]
•
•
•
•
having alkyl side chains which are oxidised to carboxyl groups [3]
•
•
with oxides of nitrogen or nitrogen-containing mineral acids [3]
•
•
•
of hydrocarbyl groups [3]
•
•
with peroxy-compounds [3]
•
•
with halogen-containing compounds which may be formed in situ [3]
•
•
with inorganic bases, e.g. by alkali fusion [3]
•
•
with sulfur or sulfur-containing compounds [3]
•
•
of cyclic compounds with ring-splitting [3]
•
by oxidation with ozone; by hydrolysis of ozonides [3]
•
by reactions not involving formation of carboxyl groups [3]
•
•
by isomerisation; by change of size of the carbon skeleton [3]
•
•
by hydrogenation of carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds [3]
•
•
by introduction of halogen; by substitution of halogen atoms by other halogen atoms [3]
•
•
by introduction of functional groups containing oxygen only in singly bound form [3]
•
•
by introduction of functional groups containing oxygen only in doubly bound form [3]
•
•
by splitting-off hydrogen or functional groups; by hydrogenolysis of functional groups [3]
•
•
•
by decarboxylation [3]
•
Preparation of salts of carboxylic acids by conversion of the acids or their salts into salts with the same carboxylic acid part (preparation of soap C11D) [3]
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [3]
•
•
by change of the physical state, e.g. crystallisation [3]
•
•
•
by distillation [3]
•
•
•
•
by azeotropic distillation [3]
•
•
by solid-liquid treatment; by chemisorption [3]
•
•
by liquid-liquid treatment
•
•
by treatment giving rise to chemical modification (by chemisorption C07C 51/47) [3]
•
•
•
whereby carboxylic acid esters are formed [3]
•
•
Use of additives, e.g. for stabilisation [3]
•
Preparation of carboxylic acid anhydrides (by oxidation C07C 51/16)
•
•
from organic acids, their salts, or their esters
•
•
by reactions not involving the carboxylic acid anhydride group [3]
•
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [3]
•
Preparation of carboxylic acid halides
•
•
by conversion of carboxylic acids or their anhydrides into halides with the same carboxylic acid part [3]
•
•
by reactions not involving the carboxylic acid halide group [3]
•
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [3]
Saturated compounds having only one carboxyl group bound to an acyclic carbon atom or hydrogen
•
Formic acid
•
•
Preparation from carbon monoxide
•
•
Salts thereof
•
Acetic acid
•
•
Salts thereof
•
Acetic anhydride (ketene C07C 49/90)
•
Propionic acid [3]
•
Acids containing four carbon atoms [3]
•
Acids containing more than four carbon atoms [3]
•
•
the carboxyl group being bound to a carbon atom bound to at least two other carbon atoms, e.g. neo-acids [3]
•
containing rings [3]
•
•
monocyclic [3]
•
•
containing condensed ring systems [3]
•
•
•
containing an adamantane ring system [3]
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
Halogenated acetic acids [3]
•
•
•
containing fluorine [3]
•
•
Acids containing three or more carbon atoms [3]
•
•
•
containing fluorine [3]
•
•
containing rings [3]
•
Acyl halides [3]
•
•
Acetyl halides [3]
•
•
of acids containing three or more carbon atoms [3]
•
•
containing rings [3]
•
•
containing halogen outside the carbonyl halide group [3]
•
•
•
Halogenated acetyl halides [3]
•
•
•
of acids containing three or more carbon atoms [3]
Saturated compounds having more than one carboxyl group bound to acyclic carbon atoms [2]
•
Dicarboxylic acids
•
•
Oxalic acid
•
•
•
Salts thereof [3]
•
•
Malonic acid
•
•
Succinic acid
•
•
Glutaric acid
•
•
Adipic acid
•
•
Pimelic acid
•
•
Azelaic acid
•
•
Sebacic acid
•
•
Dicarboxylic acids having twelve carbon atoms [3]
•
Tricarboxylic acids
•
containing more than three carboxyl groups
•
containing rings [3]
•
•
monocyclic [3]
•
•
containing condensed ring systems [3]
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
containing rings [3]
•
Acyl halides [3]
•
•
containing rings [3]
•
•
containing halogen outside the carbonyl halide group [3]
Unsaturated compounds having carboxyl groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [2]
•
with only carbon-to-carbon double bonds as unsaturation
•
•
Monocarboxylic acids [3]
•
•
•
Acrylic acid; Methacrylic acid [3]
•
•
•
•
Preparation by oxidation in the liquid phase [3]
•
•
•
•
Preparation by oxidation in the gaseous phase [3]
•
•
•
•
•
starting from unsaturated aldehydes [3]
•
•
•
•
Preparation by splitting-off H—X, X being halogen, OR, or NR2, R being hydrogen or a hydrocarbon group [3]
•
•
•
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [3]
•
•
•
•
•
Use of additives, e.g. for stabilisation [3]
•
•
•
Crotonic acid [3]
•
•
•
Sorbic acid [3]
•
•
•
Straight chain carboxylic acids containing eighteen carbon atoms [3]
•
•
Dicarboxylic acids [3]
•
•
•
Maleic acid [3]
•
•
•
Fumaric acid [3]
•
•
•
Citraconic acid [3]
•
•
•
Muconic acid [3]
•
with only carbon-to-carbon triple bonds as unsaturation
•
•
Propiolic acid
•
•
Acetylene dicarboxylic acid
•
•
Diacetylene or polyacetylene dicarboxylic acids
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
containing an adamantane ring system [3]
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
Phenylacetic acid [3]
•
•
containing more than one carboxyl group [3]
•
•
•
Phenylmalonic acid [3]
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
•
containing condensed ring systems [3]
•
•
having unsaturation outside the rings [3]
•
•
•
Cinnamic acid [3]
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings and other rings, e.g. cyclohexylphenylacetic acid [3]
•
•
having unsaturation outside the aromatic rings [3]
•
•
containing condensed ring systems [3]
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
Halogenated acrylic or methacrylic acids [3]
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
having unsaturation outside the rings [3]
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings and other rings [3]
•
Acyl halides [3]
•
•
with only carbon-to-carbon double bonds as unsaturation [3]
•
•
with only carbon-to-carbon triple bonds as unsaturation [3]
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings and other rings [3]
•
•
containing halogen outside the carbonyl halide groups [3]
Compounds having carboxyl groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms and containing any of the groups OH, O-metal, —CHO, keto, ether,  groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [2]
groups [2]
 groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [2]
groups [2]•
Saturated compounds having only one carboxyl group and containing hydroxy or O-metal groups [3]
•
•
Glycolic acid [3]
•
•
Lactic acid [3]
•
•
Polyhydroxy carboxylic acids
•
•
•
having five or more carbon atoms, e.g. aldonic acids [3]
•
•
containing rings [3]
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
Saturated compounds having only one carboxyl group and containing ether groups,  groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]
 groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]•
•
containing rings [3]
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
Saturated compounds having only one carboxyl group and containing —CHO groups [3]
•
•
Glyoxylic acid [3]
•
Saturated compounds having only one carboxyl group and containing keto groups [3]
•
•
Pyruvic acid [3]
•
•
Acetoacetic acid [3]
•
•
containing rings [3]
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
containing singly bound oxygen-containing groups [3]
•
•
containing —CHO groups [3]
•
Saturated compounds having more than one carboxyl group [3]
•
•
containing hydroxy or O-metal groups [3]
•
•
•
Tartaric acid [3]
•
•
•
Citric acid [3]
•
•
•
Polyhydroxy dicarboxylic acids having five or more carbon atoms, e.g. saccharic acids [3]
•
•
•
containing rings [3]
•
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
containing ether groups,  groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]
 groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]•
•
•
containing rings [3]
•
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
containing —CHO groups [3]
•
•
containing keto groups [3]
•
•
•
containing rings [3]
•
Unsaturated compounds [3]
•
•
containing hydroxy or O-metal groups [3]
•
•
•
Ricinoleic acid [3]
•
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
•
Mandelic acid [3]
•
•
•
a hydroxy or O-metal group being bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [3]
•
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings and other rings [3]
•
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
containing ether groups,  groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]
 groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]•
•
•
the non-carboxylic part of the ether being unsaturated [3]
•
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
•
the non-carboxylic part of the ether containing six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
•
•
the oxygen atom of the ether group being bound to a non-condensed six-membered aromatic ring [3]
•
•
•
•
•
•
Ethers of hydroxy-acetic acid [3]
•
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings and other rings [3]
•
•
containing —CHO groups [3]
•
•
containing keto groups [3]
•
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
•
the keto group being part of a ring [3]
•
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings and other rings [3]
•
•
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
•
containing singly bound oxygen-containing groups [3]
•
•
•
containing —CHO groups [3]
Compounds having carboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings
•
Saturated compounds having a carboxyl group bound to a three- or four-membered ring [3]
•
Saturated compounds having a carboxyl group bound to a five-membered ring [3]
•
Saturated compounds having a carboxyl group bound to a six-membered ring [3]
•
•
Completely hydrogenated benzenedicarboxylic acids [3]
•
Saturated compounds having a carboxyl group bound to a seven- to twelve-membered ring [3]
•
Saturated polycyclic compounds [3]
•
•
having a carboxyl group bound to a condensed ring system [3]
•
•
•
having two rings [3]
•
•
•
having three rings [3]
•
Saturated compounds containing halogen [3]
•
Unsaturated compounds [3]
•
•
having a carboxyl group bound to a five-membered ring [3]
•
•
having a carboxyl group bound to a six-membered ring [3]
•
•
•
Partially hydrogenated benzenedicarboxylic acids [3]
•
•
having a carboxyl group bound to a seven- to twelve-membered ring [3]
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
•
having a carboxyl group bound to a condensed ring system [3]
•
•
having unsaturation outside the rings [3]
•
•
•
Chrysanthemumic acid [3]
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
containing halogen [3]
Compounds having carboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings and containing any of the groups OH, O-metal, —CHO, keto, ether,  groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]
 groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]•
Saturated compounds containing hydroxy or O-metal groups [3]
•
•
with a six-membered ring [3]
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
Saturated compounds containing ether groups,  groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]
 groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]•
•
with a six-membered ring [3]
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
•
having a carboxyl group on a condensed ring system [3]
•
Saturated compounds containing —CHO groups [3]
•
Saturated compounds containing keto groups [3]
•
•
with a six-membered ring [3]
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
the keto group being part of a ring [3]
•
•
containing singly bound oxygen-containing groups [3]
•
•
containing —CHO groups [3]
•
Unsaturated compounds [3]
•
•
containing hydroxy or O-metal groups [3]
•
•
containing ether groups,  groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]
 groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]•
•
containing —CHO groups [3]
•
•
containing keto groups [3]
Compounds having carboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [2]
•
Monocyclic monocarboxylic acids
•
•
Benzoic acid
•
•
•
Salts thereof
•
•
•
Halides thereof
•
Monocyclic dicarboxylic acids
•
•
all carboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of the six-membered aromatic ring [3]
•
•
•
1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid [3]
•
•
•
•
Salts thereof [3]
•
•
•
•
Halides thereof [3]
•
•
•
1,3-Benzenedicarboxylic acid [3]
•
•
•
1,4-Benzenedicarboxylic acid [3]
•
•
•
•
Salts thereof [3]
•
•
•
•
Halides thereof [3]
•
Monocyclic tricarboxylic acids [3]
•
Monocyclic acids containing more than three carboxyl groups [3]
•
Polycyclic acids [3]
•
•
with all carboxyl groups bound to non-condensed rings [3]
•
•
•
4,4'-Diphenyldicarboxylic acids [3]
•
•
with carboxyl groups bound to condensed ring systems [3]
•
•
•
containing two rings [3]
•
•
•
•
containing one carboxyl group [3]
•
•
•
•
containing two carboxyl groups both bound to carbon atoms of the condensed ring system [3]
•
•
•
•
containing three or more carboxyl groups all bound to carbon atoms of the condensed ring system [3]
•
•
•
containing three or more rings [3]
•
•
•
•
containing one carboxyl group [3]
•
•
•
•
containing two carboxyl groups both bound to carbon atoms of the condensed ring system [3]
•
•
•
•
containing three or more carboxyl groups all bound to carbon atoms of the condensed ring system [3]
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
Monocyclic acids with unsaturation outside the aromatic ring [3]
•
Polycyclic acids with unsaturation outside the aromatic rings [3]
•
containing halogen [3]
•
•
Monocarboxylic acids [3]
•
•
Polycyclic acids [3]
•
•
having unsaturation outside the aromatic rings [3]
Compounds having carboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings and containing any of the groups OH, O-metal, —CHO, keto, ether,  groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups
groups
 groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups
groups •
containing hydroxy or O-metal groups [3]
•
•
monocyclic and having all hydroxy or O-metal groups bound to the ring [3]
•
•
•
o-Hydroxy carboxylic acids [3]
•
•
•
•
Salicylic acid [3]
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
•
with carboxyl groups on a condensed ring system containing two rings [3]
•
•
•
with carboxyl groups on a condensed ring system containing more than two rings [3]
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
having unsaturation outside the aromatic ring [3]
•
containing ether groups,  groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]
 groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  groups [3]
groups [3]•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
having unsaturation outside the aromatic rings [3]
•
containing —CHO groups [3]
•
containing keto groups [3]
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
having unsaturation outside the aromatic rings [3]
•
•
containing singly bound oxygen-containing groups [3]
•
•
containing —CHO groups [3]
Quinone carboxylic acids [2]
•
Anthraquinone carboxylic acids [2]
Preparation of carboxylic acid esters
Note(s)
- In this group, lactones used as reactants are considered as being esters.
•
by interreacting ester groups, i.e. transesterification
•
by reacting an ester group with a hydroxy group [2]
•
by reacting carboxylic acids or symmetrical anhydrides with saturated hydrocarbons [3]
•
by reacting carboxylic acids or symmetrical anhydrides onto unsaturated carbon-to-carbon bonds [2]
•
•
with oxidation [3]
•
•
•
in the presence of platinum group metals or their compounds [3]
•
by reacting carboxylic acids or symmetrical anhydrides with the hydroxy or O-metal group of organic compounds [2]
•
by reacting carboxylic acids or symmetrical anhydrides with ester groups or with a carbon-halogen bond [2]
•
•
being mineral ester groups [3]
•
from asymmetrical anhydrides [2]
•
from carboxylic acid halides [2]
•
from carboxylic acids, esters or anhydrides wherein one oxygen atom has been replaced by a sulfur, selenium or tellurium atom [2]
•
by conversion of a group containing nitrogen into an ester group [2]
•
•
from amides or lactams [2]
•
•
from nitriles [2]
•
by reacting carboxylic acids or derivatives thereof with a carbon-to-oxygen ether bond, e.g. acetal, tetrahydrofuran [2]
•
•
with an oxirane ring [2]
•
from ortho-esters [3]
•
by modifying the hydroxylic moiety of the ester, such modification not being an introduction of an ester group [2]
•
•
by hydrogenation of unsaturated carbon-to-carbon bonds [3]
•
•
by introduction of halogen; by substitution of halogen atoms by other halogen atoms [3]
•
•
by introduction of oxygen-containing functional groups [3]
•
•
by isomerisation; by change of size of the carbon skeleton [3]
•
•
by splitting-off hydrogen or functional groups; by hydrogenolysis of functional groups [3]
•
by modifying the acid moiety of the ester, such modification not being an introduction of an ester group [2]
•
•
by hydrogenation of unsaturated carbon-to-carbon bonds [3]
•
•
by introduction of halogen; by substitution of halogen atoms by other halogen atoms [3]
•
•
by introduction of functional groups containing oxygen only in singly bound form [3]
•
•
by introduction of doubly bound oxygen containing functional groups, e.g. carboxyl groups [3]
•
•
by splitting-off hydrogen or functional groups; by hydrogenolysis of functional groups [3]
•
•
•
Decarboxylation [3]
•
•
•
by elimination of functional groups containing oxygen only in singly bound form [3]
•
•
by isomerisation; by change of size of the carbon skeleton (introduction or elimination of carboxyl groups C07C 67/313, C07C 67/32) [3]
•
•
•
Migration of  groups in the molecule [3]
groups in the molecule [3]
 groups in the molecule [3]
groups in the molecule [3]•
•
•
by increase in the number of carbon atoms [3]
•
•
•
•
by addition to unsaturated carbon-to-carbon bonds [3]
•
by reaction with carbon monoxide or formates (C07C 67/02, C07C 67/03, C07C 67/10 take precedence) [2]
•
•
by reaction of ethers with carbon monoxide [2]
•
•
by addition to an unsaturated carbon-to-carbon bond [2]
•
by oxidation of groups which are precursors for the acid moiety of the ester [3]
•
•
by oxidation of primary alcohols [3]
•
•
by oxidation of secondary alcohols or ketones [3]
•
by oxidation-reduction of aldehydes, e.g. Tishchenko reaction [2]
•
from ketenes or polyketenes [2]
•
by oligomerisation [3]
•
by telomerisation (macromolecular compounds C08) [3]
•
by splitting of carbon-to-carbon bonds and redistribution, e.g. disproportionation or migration of  groups between different molecules [3]
groups between different molecules [3]
 groups between different molecules [3]
groups between different molecules [3]•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [3]
•
•
by change in the physical state, e.g. crystallisation [3]
•
•
•
by distillation [3]
•
•
by solid-liquid treatment; by chemisorption [3]
•
•
by liquid-liquid treatment [3]
•
•
by treatment giving rise to chemical modification (by chemisorption C07C 67/56) [3]
•
•
Use of additives, e.g. for stabilisation [3]
Preparation of esters of carbonic or haloformic acids [2]
•
from phosgene or haloformates [2]
•
from carbon dioxide or inorganic carbonates [2]
•
from organic carbonates [2]
•
Purification; Separation; Stabilisation [2]
Esters of carboxylic acids; Esters of carbonic or haloformic acids
Note(s)
- Attention is drawn to Note (6) following the title of this subclass.
•
Esters of saturated alcohols having the esterified hydroxy group bound to an acyclic carbon atom [3]
•
Esters of unsaturated alcohols having the esterified hydroxy group bound to an acyclic carbon atom [3]
•
•
Vinyl esters [3]
•
Esters of alcohols having the esterified hydroxy group bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [3]
•
Esters of hydroxy compounds having the esterified hydroxy group bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [3]
Note(s)
- Esters having a variably-specified acid moiety, i.e. covered by more than one of groups C07C 69/02, C07C 69/34, C07C 69/52, C07C 69/608, C07C 69/612, C07C 69/62, C07C 69/66, C07C 69/74, C07C 69/76, C07C 69/95, C07C 69/96, are covered by groups C07C 69/003-C07C 69/017 according to their hydroxylic moiety.
•
Esters of acyclic saturated monocarboxylic acids having the carboxyl group bound to an acyclic carbon atom or to hydrogen
•
•
esterified with unsaturated alcohols having the esterified hydroxy group bound to an acyclic carbon atom [3]
•
•
esterified with alcohols having the esterified hydroxy group bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [3]
•
•
esterified with a hydroxy compound having the esterified hydroxy group bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [3]
•
•
Formic acid esters
•
•
•
of monohydroxylic compounds
•
•
•
•
of unsaturated alcohols [2]
•
•
•
of dihydroxylic compounds
•
•
•
of trihydroxylic compounds
•
•
Acetic acid esters
•
•
•
of monohydroxylic compounds
•
•
•
•
of unsaturated alcohols [2]
•
•
•
•
•
Vinyl acetate [2]
•
•
•
•
•
Allyl acetate [2]
•
•
•
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [3]
•
•
•
of dihydroxylic compounds
•
•
•
of trihydroxylic compounds
•
•
•
of hydroxy compounds with more than three hydroxy groups [2]
•
•
having three or more carbon atoms in the acid moiety
•
•
•
esterified with monohydroxylic compounds
•
•
•
•
Synthetic waxes
•
•
•
esterified with dihydroxylic compounds
•
•
•
esterified with trihydroxylic compounds
•
•
•
esterified with hydroxy compounds having more than three hydroxy groups [2]
•
Esters of acyclic saturated polycarboxylic acids having an esterified carboxyl group bound to an acyclic carbon atom [3]
•
•
esterified with unsaturated alcohols having the esterified hydroxy group bound to an acyclic carbon atom [3]
•
•
esterified with a hydroxy compound having the esterified hydroxy group bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [3]
•
•
Oxalic acid esters [3]
•
•
Malonic acid esters [3]
•
•
Succinic acid esters [3]
•
•
Glutaric acid esters [3]
•
•
Adipic acid esters [3]
•
•
Pimelic acid esters [3]
•
•
Azelaic acid esters [3]
•
•
Sebacic acid esters [3]
•
Esters of acyclic unsaturated carboxylic acids having the esterified carboxyl group bound to an acyclic carbon atom [3]
•
•
of unsaturated hydroxy compounds [3]
•
•
Monocarboxylic acid esters having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond [3]
•
•
•
Acrylic acid esters; Methacrylic acid esters [3]
•
•
•
Crotonic acid esters; Vinyl acetic acid esters [3]
•
•
•
Esters of straight chain acids with eighteen carbon atoms in the acid moiety [3]
•
•
Monocarboxylic acid esters having at least two carbon-to-carbon double bonds [3]
•
•
Dicarboxylic acid esters having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond [3]
•
•
•
Maleic acid esters; Fumaric acid esters [3]
•
•
Dicarboxylic acid esters having at least two carbon-to-carbon double bonds [3]
•
•
Polycarboxylic acid esters, the acid moiety containing more than two carboxyl groups [3]
•
•
having only carbon-to-carbon triple bonds as unsaturation in the carboxylic acid moiety [3]
•
Esters of carboxylic acids having a carboxyl group bound to an acyclic carbon atom and having a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring in the acid moiety [3]
•
Esters of carboxylic acids having a carboxyl group bound to an acyclic carbon atom and having a six-membered aromatic ring in the acid moiety [3]
•
•
of phenylacetic acid [3]
•
•
polycyclic [3]
•
•
having unsaturation outside the six-membered aromatic ring [3]
•
Halogen-containing esters [2]
•
•
of saturated acids [2]
•
•
•
containing rings in the acid moiety [3]
•
•
of unsaturated acids [2]
•
•
•
Acrylic acid esters; Methacrylic acid esters; Haloacrylic acid esters; Halomethacrylic acid esters [3]
•
•
•
Maleic acid esters; Fumaric acid esters; Halomaleic acid esters; Halofumaric acid esters [3]
•
Esters of carboxylic acids having esterified carboxyl groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms and having any of the groups OH, O-metal, —CHO, keto, ether, acyloxy,  groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  in the acid moiety
in the acid moiety
 groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  in the acid moiety
in the acid moiety •
•
of saturated acids [2]
•
•
•
of saturated hydroxy-carboxylic acids [3]
•
•
•
•
Lactic acid esters [3]
•
•
•
•
Tartaric acid esters [3]
•
•
•
•
Citric acid esters [3]
•
•
•
Ethers [3]
•
•
•
•
the hydroxy group of the ester being etherified with a hydroxy compound having the hydroxy group bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [3]
•
•
•
Esters of keto-carboxylic acids [3]
•
•
•
•
Acetoacetic acid esters [3]
•
•
of unsaturated acids [2]
•
•
•
of unsaturated hydroxy carboxylic acids [3]
•
•
•
Ethers [3]
•
•
•
•
the hydroxy group of the ester being etherified with a hydroxy compound having the hydroxy group bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [3]
•
•
•
Esters of keto-carboxylic acids [3]
•
Esters of carboxylic acids having an esterified carboxyl group bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring
•
•
of acids with a three-membered ring and with unsaturation outside the ring [3]
•
•
•
Chrysanthemumic acid esters [3]
•
•
of acids with a six-membered ring [3]
•
•
of polycyclic acids [3]
•
•
having any of the groups OH, O-metal, —CHO, keto, ether, acyloxy,  groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  in the acid moiety [3]
in the acid moiety [3]
 groups,
groups,  groups, or
groups, or  in the acid moiety [3]
in the acid moiety [3]•
Esters of carboxylic acids having an esterified carboxyl group bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring
•
•
esterified with unsaturated alcohols having the esterified hydroxy group bound to an acyclic carbon atom [3]
•
•
esterified with a hydroxy compound having the esterified hydroxy group bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [3]
•
•
Benzoic acid esters
•
•
Phthalic acid esters [2]
•
•
•
Terephthalic acid esters
•
•
•
of unsaturated alcohols [2]
•
•
of monocyclic hydroxy carboxylic acids, the hydroxy groups and the carboxyl groups of which are bound to carbon atoms of a six-membered aromatic ring
•
•
•
with esterified hydroxyl groups
•
•
•
with esterified carboxyl groups
•
•
•
with esterified hydroxyl and carboxyl groups
•
•
•
with etherified hydroxyl groups [2]
•
•
of polycyclic hydroxy carboxylic acids, the hydroxy groups and the carboxyl groups of which are bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [2]
•
Esters of quinone carboxylic acids [2]
•
Esters of carbonic or haloformic acids [2]
Esters of oxyacids of halogens
Compounds containing carbon and nitrogen with or without hydrogen, halogens or oxygen [5]
Preparation of esters of nitric or nitrous acid or of compounds containing nitro or nitroso groups bound to a carbon skeleton [5]
•
Preparation of esters of nitric acid [5]
•
Preparation of esters of nitrous acid [5]
•
Preparation of nitro compounds [5]
•
•
by substitution of hydrogen atoms by nitro groups [5]
•
•
by substitution of functional groups by nitro groups [5]
•
•
by reactions not involving the formation of nitro groups [5]
•
•
by formation of nitro groups together with reactions not involving the formation of nitro groups [5]
•
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [5]
Esters of nitric or nitrous acid [5]
•
Esters of nitric acid [5]
•
•
having nitrate groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
Glycerol trinitrate [5]
•
•
having nitrate groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having nitrate groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
Compounds containing nitro groups bound to a carbon skeleton [5]
•
having nitro groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
of a saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
having nitro groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
having nitro groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by halogen atoms [5]
•
•
having nitro groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having nitro groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having nitro groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
the six-membered aromatic ring or a condensed ring system containing that ring being substituted by halogen atoms [5]
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by hydroxy groups [5]
•
•
having nitro groups and hydroxy groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
of a saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
of a carbon skeleton containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having nitro groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms and hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having nitro groups or hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having nitro groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings and hydroxy groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
having nitro groups and hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
having nitro groups and hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of the same non-condensed six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
•
having one nitro group bound to the ring [5]
•
•
•
•
having two nitro groups bound to the ring [5]
•
•
•
•
having three, and only three, nitro groups bound to the ring [5]
•
•
•
having nitro groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings being part of a condensed ring system [5]
•
•
and being further substituted by halogen atoms [5]
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by etherified hydroxy groups [5]
•
•
having nitro groups and etherified hydroxy groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being saturated [5]
•
•
•
•
the oxygen atom of at least one of the etherified hydroxy groups being further bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having nitro groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms and etherified hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having nitro groups or etherified hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having nitro groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings and etherified hydroxy groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having nitro groups and etherified hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of the same non-condensed six-membered aromatic ring or to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings being part of the same condensed ring system [5]
•
•
•
•
the oxygen atom of at least one of the etherified hydroxy groups being further bound to an acyclic carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
•
the oxygen atom of at least one of the etherified hydroxy groups being further bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring, e.g. nitrodiphenyl ethers [5]
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by esterified hydroxy groups [5]
•
•
having nitro groups and esterified hydroxy groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having nitro groups or esterified hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having nitro groups or esterified hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of the same non-condensed six-membered aromatic ring or to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings being part of the same condensed ring system [5]
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by —CHO groups [5]
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by at least one doubly-bound oxygen atom, not being part of a —CHO group [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton containing carbon atoms of quinone rings [5]
•
•
•
Anthraquinones containing nitro groups [5]
•
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
having nitro groups and carboxyl groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being saturated [5]
•
•
•
•
Nitro-acetic acids [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having nitro groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms and carboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having nitro groups or carboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having nitro groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings and carboxyl groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having nitro groups and carboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by halogen atoms [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
in ortho-position to the carboxyl group, e.g. nitro-salicylic acids [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by doubly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
Compounds containing nitroso groups bound to a carbon skeleton [5]
•
the carbon skeleton not being further substituted [5]
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
Preparation of compounds containing amino groups bound to a carbon skeleton [5]
•
by substitution of hydrogen atoms by amino groups [5]
•
by substitution of functional groups by amino groups [5]
•
•
by substitution of halogen atoms [5]
•
•
•
with formation of amino groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms or to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
with formation of amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings or from amines having nitrogen atoms bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
with formation of quaternary ammonium compounds [5]
•
•
by substitution of hydroxy groups or of etherified or esterified hydroxy groups [5]
•
•
•
with formation of amino groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms or to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
with formation of amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings or from amines having nitrogen atoms bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
with formation of quaternary ammonium compounds [5]
•
•
by substitution of other functional groups [5]
•
by reductive alkylation of ammonia, amines or compounds having groups reducible to amino groups, with carbonyl compounds [5]
•
•
by reduction with hydrogen [5]
•
•
by reduction with other reducing agents [5]
•
by reduction of nitrogen-to-oxygen or nitrogen-to-nitrogen bonds [5]
•
•
by reduction of nitro groups [5]
•
•
•
by reduction of nitro groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms or to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
by reduction of nitro groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
by reduction of nitroso groups [5]
•
•
by reduction of hydroxylamino or oxyimino groups [5]
•
•
by reduction of nitrogen-to-nitrogen bonds [5]
•
by reduction of carboxylic acids or esters thereof in presence of ammonia or amines, or by reduction of nitriles, carboxylic acid amides, imines or imino-ethers [5]
•
•
by reduction of carboxylic acids or esters thereof in presence of ammonia or amines [5]
•
•
by reduction of nitriles [5]
•
•
by reduction of carboxylic acid amides [5]
•
•
by reduction of imines or imino-ethers (C07C 209/24 takes precedence) [5]
•
by rearrangement reactions [5]
•
•
from carboxylic acids involving a Hofmann, Curtius, Schmidt, or Lossen-type rearrangement [5]
•
•
from or via amides [5]
•
by condensation or addition reactions, e.g. Mannich reaction, addition of ammonia or amines to alkenes or to alkynes or addition of compounds containing an active hydrogen atom to Schiff's bases, quinone imines, or aziranes [5]
•
by cleaving carbon-to-nitrogen, sulfur-to-nitrogen, or phosphorus-to-nitrogen bonds, e.g. hydrolysis of amides, N-dealkylation of amines or quaternary ammonium compounds (C07C 209/24 takes precedence) [5]
•
by disproportionation [5]
•
from or via metallo-organic compounds [5]
•
from amines, by reactions not involving amino groups, e.g. reduction of unsaturated amines, aromatisation, or substitution of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
by reduction of unsaturated amines [5]
•
•
•
by reduction of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
by halogenation, hydrohalogenation, dehalogenation, or dehydrohalogenation [5]
•
•
by nitration [5]
•
•
from carbonyl compounds, e.g. from formaldehyde, and amines having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings, with formation of methylene-diarylamines [5]
•
by photochemical reactions; by using free radicals [5]
•
Purification; Separation; Stabilisation; Use of additives [5]
•
•
Purification [5]
•
•
Separation [5]
•
•
•
Separation of optical isomers [5]
•
•
Stabilisation; Use of additives [5]
Compounds containing amino groups bound to a carbon skeleton [5]
•
having amino groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
of an acyclic saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
Monoamines [5]
•
•
•
•
Mono-, di- or tri-methylamine [5]
•
•
•
•
Mono-, di- or tri-ethylamine [5]
•
•
•
•
containing only n- or iso-propyl groups [5]
•
•
•
•
containing one, two or three alkyl groups, each having the same number of carbon atoms in excess of three [5]
•
•
•
•
containing alkyl groups having a different number of carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
Diamines [5]
•
•
•
•
Diaminoethanes [5]
•
•
•
•
Diaminopropanes [5]
•
•
•
•
1,6-Diaminohexanes [5]
•
•
•
Amines containing three or more amino groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
Amines containing amino groups bound to at least two aminoalkyl groups, e.g. diethylenetriamines [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by halogen atoms or by nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
of a saturated carbon skeleton containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
containing only non-condensed rings [5]
•
•
•
containing at least two amino groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing condensed ring systems [5]
•
•
of an acyclic unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
Monoamines [5]
•
•
•
containing at least two amino groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton containing carbon-to-carbon triple bonds [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by halogen atoms or by nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton containing at least one six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
having amino groups linked to the six-membered aromatic ring by saturated carbon chains [5]
•
•
•
having amino groups linked to the six-membered aromatic ring by unsaturated carbon chains [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by halogen atoms or by nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
the six-membered aromatic ring being part of a condensed ring system formed by two rings [5]
•
•
•
the six-membered aromatic ring being part of a condensed ring system formed by at least three rings [5]
•
•
•
•
containing dibenzocycloheptane or dibenzocycloheptene ring systems or condensed derivatives thereof [5]
•
having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
of a saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing only non-condensed rings [5]
•
•
•
containing at least two amino groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
being further substituted by halogen atoms or by nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
containing condensed ring systems [5]
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing only non-condensed rings [5]
•
•
•
containing condensed ring systems [5]
•
•
•
•
with six-membered aromatic rings being part of the condensed ring systems [5]
•
having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having amino groups bound to only one six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
Monoamines [5]
•
•
•
•
Aniline [5]
•
•
•
•
Toluidines; Homologues thereof [5]
•
•
•
•
N-alkylated amines [5]
•
•
•
having at least two amino groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
with at least two amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
•
Phenylenediamines [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by halogen atoms or by nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the amino groups further bound to a hydrocarbon radical substituted by amino groups [5]
•
•
having amino groups bound to two or three six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
Diphenylamines [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by halogen atoms or by nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings being part of condensed ring systems of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
Naphthylamines; N-substituted derivatives thereof [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by halogen atoms or by nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
containing a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring forming part of at least one of the condensed ring systems [5]
•
•
•
with at least one of the condensed ring systems formed by three or more rings [5]
•
Quaternary ammonium compounds [5]
•
•
having quaternised nitrogen atoms bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
having quaternised nitrogen atoms bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
Metal complexes of amines [5]
Preparation of compounds containing amino and hydroxy, amino and etherified hydroxy or amino and esterified hydroxy groups bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
by reactions involving the formation of amino groups from compounds containing hydroxy groups or etherified or esterified hydroxy groups [5]
•
by reaction of ammonia or amines with olefin oxides or halohydrins [5]
•
from hydroxy amines by reactions involving the etherification or esterification of hydroxy groups [5]
•
by reactions not involving the formation of amino groups, hydroxy groups or etherified or esterified hydroxy groups [5]
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [5]
Compounds containing amino and hydroxy groups bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
having hydroxy groups and amino groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being saturated [5]
•
•
•
and acyclic [5]
•
•
•
•
with only one hydroxy group and one amino group bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
with one amino group and at least two hydroxy groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
the nitrogen atom of the amino group being further bound to hydrocarbon groups substituted by hydroxy groups [5]
•
•
•
•
the nitrogen atom of the amino group being further bound to hydrocarbon groups substituted by amino groups [5]
•
•
•
•
the nitrogen atom of the amino group being further bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
with hydroxy groups and at least two amino groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being saturated and containing rings [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being unsaturated [5]
•
•
•
and acyclic [5]
•
•
•
and containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
and containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
containing hydroxy groups and carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings bound to the same carbon atom of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
•
containing hydroxy groups and carbon atoms of two six-membered aromatic rings bound to the same carbon atom of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
containing hydroxy groups and carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings bound to the same carbon atom of the carbon skeleton and at least one hydroxy group bound to another carbon atom of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
•
1-Aryl-2-amino-1,3-propane diols [5]
•
•
•
•
with rings other than six-membered aromatic rings being part of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
with quaternised nitrogen atoms bound to carbon atoms of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
having amino groups or hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings of the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
bound to carbon atoms of the same ring or condensed ring system [5]
•
having hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of at least one six-membered aromatic ring and amino groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms or to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings of the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
with amino groups linked to the six-membered aromatic ring, or to the condensed ring system containing that ring, by carbon chains not further substituted by hydroxy groups [5]
•
•
•
with amino groups and the six-membered aromatic ring, or the condensed ring system containing that ring, bound to the same carbon atom of the carbon chain [5]
•
•
•
linked by carbon chains having two carbon atoms between the amino groups and the six-membered aromatic ring or the condensed ring system containing that ring [5]
•
•
•
linked by carbon chains having at least three carbon atoms between the amino groups and the six-membered aromatic ring or the condensed ring system containing that ring [5]
•
•
with amino groups linked to the six-membered aromatic ring, or to the condensed ring system containing that ring, by carbon chains further substituted by hydroxy groups [5]
•
•
•
with hydroxy groups and the six-membered aromatic ring, or the condensed ring system containing that ring, bound to the same carbon atom of the carbon chain [5]
•
•
•
•
the chain having two carbon atoms between the amino groups and the six-membered aromatic ring or the condensed ring system containing that ring [5]
•
•
•
•
the chain having at least three carbon atoms between the amino groups and the six-membered aromatic ring or the condensed ring system containing that ring [5]
•
•
with rings other than six-membered aromatic rings being part of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
with quaternised amino groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings and hydroxy groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms or to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings of the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
with rings other than six-membered aromatic rings being part of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
with quaternised amino groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
having hydroxy groups and amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
of the same non-condensed six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
containing at least two hydroxy groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing at least two amino groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the amino groups further bound to a carbon atom of another six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings being part of condensed ring systems [5]
•
•
•
being formed by two rings [5]
•
•
•
being formed by at least three rings [5]
•
•
with quaternised amino groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
Compounds containing amino and etherified hydroxy groups bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
having etherified hydroxy groups and amino groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being acyclic and saturated [5]
•
•
•
having only one etherified hydroxy group and one amino group bound to the carbon skeleton, which is not further substituted [5]
•
•
•
•
the oxygen atom of the etherified hydroxy group being further bound to an acyclic carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
•
•
to an acyclic carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
the oxygen atom of the etherified hydroxy group being further bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
•
the oxygen atom of the etherified hydroxy group being further bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
•
•
the six-membered aromatic ring or condensed ring system containing that ring not being further substituted [5]
•
•
•
•
•
the six-membered aromatic ring or condensed ring system containing that ring being further substituted [5]
•
•
•
•
•
•
by halogen atoms, by trihalomethyl, nitro or nitroso groups, or by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
•
•
by carbon atoms having at least two bonds to oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
•
the six-membered aromatic ring being part of a condensed ring system containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
having only one etherified hydroxy group and one amino group bound to the carbon skeleton, which is further substituted by halogen atoms or by nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
having one amino group and at least two singly-bound oxygen atoms, with at least one being part of an etherified hydroxy group, bound to the carbon skeleton, e.g. ethers of polyhydroxy amines [5]
•
•
•
•
having the oxygen atom of at least one of the etherified hydroxy groups further bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
•
•
the six-membered aromatic ring or condensed ring system containing that ring being further substituted [5]
•
•
•
•
•
•
by halogen atoms, by trihalomethyl, nitro or nitroso groups, or by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
•
•
by carbon atoms having at least two bonds to oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
•
the six-membered aromatic ring being part of a condensed ring system containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
having at least two singly-bound oxygen atoms, with at least one being part of an etherified hydroxy group, bound to the same carbon atom of the carbon skeleton, e.g. amino-ketals, ortho esters [5]
•
•
•
having etherified hydroxy groups and at least two amino groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being saturated and containing rings [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being acyclic and unsaturated [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being unsaturated and containing rings [5]
•
•
Ethers of hydroxy amines of undetermined structure, e.g. obtained by reactions of epoxides with hydroxy amines [5]
•
having etherified hydroxy groups or amino groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings of the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
having etherified hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of at least one six-membered aromatic ring and amino groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms or to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings of the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
with amino groups linked to the six-membered aromatic ring, or to the condensed ring system containing that ring, by carbon chains not further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
with amino groups and the six-membered aromatic ring, or the condensed ring system containing that ring, bound to the same carbon atom of the carbon chain [5]
•
•
•
linked by carbon chains having two carbon atoms between the amino groups and the six-membered aromatic ring or the condensed ring system containing that ring [5]
•
•
•
linked by carbon chains having at least three carbon atoms between the amino groups and the six-membered aromatic ring or the condensed ring system containing that ring [5]
•
•
with amino groups linked to the six-membered aromatic ring, or to the condensed ring system containing that ring, by carbon chains further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
with singly-bound oxygen atoms and six-membered aromatic rings bound to the same carbon atom of the carbon chain [5]
•
•
•
•
with singly-bound oxygen atoms, six-membered aromatic rings and amino groups bound to the same carbon atom of the carbon chain [5]
•
•
•
•
linked by carbon chains having two carbon atoms between the amino groups and the six-membered aromatic ring or the condensed ring system containing that ring [5]
•
•
•
•
linked by carbon chains having at least three carbon atoms between the amino groups and the six-membered aromatic ring or the condensed ring system containing that ring [5]
•
•
with rings other than six-membered aromatic rings being part of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings and etherified hydroxy groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms or to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings of the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
having amino groups and etherified hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having amino groups and etherified hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of non-condensed six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
of the same non-condensed six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
•
the oxygen atom of at least one of the etherified hydroxy groups being further bound to an acyclic carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
•
•
to an acyclic carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
the oxygen atom of at least one of the etherified hydroxy groups being further bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
•
the oxygen atom of at least one of the etherified hydroxy groups being further bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring, e.g. amino-diphenylethers [5]
•
•
•
•
the nitrogen atom of at least one of the amino groups being further bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings being part of condensed ring systems and etherified hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the same carbon skeleton [5]
Compounds containing amino and esterified hydroxy groups bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
having esterified hydroxy groups and amino groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being acyclic and saturated [5]
•
•
•
having the hydroxy groups esterified by carboxylic acids having the esterifying carboxyl groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms of an acyclic saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
having at least one of the hydroxy groups esterified by a carboxylic acid having the esterifying carboxyl group bound to an acyclic carbon atom of an acyclic unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
having at least one of the hydroxy groups esterified by a carboxylic acid having the esterifying carboxyl group bound to an acyclic carbon atom of a carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
•
having at least one of the hydroxy groups esterified by a carboxylic acid having the esterifying carboxyl group bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
having at least one of the hydroxy groups esterified by a carboxylic acid having the esterifying carboxyl group bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
having at least one of the hydroxy groups esterified by an inorganic acid or a derivative thereof [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being saturated and containing rings [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being unsaturated [5]
•
•
•
and containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
having esterified hydroxy groups or amino groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings of the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
having esterified hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of at least one six-membered aromatic ring and amino groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms or to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings of the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having amino groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
with amino groups linked to the six-membered aromatic ring, or to the condensed ring system containing that ring, by carbon chains further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings and esterified hydroxy groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms or to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings of the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
having amino groups and esterified hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the same carbon skeleton [5]
Preparation of compounds containing amino groups and doubly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
Compounds containing amino and —CHO groups bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
having amino groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton [5]
Compounds containing amino groups and doubly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the same carbon skeleton, at least one of the doubly-bound oxygen atoms not being part of a —CHO group, e.g. amino ketones [5]
•
having amino groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being saturated [5]
•
•
•
and acyclic [5]
•
•
•
and containing rings [5]
•
•
•
•
with doubly-bound oxygen atoms bound to carbon atoms not being part of rings [5]
•
•
•
•
with doubly-bound oxygen atoms bound to carbon atoms being part of rings [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being unsaturated [5]
•
•
•
and containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton containing also rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
the carbon skeleton containing carbon atoms of quinone rings [5]
•
•
having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of quinone rings or of condensed ring systems containing quinone rings [5]
•
•
•
of non-condensed quinone rings [5]
•
•
•
of condensed quinone ring systems formed by two rings [5]
•
•
•
of condensed quinone ring systems formed by at least three rings [5]
•
•
•
•
Amino anthraquinones [5]
•
•
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
Preparation of compounds containing amino and carboxyl groups bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
Formation of carboxyl groups in compounds containing amino groups, e.g. by oxidation of amino alcohols [5]
•
Formation of amino groups in compounds containing carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
by addition or substitution reactions, without increasing the number of carbon atoms in the carbon skeleton of the acid [5]
•
•
•
by reaction of ammonia or amines with acids containing functional groups [5]
•
•
with simultaneously increasing the number of carbon atoms in the carbon skeleton [5]
•
Formation of amino and carboxyl groups [5]
•
from compounds containing already amino and carboxyl groups or derivatives thereof [5]
•
•
by reactions not involving the amino or carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
by reactions involving amino or carboxyl groups, e.g. hydrolysis of esters or amides, by formation of halides, salts or esters [5]
•
•
•
by hydrolysis of N-acylated amino acids or derivatives thereof, e.g. hydrolysis of carbamates [5]
•
from lactams, cyclic ketones or cyclic oximes, e.g. by reaction involving Beckmann rearrangement [5]
•
from hydantoins [5]
•
from compounds containing carboxyl groups by reaction with HCN, or a salt thereof, and amines, or from aminonitriles [5]
•
from natural products [5]
•
Preparation of optical isomers [5]
•
•
by stereospecific synthesis [5]
•
•
by separation of optical isomers [5]
•
Racemisation of optical isomers [5]
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives (separation of optical isomers C07C 227/34) [5]
•
•
Separation; Purification [5]
•
•
•
Crystallisation [5]
•
•
Stabilisation; Use of additives [5]
Compounds containing amino and carboxyl groups bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
having amino and carboxyl groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being acyclic and saturated [5]
•
•
•
having only one amino and one carboxyl group bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
the nitrogen atom of the amino group being further bound to hydrogen atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
the nitrogen atom of the amino group being further bound to acyclic carbon atoms or to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of acyclic carbon skeletons [5]
•
•
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of carbon skeletons containing rings [5]
•
•
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by amino or carboxyl groups, e.g. ethylenediamine-tetra-acetic acid, iminodiacetic acids [5]
•
•
•
•
the nitrogen atom of the amino group being further bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by halogen atoms or by nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
having more than one carboxyl group bound to the carbon skeleton, e.g. aspartic acid [5]
•
•
•
having more than one amino group bound to the carbon skeleton, e.g. lysine [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being saturated and containing rings [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being acyclic and unsaturated [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being unsaturated and containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
with at least one amino group and one carboxyl group bound to the same carbon atom of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
having amino groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms and carboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
having amino groups bound to carbon atoms of at least one six-membered aromatic ring and carboxyl groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
with carboxyl groups linked to the six-membered aromatic ring, or to the condensed ring system containing that ring, by saturated carbon chains [5]
•
•
with carboxyl groups linked to the six-membered aromatic ring, or to the condensed ring system containing that ring, by unsaturated carbon chains [5]
•
having amino or carboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings of the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
with amino groups and carboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of the same non-condensed ring [5]
•
•
with amino groups and carboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms being part of the same condensed ring system [5]
•
having amino and carboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
with amino and carboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of the same non-condensed six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
with amino and carboxyl groups bound in ortho- position [5]
•
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the amino groups further bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring, e.g. N-phenyl-anthranilic acids [5]
•
•
•
with amino and carboxyl groups bound in meta- or para- positions [5]
•
•
•
with amino groups and at least two carboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of the same six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by doubly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
with amino and carboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings being part of the same condensed ring system [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by doubly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
the condensed ring system being formed by at least three rings, e.g. amino anthraquinone carboxylic acids [5]
•
Metal complexes of amino carboxylic acids [5]
Preparation of carboxylic acid amides [5]
•
from carboxylic acids or from esters, anhydrides, or halides thereof by reaction with ammonia or amines [5]
•
from ketenes by reaction with ammonia or amines [5]
•
from nitriles by transformation of cyano groups into carboxamide groups [5]
•
from amides by reaction at nitrogen atoms of carboxamide groups [5]
•
from compounds not provided for in groups C07C 231/02-C07C 231/08 [5]
•
by reactions not involving the formation of carboxamide groups [5]
•
by formation of carboxamide groups together with reactions not involving the carboxamide groups [5]
•
Preparation of optical isomers [5]
•
•
by stereospecific synthesis [5]
•
•
by separation of optical isomers [5]
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives (separation of optical isomers C07C 231/20) [5]
•
•
Separation; Purification [5]
Carboxylic acid amides [5]
•
having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to carbon atoms of unsubstituted hydrocarbon radicals [5]
•
•
•
with carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms [5]
•
•
•
with carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to carbon atoms of an acyclic saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atoms of the carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
with carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of a saturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
•
with carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to carbon atoms of an acyclic unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
with carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to carbon atoms of an unsaturated carbon skeleton containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
with carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to carbon atoms of an unsaturated carbon skeleton containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by halogen atoms or by nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by an acyclic carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by an acyclic carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to a hydrogen atom or to a carbon atom of an acyclic saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to an acyclic carbon atom of a saturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to a carbon atom of an acyclic unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to an acyclic carbon atom of an unsaturated carbon skeleton containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to an acyclic carbon atom of a carbon skeleton containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to a hydrogen atom or to a carbon atom of an acyclic saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to an acyclic carbon atom of a saturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to a carbon atom of an acyclic unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to an acyclic carbon atom of an unsaturated carbon skeleton containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to an acyclic carbon atom of a carbon skeleton containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by doubly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by an acyclic carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by amino groups [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by an acyclic carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to a hydrogen atom or to a carbon atom of an acyclic saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to an acyclic carbon atom of a saturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to a carbon atom of an acyclic unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to an acyclic carbon atom of an unsaturated carbon skeleton containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to an acyclic carbon atom of a carbon skeleton containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to a hydrogen atom or to a carbon atom of a saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to a carbon atom of an unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by an acyclic carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to a hydrogen atom or to a carbon atom of an acyclic saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to an acyclic carbon atom of a saturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to a carbon atom of an acyclic unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to an acyclic carbon atom of an unsaturated carbon skeleton containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to an acyclic carbon atom of a carbon skeleton containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to a hydrogen atom or to a carbon atom of a saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to a carbon atom of an unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to carbon atoms of carboxyl groups, e.g. oxamides [5]
•
having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atoms of the carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to carbon atoms of unsubstituted hydrocarbon radicals [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by halogen atoms or by nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by doubly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by amino groups [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atoms of the carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to carbon atoms of unsubstituted hydrocarbon radicals [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by halogen atoms or by nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by an acyclic carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
•
of an acyclic saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
of a saturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
•
•
of an acyclic unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
of a carbon skeleton containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by doubly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by amino groups [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by an acyclic carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
•
with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by an acyclic carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
•
of an acyclic saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
of a saturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
•
•
of an acyclic unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
of a carbon skeleton containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
having nitrogen atoms of carboxamide groups bound to an acyclic carbon atom and to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring wherein at least one ortho-hydrogen atom has been replaced [5]
•
having nitrogen atoms of carboxamide groups quaternised [5]
•
having nitrogen atoms of carboxamide groups further acylated [5]
•
•
with carbon atoms of the carboxamide groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
with at least one carbon atom of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
Carboxylic acid amides, the carbon skeleton of the acid part being further substituted by oxygen atoms [5]
•
having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms and singly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being acyclic and saturated [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atoms of the carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to an acyclic carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to an acyclic carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to an acyclic carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
having at least one of the singly-bound oxygen atoms further bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring, e.g. phenoxyacetamides [5]
•
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atoms of the carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being saturated and containing rings [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being acyclic and unsaturated [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being unsaturated and containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atoms of the carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings and singly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings and singly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
with carbon atoms of carboxamide groups and singly-bound oxygen atoms bound to carbon atoms of the same non-condensed six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atoms of the carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to an acyclic carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to an acyclic carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to an acyclic carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
with carbon atoms of carboxamide groups and singly-bound oxygen atoms, bound in ortho- position to carbon atoms of the same non-condensed six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atoms of the carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
with carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings being part of condensed ring systems and singly-bound oxygen atoms, bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to an acyclic carbon atom and to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring wherein at least one ortho-hydrogen atom has been replaced [5]
•
having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups and doubly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
with the carbon atoms of the carboxamide groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
of a saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
•
having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups and keto groups bound to the same carbon atom, e.g. acetoacetamides [5]
•
•
with the carbon atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
with the carbon atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups quaternised [5]
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups further acylated [5]
Carboxylic acid amides, the carbon skeleton of the acid part being further substituted by amino groups [5]
•
having the carbon atoms of the carboxamide groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being acyclic and saturated [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atoms of the carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to an acyclic carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to an acyclic carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to an acyclic carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being saturated and containing rings [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being acyclic and unsaturated [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being unsaturated and containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of amino groups bound to the carbon skeleton of the acid part, further acylated [5]
•
having the carbon atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
of a ring being part of a condensed ring system formed by at least four rings, e.g. tetracycline [5]
•
having the carbon atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a non-condensed six-membered aromatic ring of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group bound to an acyclic carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group bound to an acyclic carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group bound to an acyclic carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of amino groups bound to the carbon skeleton of the acid part, further acylated [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups, amino groups and singly-bound oxygen atoms bound to carbon atoms of the same non-condensed six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups, amino groups and at least three atoms of bromine or iodine, bound to carbon atoms of the same non-condensed six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
having the carbon atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring being part of a condensed ring system of the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups quaternised [5]
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups further acylated [5]
Compounds containing nitrogen-to-halogen bonds; Hydroxylamino compounds or ethers or esters thereof [5]
•
Compounds containing nitrogen-to-halogen bonds [5]
•
•
N-halogenated amines [5]
•
•
N-halogenated carboxamides [5]
•
Hydroxylamino compounds or their ethers or esters [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of hydroxylamino groups further bound to carbon atoms of unsubstituted hydrocarbon radicals or of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by halogen atoms or by nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of hydroxylamino groups further bound to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of hydroxylamino groups further bound to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by doubly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of hydroxylamino groups further bound to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of hydroxylamino groups further bound to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
having oxygen atoms of hydroxylamino groups etherified [5]
•
•
having oxygen atoms of hydroxylamino groups esterified [5]
Preparation of compounds containing chains of nitrogen atoms singly-bound to each other, e.g. hydrazines, triazanes [5]
•
Preparation of hydrazines [5]
•
Preparation of hydrazides [5]
Compounds containing chains of nitrogen atoms singly-bound to each other, e.g. hydrazines, triazanes [5]
•
N-nitro compounds [5]
•
N-nitroso compounds [5]
•
•
N-nitroso-amines [5]
•
•
N-nitroso-carboxamides [5]
•
Hydrazines [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of hydrazine groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
of a saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
containing rings [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of hydrazine groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of hydrazine groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
Hydrazines having nitrogen atoms of hydrazine groups acylated by carboxylic acids [5]
•
•
with acylating carboxyl groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
to hydrogen atoms or to carbon atoms of a saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of an unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of a carbon skeleton further substituted by nitrogen atoms [5]
•
•
with acylating carboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
with acylating carboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
Hydrazines having nitrogen atoms of hydrazine groups being quaternised [5]
•
Hydrazines having nitrogen atoms of hydrazine groups further singly-bound to hetero atoms [5]
Compounds containing chains of at least two nitrogen atoms with at least one nitrogen-to-nitrogen multiple bond (azoxy compound C07C 291/08) [5]
•
Azo compounds, i.e. compounds having the free valencies of —N=N— groups attached to different atoms, e.g. diazohydroxides [5]
•
•
with nitrogen atoms of azo groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms or to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
with nitrogen atoms of azo groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
with the two nitrogen atoms of azo groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings, e.g. azobenzene [5]
•
•
•
with nitrogen atoms of azo groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings being part of condensed ring systems [5]
•
Diazo compounds, i.e. compounds having the free valencies of  N2 groups attached to the same carbon atom [5]
N2 groups attached to the same carbon atom [5]
 N2 groups attached to the same carbon atom [5]
N2 groups attached to the same carbon atom [5]•
•
having diazo groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of a carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
Diazomethane [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
Diazonium compounds [5]
•
containing chains of three or more nitrogen atoms with one or more nitrogen-to-nitrogen double bonds [5]
•
•
Chains of only three nitrogen atoms, e.g. diazoamines [5]
Compounds containing azido groups [5]
•
with azido groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of a carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
being saturated [5]
•
•
•
and containing rings [5]
•
•
being unsaturated [5]
•
•
•
and containing rings [5]
•
•
being further substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
with azido groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
with azido groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of a carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
being further substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
with azido groups acylated by carboxylic acids [5]
•
•
with the acylating carboxyl groups bound to hydrogen atoms, to acyclic carbon atoms or to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
with at least one of the acylating carboxyl groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
Preparation of compounds containing nitrogen atoms doubly-bound to a carbon skeleton (of diazo compounds C07C 245/12) [5]
•
of compounds containing imino groups [5]
•
of oximes [5]
•
•
by nitrosation of hydrocarbons or substituted hydrocarbons [5]
•
•
by reaction of hydroxylamines with carbonyl compounds [5]
•
•
from nitro compounds or salts thereof [5]
•
•
by reactions not involving the formation of oxyimino groups [5]
•
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [5]
•
of hydrazones [5]
Compounds containing nitrogen atoms doubly- bound to a carbon skeleton (diazo compounds C07C 245/12) [5]
•
containing imino groups [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of imino groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of a saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
being acyclic [5]
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of an unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
being acyclic [5]
•
•
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of imino groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of imino groups being part of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
Quinone imines [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of imino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of imino groups further bound to halogen atoms [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of imino groups acylated [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of imino groups quaternised [5]
•
Oximes [5]
•
•
with oxygen atoms of oxyimino groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to carbon atoms of unsubstituted hydrocarbon radicals [5]
•
•
•
with the carbon atoms of the oxyimino groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of a saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of an unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
with the carbon atom of at least one of the oxyimino groups bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
with the carbon atom of at least one of the oxyimino groups being part of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
•
Quinone oximes [5]
•
•
•
with the carbon atom of at least one of the oxyimino groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
having oxygen atoms of oxyimino groups bound to carbon atoms of substituted hydrocarbon radicals [5]
•
•
•
of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by halogen atoms or by nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by doubly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
having oxygen atoms of oxyimino groups esterified [5]
•
•
•
by carboxylic acids [5]
•
•
•
•
with the esterifying carboxyl groups bound to hydrogen atoms, to acyclic carbon atoms or to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
with at least one of the esterifying carboxyl groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
Metal complexes of oximes [5]
•
Hydrazones [5]
•
•
having doubly-bound carbon atoms of hydrazone groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of a saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of an unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
having doubly-bound carbon atoms of hydrazone groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having doubly-bound carbon atoms of hydrazone groups being part of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having doubly-bound carbon atoms of hydrazone groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having also the other nitrogen atom doubly-bound to a carbon atom, e.g. azines [5]
Preparation of carboxylic acid nitriles (of cyanogen or compounds thereof C01C 3/00) [5]
•
by reaction of nitrogen oxide with organic compounds [5]
•
by reaction of cyanogen halides, e.g. ClCN, with organic compounds [5]
•
from N-formylated amino compounds [5]
•
by addition of hydrogen cyanide or salts thereof to unsaturated compounds [5]
•
•
to compounds containing carbon-to-carbon double bonds [5]
•
•
to compounds containing carbon-to-carbon triple bonds [5]
•
by reaction of cyanides with halogen-containing compounds with replacement of halogen atoms by cyano groups [5]
•
by reaction of cyanides with lactones or compounds containing hydroxy groups or etherified or esterified hydroxy groups [5]
•
by reaction of ammonia or amines with compounds containing carbon-to-carbon multiple bonds other than in six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
by dehydratation of carboxylic acid amides [5]
•
by reaction of ammonia with carboxylic acids with replacement of carboxyl groups by cyano groups [5]
•
by ammoxidation of hydrocarbons or substituted hydrocarbons [5]
•
•
containing carbon-to-carbon multiple bonds, e.g. unsaturated aldehydes [5]
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings, e.g. styrene [5]
•
by reactions not involving the formation of cyano groups [5]
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [5]
•
•
Separation; Purification [5]
Carboxylic acid nitriles (cyanogen or compounds thereof C01C 3/00) [5]
•
having cyano groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
of an acyclic and saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
Mononitriles [5]
•
•
•
containing two cyano groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing at least three cyano groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
of an acyclic and unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
Mononitriles [5]
•
•
•
•
Acrylonitrile; Methacrylonitrile [5]
•
•
•
containing at least two cyano groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
containing cyano groups and halogen atoms, or nitro or nitroso groups, bound to the same acyclic carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
containing cyano groups and singly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the same saturated acyclic carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing cyano groups and hydroxy groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing cyano groups and etherified hydroxy groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing cyano groups and esterified hydroxy groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
containing cyano groups and singly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the same unsaturated acyclic carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
containing cyano groups and singly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the same carbon atom of an acyclic carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
containing cyano groups and doubly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the same acyclic carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
containing cyano groups bound to carbon atoms of carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
containing cyano groups and carboxyl groups, other than cyano groups, bound to the same saturated acyclic carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by doubly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
containing cyano groups and at least two carboxyl groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
containing cyano groups and carboxyl groups, other than cyano groups, bound to the same unsaturated acyclic carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
containing cyano groups and singly-bound nitrogen atoms, not being further bound to other hetero atoms, bound to the same saturated acyclic carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
Aminoacetonitriles [5]
•
•
•
containing cyano groups, amino groups and singly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing cyano groups, amino groups and doubly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing cyano groups, amino groups and carboxyl groups, other than cyano groups, bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing cyano groups and acylated amino groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
containing cyano groups and singly-bound nitrogen atoms, not being further bound to other hetero atoms, bound to the same unsaturated acyclic carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having cyano groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of a carbon skeleton containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having cyano groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of a carbon skeleton containing at least one six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
with cyano groups linked to the six-membered aromatic ring, or to the condensed ring system containing that ring, by saturated carbon chains [5]
•
•
•
with cyano groups linked to the six-membered aromatic ring, or to the condensed ring system containing that ring, by unsaturated carbon chains [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by halogen atoms, or by nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by hydroxy groups [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by etherified hydroxy groups [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by esterified hydroxy groups [5]
•
•
•
•
with hydroxy groups esterified by derivatives of 2,2-dimethylcyclopropane carboxylic acids, e.g. chrysanthemumic acids [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by doubly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by carboxyl groups, other than cyano groups [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by singly-bound nitrogen atoms, not being further bound to other hetero atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
at least one of the singly-bound nitrogen atoms being acylated [5]
•
having cyano groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
to carbon atoms of non-condensed rings [5]
•
•
to carbon atoms of rings being part of condensed ring systems [5]
•
•
to carbon atoms of 2,2-dimethylcyclopropane rings, e.g. nitrile of chrysanthemumic acids [5]
•
having cyano groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of a carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
to carbon atoms of non-condensed six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
containing at least two cyano groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings being part of condensed ring systems [5]
•
•
containing cyano groups and hydroxy groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
containing cyano groups and etherified hydroxy groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
containing cyano groups and esterified hydroxy groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
containing cyano groups and doubly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
containing cyano groups and carboxyl groups, other than cyano groups, bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
containing cyano groups and singly-bound nitrogen atoms, not being further bound to other hetero atoms, bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
at least one of the singly-bound nitrogen atoms being acylated [5]
•
containing cyano groups and nitrogen atoms being part of imino groups bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
containing cyano groups and oxygen atoms being part of oxyimino groups bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
containing cyano groups and nitrogen atoms further bound to other hetero atoms, other than oxygen atoms of nitro or nitroso groups, bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
with the nitrogen atoms further bound to oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
with the nitrogen atoms further bound to nitrogen atoms [5]
•
•
•
having cyano groups and nitrogen atoms being part of hydrazine or hydrazone groups bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
having cyano groups and azido groups bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
Compounds containing carboxyl groups, the doubly-bound oxygen atom of a carboxyl group being replaced by a doubly-bound nitrogen atom, this nitrogen atom not being further bound to an oxygen atom, e.g. imino-ethers, amidines [5]
•
with replacement of the other oxygen atom of the carboxyl group by halogen atoms, e.g. imino-halides [5]
•
without replacement of the other oxygen atom of the carboxyl group, e.g. imino-ethers [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of imino-carboxyl groups bound to hydrogen atoms, to acyclic carbon atoms, or to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of imino-carboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
with replacement of the other oxygen atom of the carboxyl group by nitrogen atoms, e.g. amidines [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of amidino groups bound to hydrogen atoms [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of amidino groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of amidino groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of amidino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of amidino groups acylated [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of amidino groups further bound to nitrogen atoms, e.g. hydrazidines [5]
Compounds containing carboxyl groups, an oxygen atom of a carboxyl group being replaced by a nitrogen atom, this nitrogen atom being further bound to an oxygen atom and not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
with replacement of the other oxygen atom of the carboxyl group by halogen atoms [5]
•
without replacement of the other oxygen atom of the carboxyl group, e.g. hydroxamic acids [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of hydroxamic groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of hydroxamic groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of hydroxamic groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
with replacement of the other oxygen atom of the carboxyl group by nitrogen atoms, e.g. N-hydroxyamidines [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of hydroxyamidine groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of hydroxyamidine groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of hydroxyamidine groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
with at least one nitrogen atom of hydroxyamidine groups bound to another nitrogen atom [5]
Derivatives of cyanic acid [5]
•
Cyanates [5]
•
Cyanamides (unsubstituted cyanamide C01C 3/16) [5]
Preparation of derivatives of isocyanic acid [5]
•
by reaction of halides with isocyanic acid or its derivatives [5]
•
from or via carbamates or carbamoyl halides [5]
•
from or via ureas [5]
•
from or via heterocyclic compounds, e.g. pyrolysis of furoxans [5]
•
by reaction of amines with carbonyl halides, e.g. with phosgene [5]
•
from or via nitrogen analogues of carboxylic acids, e.g. from hydroxamic acids, involving a Hofmann, Curtius or Lossen-type rearrangement (C07C 209/56 takes precedence) [5]
•
by catalytic reaction of nitro compounds with carbon monoxide [5]
•
by reactions not involving the formation of isocyanate groups [5]
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [5]
•
•
Separation; Purification [5]
Derivatives of isocyanic acid [5]
•
having isocyanate groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
of a saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
having isocyanate groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
having isocyanate groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
containing at least two isocyanate groups bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
having isocyanate groups acylated [5]
Carbodiimides [5]
Preparation of derivatives of carbamic acid, i.e. compounds containing any of the groups  the nitrogen atom not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
the nitrogen atom not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
 the nitrogen atom not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
the nitrogen atom not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]•
from isocyanates with formation of carbamate groups [5]
•
from amines with formation of carbamate groups [5]
•
by reactions not involving the formation of carbamate groups [5]
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [5]
Derivatives of carbamic acid, i.e. compounds containing any of the groups 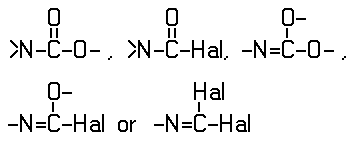 the nitrogen atom not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
the nitrogen atom not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
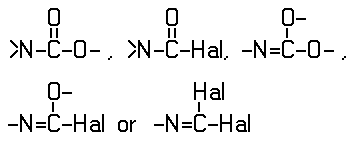 the nitrogen atom not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
the nitrogen atom not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]•
Carbamic acids; Salts of carbamic acids (unsubstituted carbamic acid or salts thereof C01B 21/12) [5]
•
Carbamic acid halides [5]
•
Esters of carbamic acids [5]
•
•
having oxygen atoms of carbamate groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
with the nitrogen atoms of the carbamate groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
to hydrogen atoms or to carbon atoms of unsubstituted hydrocarbon radicals [5]
•
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by halogen atoms or by nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by doubly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
•
with the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carbamate groups bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
with the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carbamate groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
•
to a carbon atom of a non-condensed six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
•
to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring being part of a condensed ring system [5]
•
•
having oxygen atoms of carbamate groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
with the nitrogen atoms of the carbamate groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
with the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carbamate groups bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
with the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carbamate groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
having oxygen atoms of carbamate groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
with the nitrogen atoms of the carbamate groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
to hydrogen atoms or to carbon atoms of unsubstituted hydrocarbon radicals [5]
•
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by halogen atoms or by nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by doubly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
•
with the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carbamate groups bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
with the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carbamate groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
having oxygen atoms of carbamate groups bound to nitrogen atoms [5]
•
Compounds containing any of the groups  X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. N-acylcarbamates [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. N-acylcarbamates [5]
 X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. N-acylcarbamates [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. N-acylcarbamates [5]•
•
Y being a hydrogen or a carbon atom, e.g. benzoylcarbamates [5]
•
•
Y being a hetero atom [5]
•
Compounds containing any of the groups  [5]
[5]
 [5]
[5]Preparation of urea or its derivatives, i.e. compounds containing any of the groups  the nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
the nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
 the nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
the nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]•
of urea, its salts, complexes or addition compounds [5]
•
•
from carbon dioxide and ammonia [5]
•
•
from cyanamide or calcium cyanamide [5]
•
•
from ammoniacal liquor [5]
•
•
combined with the synthesis of ammonia [5]
•
•
combined with the synthesis of melamine [5]
•
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [5]
•
•
•
Separation; Purification [5]
•
of substituted ureas [5]
Derivatives of urea, i.e. compounds containing any of the groups  the nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
the nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
 the nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
the nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]•
Salts; Complexes; Addition compounds [5]
•
having nitrogen atoms of urea groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
of an acyclic and saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
being further substituted by halogen atoms, or by nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
being further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
being further substituted by doubly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
being further substituted by nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
being further substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
of a saturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
having nitrogen atoms of urea groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
having nitrogen atoms of urea groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of a carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
being further substituted by halogen atoms, or by nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
being further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of urea groups and singly-bound oxygen atoms bound to carbon atoms of the same non-condensed six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
•
with at least one of the oxygen atoms further bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring, e.g. N-aryloxyphenylureas [5]
•
•
being further substituted by doubly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
being further substituted by nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
being further substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
having nitrogen atoms of urea groups doubly-bound to carbon atoms [5]
•
containing any of the groups  X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. acylureas [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. acylureas [5]
 X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. acylureas [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. acylureas [5]•
•
Y being a hydrogen or a carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
Y being a hydrogen or an acyclic carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
Y being a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
Y being a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring, e.g. benzoylureas [5]
•
•
•
X being a nitrogen atom [5]
•
•
Y being a hetero atom [5]
•
•
•
Y being an oxygen atom, e.g. allophanic acids [5]
•
•
•
Y being a nitrogen atom, e.g. biuret [5]
•
having nitrogen atoms of urea groups singly-bound to oxygen atoms [5]
•
having nitrogen atoms of urea groups bound to halogen atoms or to nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
N-nitroso ureas [5]
•
Compounds containing any of the groups  e.g. isoureas [5]
e.g. isoureas [5]
 e.g. isoureas [5]
e.g. isoureas [5]Preparation of guanidine or its derivatives, i.e. compounds containing the group  the singly-bound nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
the singly-bound nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
 the singly-bound nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
the singly-bound nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]•
of guanidine from cyanamide, calcium cyanamide or dicyandiamides [5]
•
of guanidine from ammonium thiocyanate [5]
•
Purification or separation of guanidine [5]
•
of substituted guanidines [5]
Derivatives of guanidine, i.e. compounds containing the group  the singly-bound nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
the singly-bound nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
 the singly-bound nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
the singly-bound nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]•
Guanidine; Salts, complexes or addition compounds thereof [5]
•
having nitrogen atoms of guanidine groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of a carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
being further substituted by halogen atoms, or by nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
being further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
being further substituted by doubly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
being further substituted by nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
being further substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
having nitrogen atoms of guanidine groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
having nitrogen atoms of guanidine groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
containing any of the groups  X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. acylguanidines [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. acylguanidines [5]
 X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. acylguanidines [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. acylguanidines [5]•
•
Y being a hydrogen or a carbon atom, e.g. benzoylguanidines [5]
•
•
Y being a hetero atom [5]
•
•
•
X and Y being nitrogen atoms, i.e. biguanides [5]
•
having nitrogen atoms of guanidine groups bound to cyano groups, e.g. cyanoguanidines, dicyandiamides [5]
•
having nitrogen atoms of guanidine groups bound to nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
N-nitroguanidines [5]
•
•
•
N-nitroguanidine [5]
•
•
•
Substituted N-nitroguanidines [5]
Derivatives of carbonic acid containing functional groups covered by groups C07C 269/00-C07C 279/00 in which at least one nitrogen atom of these functional groups is further bound to another nitrogen atom not being part of a nitro or nitroso group [5]
•
Compounds containing any of the groups  e.g. carbazates [5]
e.g. carbazates [5]
 e.g. carbazates [5]
e.g. carbazates [5]•
•
the other nitrogen atom being further doubly-bound to a carbon atom [5]
•
Compounds containing any of the groups  e.g. semicarbazides [5]
e.g. semicarbazides [5]
 e.g. semicarbazides [5]
e.g. semicarbazides [5]•
•
the other nitrogen atom being further doubly-bound to a carbon atom, e.g. semicarbazones [5]
•
•
•
the carbon atom being further bound to an acyclic carbon atom or to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
the carbon atom being part of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
the carbon atom being further bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
Compounds containing any of the groups  e.g. aminoguanidine [5]
e.g. aminoguanidine [5]
 e.g. aminoguanidine [5]
e.g. aminoguanidine [5]•
•
the other nitrogen atom being further doubly-bound to a carbon atom, e.g. guanylhydrazones [5]
•
the two nitrogen atoms of the functional groups being doubly-bound to each other, e.g. azoformamide [5]
Compounds containing carbon and nitrogen and having functional groups not covered by groups C07C 201/00-C07C 281/00 [5]
•
containing nitrogen-oxide bonds [5]
•
•
containing amino-oxide bonds [5]
•
•
Nitrile oxides [5]
•
•
Azoxy compounds [5]
•
Isocyanides [5]
•
Fulminates [5]
•
containing at least one carbon atom bound to a nitro or nitroso group and doubly-bound to a hetero atom [5]
Compounds containing carbon together with sulfur, selenium or tellurium, with or without hydrogen, halogens, oxygen or nitrogen [5]
Esters of sulfurous acid [5]
•
having sulfite groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
Preparation of esters or amides of sulfuric acids; Preparation of sulfonic acids or of their esters, halides, anhydrides or amides [5]
•
of sulfonic acids or halides thereof [5]
•
•
by substitution of hydrogen atoms by sulfo or halosulfonyl groups [5]
•
•
•
by reaction with sulfuric acid or sulfur trioxide [5]
•
•
•
by reaction with halogenosulfonic acids [5]
•
•
•
by reaction with sulfur dioxide and halogen or by reaction with sulfuryl halides [5]
•
•
•
by reaction with thionylhalides [5]
•
•
by sulfoxidation, i.e. by reaction with sulfur dioxide and oxygen with formation of sulfo or halosulfonyl groups [5]
•
•
by oxidation of thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides, or polysulfides with formation of sulfo or halosulfonyl groups [5]
•
•
by reaction of sulfides with compounds having functional groups with formation of sulfo or halosulfonyl groups [5]
•
•
by addition of sulfurous acid or salts thereof to compounds having carbon-to-carbon multiple bonds [5]
•
•
from sulfonic acids by reactions not involving the formation of sulfo or halosulfonyl groups [5]
•
of esters of sulfuric acids [5]
•
of esters of sulfonic acids [5]
•
•
by reaction of hydroxy compounds with sulfonic acids or derivatives thereof [5]
•
•
by reactions not involving the formation of esterified sulfo groups [5]
•
of salts of sulfonic acids [5]
•
of amides of sulfuric acids [5]
•
of amides of sulfonic acids [5]
•
•
by reaction of ammonia or amines with sulfonic acids, or with esters, anhydrides, or halides thereof [5]
•
•
by reactions not involving the formation of sulfonamide groups [5]
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [5]
•
•
Separation; Purification [5]
•
•
•
from by-products of refining mineral oils with sulfuric acid [5]
Esters of sulfuric acids [5]
•
having oxygen atoms of sulfate groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of a carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
being acyclic and saturated [5]
•
•
•
Hydrogenosulfates [5]
•
•
•
Dialkylsulfates; Substituted dialkylsulfates [5]
•
•
•
being further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
being saturated and containing rings [5]
•
•
being acyclic and unsaturated [5]
•
•
being unsaturated and containing rings [5]
•
•
•
containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
having oxygen atoms of sulfate groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
having oxygen atoms of sulfate groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
of non-condensed six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
Halogenosulfates, i.e. monoesters of halogenosulfuric acids [5]
Amides of sulfuric acids, i.e. compounds having singly-bound oxygen atoms of sulfate groups replaced by nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
Monoamides of sulfuric acids or esters thereof, e.g. sulfamic acids [5]
•
Diamides of sulfuric acids [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of the sulfamide groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of the sulfamide groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of the sulfamide groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
Sulfonic acids; Halides, esters, or anhydrides thereof [5]
•
Sulfonic acids [5]
•
•
having sulfo groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
of an acyclic saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
containing only one sulfo group [5]
•
•
•
•
containing at least two sulfo groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
containing halogen atoms, or nitro or nitroso groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
containing oxygen atoms bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
•
containing hydroxy groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
•
containing etherified hydroxy groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
•
•
with the oxygen atom of at least one of the etherified hydroxy groups further bound to an acyclic carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
•
•
•
with the oxygen atom of at least one of the etherified hydroxy groups further bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
•
•
containing esterified hydroxy groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
containing nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups, bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
•
containing amino groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
•
•
the nitrogen atom of at least one of the amino groups being part of any of the groups  X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
 X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]•
•
•
•
•
containing doubly-bound nitrogen atoms bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
containing carboxyl groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
•
containing amino groups bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
of a saturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
•
of an acyclic unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
containing nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups, bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
containing carboxyl groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
of a carbon skeleton containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having sulfo groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings of a carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups, bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing carboxyl groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having sulfo groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of a carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
of non-condensed six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
of six-membered aromatic rings substituted by alkyl groups [5]
•
•
•
•
•
by alkyl groups containing at least three carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
containing at least two non-condensed six-membered aromatic rings in the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
of six-membered aromatic rings being part of condensed ring systems [5]
•
•
•
•
formed by two rings [5]
•
•
•
•
•
Naphthalene sulfonic acids [5]
•
•
•
•
•
•
substituted by alkyl groups [5]
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
by alkyl groups containing at least three carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
formed by at least three rings [5]
•
•
•
containing halogen atoms bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing nitro or nitroso groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing singly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
having the sulfo groups bound to carbon atoms of non-condensed six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
having at least one of the sulfo groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring being part of a condensed ring system [5]
•
•
•
containing doubly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups, bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
having the sulfo groups bound to carbon atoms of non-condensed six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
having at least one of the sulfo groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring being part of a condensed ring system [5]
•
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by halogen atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
•
having at least one of the sulfo groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring being part of a condensed ring system [5]
•
•
•
•
at least one of the nitrogen atoms being part of any of the groups  X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
 X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]•
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by doubly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton containing carbon atoms of quinone rings [5]
•
•
•
•
•
•
at least one of the nitrogen atoms being part of any of the groups  X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
 X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Y being a hydrogen or a carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Y being a hetero atom [5]
•
•
•
containing carboxyl groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
Carboxylic acid groups or esters thereof [5]
•
•
•
•
Nitrogen analogues of carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
Sulfonated fats, oils or waxes of undetermined constitution [5]
•
Esters of sulfonic acids [5]
•
•
having sulfur atoms of esterified sulfo groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
of a saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
Methanesulfonates [5]
•
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
of a carbon skeleton substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
of a carbon skeleton substituted by nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
of a carbon skeleton substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
having sulfur atoms of esterified sulfo groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having sulfur atoms of esterified sulfo groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of a carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of non-condensed six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings being part of condensed ring systems [5]
•
•
•
containing singly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups, bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing carboxyl groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
Halides of sulfonic acids [5]
•
•
having halosulfonyl groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
of a saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
of a carbon skeleton substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
of a carbon skeleton substituted by nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
of a carbon skeleton substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
having halosulfonyl groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having halosulfonyl groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of a carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing singly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups, bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
containing carboxyl groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
Amides of sulfonic acids, i.e. compounds having singly-bound oxygen atoms of sulfo groups replaced by nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
Sulfonamides having sulfur atoms of sulfonamide groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
of an acyclic saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atoms of the sulfonamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
to acyclic carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
to acyclic carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
•
to acyclic carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the sulfonamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the sulfonamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by at least two halogen atoms [5]
•
•
of a saturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
of an acyclic unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
Sulfonamides having sulfur atoms of sulfonamide groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
Sulfonamides having sulfur atoms of sulfonamide groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the sulfonamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to an acyclic carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
to an acyclic carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
to an acyclic carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
to an acyclic carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the sulfonamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the sulfonamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
Sulfonamides, the carbon skeleton of the acid part being further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
having the sulfur atoms of the sulfonamide groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
of an acyclic saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
of a saturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
•
of an acyclic unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
having the sulfur atom of at least one of the sulfonamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
having the sulfur atom of at least one of the sulfonamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
Sulfonamides, the carbon skeleton of the acid part being further substituted by singly-bound nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
having the sulfur atoms of the sulfonamide groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
of an acyclic saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
of a saturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
•
of an acyclic unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
having the sulfur atom of at least one of the sulfonamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
having the sulfur atom of at least one of the sulfonamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
having sulfur atoms of sulfonamide groups and amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the sulfonamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to an acyclic carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
•
•
to an acyclic carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
•
to an acyclic carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
•
•
to an acyclic carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the sulfonamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
•
having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the sulfonamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
at least one of the singly-bound nitrogen atoms being part of any of the groups  X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. N-acylaminosulfonamides [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. N-acylaminosulfonamides [5]
 X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. N-acylaminosulfonamides [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. N-acylaminosulfonamides [5]•
•
•
Y being a hydrogen or a carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
Y being a hetero atom [5]
•
having nitrogen atoms of sulfonamide groups further bound to another hetero atom [5]
•
•
to nitrogen atoms [5]
•
Compounds containing any of the groups  X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
 X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]•
•
Y being a hydrogen or a carbon atom [5]
•
•
Y being a hetero atom [5]
•
•
•
X and Y not being nitrogen atoms, e.g. N-sulfonylcarbamic acid [5]
•
•
•
either X or Y, but not both, being nitrogen atoms, e.g. N-sulfonylurea [5]
•
•
•
•
having sulfur atoms of the sulfonylurea groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
having sulfur atoms of the sulfonylurea groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
having sulfur atoms of the sulfonylurea groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of the sulfonylurea groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of the sulfonylurea groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of the sulfonylurea groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of the sulfonylurea groups further bound to another hetero atom [5]
•
•
•
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of the sulfonylurea groups further acylated [5]
•
•
•
•
N-sulfonylisoureas [5]
•
•
•
X and Y being nitrogen atoms, e.g. N-sulfonylguanidine [5]
•
N-sulfonylisocyanates [5]
Sulfinic acids; Sulfenic acids; Halides, esters or anhydrides thereof; Amides of sulfinic or sulfenic acids, i.e. compounds having singly-bound oxygen atoms of sulfinic or sulfenic groups replaced by nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
Sulfinic acids; Derivatives thereof [5]
•
•
Sulfinic acids; Esters thereof [5]
•
•
Sulfinamides [5]
•
Sulfenic acids; Derivatives thereof [5]
•
•
Sulfenic acids; Esters thereof [5]
•
•
•
having sulfur atoms of sulfenic groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
having sulfur atoms of sulfenic groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
having sulfur atoms of sulfenic groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
Sulfenamides [5]
•
•
•
having sulfur atoms of sulfenamide groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
having sulfur atoms of sulfenamide groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
having sulfur atoms of sulfenamide groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
Compounds containing any of the groups  X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
 X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]•
•
•
•
Y being a hydrogen or a carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
•
Y being a hetero atom [5]
•
•
•
•
•
X and Y not being nitrogen atoms, e.g. N-sulfenylcarbamic acid [5]
•
•
•
•
•
either X or Y, but not both, being nitrogen atoms, e.g. N-sulfenylureas [5]
•
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of sulfenamide groups further bound to other hetero atoms [5]
•
•
•
N-sulfenylisocyanates [5]
Preparation of sulfones; Preparation of sulfoxides [5]
•
by formation of sulfone or sulfoxide groups by oxidation of sulfides, or by formation of sulfone groups by oxidation of sulfoxides [5]
•
by reactions not involving the formation of sulfone or sulfoxide groups [5]
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [5]
Sulfones; Sulfoxides [5]
•
having sulfone or sulfoxide groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
of an acyclic saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
of a saturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
of an acyclic unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
having sulfone or sulfoxide groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
having sulfone or sulfoxide groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
having sulfone or sulfoxide groups and singly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
with sulfone or sulfoxide groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
with sulfone or sulfoxide groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
with sulfone or sulfoxide groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
having sulfone or sulfoxide groups and doubly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
having sulfone or sulfoxide groups and nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups, bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
with sulfone or sulfoxide groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
with sulfone or sulfoxide groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
with sulfone or sulfoxide groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
having sulfone or sulfoxide groups and amino groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings being part of the same non-condensed ring or of a condensed ring system containing that ring [5]
•
•
•
•
with the nitrogen atoms of the amino groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
•
with the nitrogen atom of at least one amino group being part of any of the groups  X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. N-acylaminosulfones [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. N-acylaminosulfones [5]
 X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. N-acylaminosulfones [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. N-acylaminosulfones [5]•
•
•
•
•
Y being a hydrogen or a carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
•
•
Y being a hetero atom [5]
•
having sulfone or sulfoxide groups and carboxyl groups bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by singly-bound nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
at least one of the nitrogen atoms being part of any of the groups  X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
 X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]Preparation of thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides [5]
•
of thiols [5]
•
•
by addition of hydrogen sulfide or its salts to unsaturated compounds [5]
•
•
from sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides [5]
•
•
by replacement of hydroxy groups or etherified or esterified hydroxy groups [5]
•
•
•
by replacement of hydroxy groups or etherified or esterified hydroxy groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
by reactions not involving the formation of mercapto groups [5]
•
of sulfides [5]
•
•
by addition of hydrogen sulfide or its salts to unsaturated compounds [5]
•
•
by addition of thiols to unsaturated compounds [5]
•
•
by reactions not involving the formation of sulfide groups [5]
•
of hydropolysulfides or polysulfides [5]
•
•
by reactions involving the formation of sulfur-to-sulfur bonds [5]
•
Separation; Purification; Stabilisation; Use of additives [5]
•
•
Separation; Purification [5]
•
•
•
from the by-products of refining mineral oils [5]
Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides [5]
•
Thiols having mercapto groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
of an acyclic saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
of a saturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
of an acyclic unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
Sulfides, hydropolysulfides, or polysulfides having thio groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
of an acyclic saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
of a saturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
of an acyclic unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides, or polysulfides having thio groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides, or polysulfides having thio groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
Thiols [5]
•
•
Sulfides, hydropolysulfides, or polysulfides having thio groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
Sulfides having the sulfur atom of at least one thio group bound to two carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups [5]
•
containing thio groups and halogen atoms, or nitro or nitroso groups bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having sulfur atoms of thio groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being acyclic and saturated [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being saturated and containing rings [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being acyclic and unsaturated [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being unsaturated and containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having sulfur atoms of thio groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having sulfur atoms of thio groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
containing thio groups and singly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having the sulfur atoms of the thio groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being acyclic and saturated [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being saturated and containing rings [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being acyclic and unsaturated [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being unsaturated and containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having the sulfur atom of at least one of the thio groups bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having the sulfur atom of at least one of the thio groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
with singly-bound oxygen atoms bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
with singly-bound oxygen atoms bound to carbon atoms of the same non-condensed six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
with the sulfur atom of the thio group bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring being part of a condensed ring system [5]
•
containing thio groups and doubly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
containing thio groups and nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups, bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having the sulfur atoms of the thio groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being acyclic and saturated [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being saturated and containing rings [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being acyclic and unsaturated [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being unsaturated and containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having the sulfur atom of at least one of the thio groups bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having the sulfur atom of at least one of the thio groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
having at least one of the nitrogen atoms bound to an acyclic carbon atom of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
having at least one of the nitrogen atoms bound to a carbon atom of the same non-condensed six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
•
the thio group being a mercapto group [5]
•
•
•
•
the thio group being a sulfide group [5]
•
•
•
•
•
the sulfur atom of the sulfide group being further bound to an acyclic carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
•
•
the sulfur atom of the sulfide group being further bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
with the sulfur atom of the thio group bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring being part of a condensed ring system [5]
•
•
at least one of the nitrogen atoms being part of any of the groups  X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
 X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]•
•
•
Y being a hydrogen or a carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
•
Y being a hydrogen or an acyclic carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
•
Y being a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
•
Y being a hetero atom [5]
•
•
•
•
X or Y being nitrogen atoms [5]
•
•
having at least one of the nitrogen atoms doubly-bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having at least one of the nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups, further bound to other hetero atoms [5]
•
•
•
to oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
to nitrogen atoms [5]
•
•
•
to sulfur atoms [5]
•
containing thio groups and carboxyl groups bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having the sulfur atoms of the thio groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being acyclic and saturated [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being saturated and containing rings [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being acyclic and unsaturated [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being unsaturated and containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
•
with amino groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
•
with acylated amino groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
with the carbon atom of at least one of the carboxyl groups bound to nitrogen atoms [5]
•
•
having the sulfur atom of at least one of the thio groups bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having the sulfur atom of at least one of the thio groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring of the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton being further substituted by nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
containing thio groups and sulfur atoms, not being part of thio groups, bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
containing sulfur atoms of sulfone or sulfoxide groups bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
containing sulfur atoms of sulfo, esterified sulfo or halosulfonyl groups, bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
containing sulfur atoms of sulfonamide groups, bound to the carbon skeleton [5]
Thioaldehydes; Thioketones; Thioquinones; Oxides thereof [5]
•
Thioketones; Oxides thereof [5]
•
Thioquinones; Oxides thereof [5]
Thiocarboxylic acids [5]
•
Monothiocarboxylic acids [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of thiocarboxyl groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
to hydrogen atoms or to carbon atoms of an acyclic saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of a saturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of an acyclic unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of an unsaturated carbon skeleton containing rings [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of thiocarboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of thiocarboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
Dithiocarboxylic acids [5]
•
Esters of monothiocarboxylic acids [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of esterified thiocarboxyl groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of esterified thiocarboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of esterified thiocarboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having sulfur atoms of esterified thiocarboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
having sulfur atoms of esterified thiocarboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
having sulfur atoms of esterified thiocarboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
•
with amino groups bound to the same hydrocarbon radicals [5]
•
Esters of dithiocarboxylic acids [5]
•
Amides of thiocarboxylic acids [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of thiocarboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
to hydrogen atoms or to carbon atoms of a saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
to carbon atoms of an unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of thiocarboxamide groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having carbon atoms of thiocarboxamide groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
Compounds containing any of the groups  X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
 X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]•
•
•
Y being a hydrogen or a carbon atom [5]
•
•
•
Y being a hetero atom [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of thiocarboxamide groups further bound to another hetero atom [5]
•
Derivatives of thiocarboxylic acids, the doubly-bound oxygen atoms being replaced by nitrogen atoms, e.g. imino-thio ethers [5]
•
Thiocarboxylic acids having sulfur atoms of thiocarboxyl groups further doubly-bound to oxygen atoms [5]
Thiocarbonic acids; Halides, esters or anhydrides thereof [5]
•
Monothiocarbonic acids; Derivatives thereof [5]
•
•
Esters of monothiocarbonic acids [5]
•
•
•
having sulfur atoms of thiocarbonic groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
having sulfur atoms of thiocarbonic groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
having sulfur atoms of thiocarbonic groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
Dithiocarbonic acids; Derivatives thereof [5]
•
•
Esters of dithiocarbonic acids [5]
•
•
•
having sulfur atoms of dithiocarbonic groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
having sulfur atoms of dithiocarbonic groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
having sulfur atoms of dithiocarbonic groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
Derivatives of thiocyanic acid or of isothiocyanic acid [5]
•
Thiocyanates [5]
•
•
having sulfur atoms of thiocyanate groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
having sulfur atoms of thiocyanate groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having sulfur atoms of thiocyanate groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having sulfur atoms of thiocyanate groups bound to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
having sulfur atoms of thiocyanate groups bound to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
having sulfur atoms of thiocyanate groups bound to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
Isothiocyanates [5]
•
•
having isothiocyanate groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
of a saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having isothiocyanate groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having isothiocyanate groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
containing at least two isothiocyanate groups bound to the same carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
having isothiocyanate groups acylated [5]
Derivatives of thiocarbamic acids, i.e. compounds containing any of the groups  the nitrogen atom not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
the nitrogen atom not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
 the nitrogen atom not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
the nitrogen atom not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]•
Monothiocarbamic acids; Derivatives thereof [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of thiocarbamic groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of thiocarbamic groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of thiocarbamic groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of thiocarbamic groups being part of any of the groups  X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g., N-acyl-thiocarbamates [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g., N-acyl-thiocarbamates [5]
 X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g., N-acyl-thiocarbamates [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g., N-acyl-thiocarbamates [5]•
•
having nitrogen atoms of thiocarbamic groups bound to other hetero atoms [5]
•
Dithiocarbamic acids; Derivatives thereof [5]
•
•
Salts of dithiocarbamic acids [5]
•
•
Esters of dithiocarbamic acids [5]
•
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of dithiocarbamate groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of dithiocarbamate groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of dithiocarbamate groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
containing any of the groups  X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. N-acyldithiocarbamates [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. N-acyldithiocarbamates [5]
 X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. N-acyldithiocarbamates [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. N-acyldithiocarbamates [5]•
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of dithiocarbamate groups bound to other hetero atoms [5]
•
•
having sulfur atoms of dithiocarbamic groups bound to other sulfur atoms [5]
•
•
•
Thiuramsulfides; Thiurampolysulfides [5]
Thioureas, i.e. compounds containing any of the groups  the nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
the nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
 the nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
the nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]•
Thiourea [5]
•
Derivatives of thiourea [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of thiourea groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
•
of a saturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
of an unsaturated carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
•
the carbon skeleton containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of thiourea groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having nitrogen atoms of thiourea groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings of a carbon skeleton [5]
•
•
•
being further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
•
being further substituted by nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups [5]
•
•
•
being further substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
•
containing any of the groups  X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
 X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]•
•
•
Y being a hydrogen or a carbon atom, e.g. benzoylthioureas [5]
•
•
•
Y being a hetero atom, e.g. thiobiuret [5]
•
Isothioureas [5]
•
•
having sulfur atoms of isothiourea groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms [5]
•
•
having sulfur atoms of isothiourea groups bound to carbon atoms of rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
having sulfur atoms of isothiourea groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
containing any of the groups  X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
 X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]
X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom [5]•
having nitrogen atoms of thiourea or isothiourea groups further bound to other hetero atoms [5]
•
•
Sulfonylthioureas; Sulfonylisothioureas [5]
•
•
Sulfenylthioureas; Sulfenylisothioureas [5]
Derivatives of thiocarbonic acids containing functional groups covered by groups C07C 333/00 or C07C 335/00 in which at least one nitrogen atom of these functional groups is further bound to another nitrogen atom not being part of a nitro or nitroso group [5]
•
Compounds containing any of the groups  e.g. thiocarbazates [5]
e.g. thiocarbazates [5]
 e.g. thiocarbazates [5]
e.g. thiocarbazates [5]•
•
the other nitrogen atom being further doubly-bound to a carbon atom [5]
•
Compounds containing any of the groups  e.g. thiosemicarbazides [5]
e.g. thiosemicarbazides [5]
 e.g. thiosemicarbazides [5]
e.g. thiosemicarbazides [5]•
•
the other nitrogen atom being further doubly-bound to a carbon atom, e.g. thiosemicarbazones [5]
•
the two nitrogen atoms of the functional group being doubly-bound to each other [5]
Compounds containing carbon and sulfur and having functional groups not covered by groups C07C 301/00-C07C 337/00 [5]
•
Thiosulfates [5]
•
Thiosulfonates [5]
•
Compounds containing sulfur atoms only bound to two nitrogen atoms [5]
•
•
having at least one of the nitrogen atoms acylated [5]
•
Compounds containing sulfur atoms doubly-bound to nitrogen atoms [5]
•
Sulfonium compounds [5]
•
Compounds containing a carbon atom having four bonds to hetero atoms, with a double bond to one hetero atom and at least one bond to a sulfur atom further doubly-bound to oxygen atoms [5]
Compounds containing selenium [5]
•
having selenium atoms bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings [5]
Compounds containing tellurium [5]
Irradiation products of cholesterol or its derivatives; Vitamin D derivatives, 9,10-seco cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene or analogues obtained by chemical preparation without irradiation [5]
Derivatives of cyclohexane or of a cyclohexene, having a side-chain containing an acyclic unsaturated part of at least four carbon atoms, this part being directly attached to the cyclohexane or cyclohexene rings, e.g. vitamin A, beta-carotene, beta-ionone [5]
•
having side-chains containing only carbon and hydrogen atoms [5]
•
having side-chains substituted by halogen atoms [5]
•
having side-chains substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
by hydroxy groups [5]
•
•
by etherified hydroxy groups [5]
•
•
by esterified hydroxy groups [5]
•
having side-chains substituted by doubly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
not being part of —CHO groups [5]
•
having side-chains substituted by nitrogen atoms [5]
•
having side-chains substituted by carboxyl groups [5]
•
having side-chains substituted by sulfur atoms [5]
•
having side-chains substituted by six-membered non-aromatic rings, e.g. beta-carotene [5]
Compounds containing a five-membered ring having two side-chains in ortho position to each other, and having oxygen atoms directly attached to the ring in ortho position to one of the side-chains, one side-chain containing, not directly attached to the ring, a carbon atom having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, and the other side-chain having oxygen atoms attached in gamma-position to the ring, e.g. prostaglandins [5]
Preparation of peroxy compounds [5]
Peroxy compounds [5]
•
the —O—O— group being bound between a carbon atom, not further substituted by oxygen atoms, and hydrogen, i.e. hydroperoxides [5]
•
•
the carbon atom being acyclic [5]
•
•
•
Compounds containing rings other than six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
Compounds containing six-membered aromatic rings [5]
•
•
•
•
Cumene hydroperoxide [5]
•
•
•
•
with two alpha,alpha-dialkylmethyl-hydroperoxy groups bound to carbon atoms of the same six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
•
the carbon atom belonging to a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
the —O—O— group being bound between two carbon atoms not further substituted by oxygen atoms, i.e. peroxides [5]
•
•
at least one of the carbon atoms belonging to a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
•
the —O—O— group being bound to a carbon atom further substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms [5]
•
•
having two —O—O— groups bound to the carbon atom [5]
•
the —O—O— group being bound between a  C=O group and hydrogen, i.e. peroxy acids [5]
C=O group and hydrogen, i.e. peroxy acids [5]
 C=O group and hydrogen, i.e. peroxy acids [5]
C=O group and hydrogen, i.e. peroxy acids [5]•
•
Peracetic acid [5]
•
•
a  C=O group being bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
C=O group being bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
 C=O group being bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
C=O group being bound to a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring [5]•
•
a  C=O group being bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
C=O group being bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
 C=O group being bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]
C=O group being bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring [5]•
the —O—O— group being bound between two  C=O groups [5]
C=O groups [5]
 C=O groups [5]
C=O groups [5]•
•
both belonging to carboxylic acids [5]
•
•
•
Diacetyl peroxide [5]
•
the —O—O— group being bound between a  C=O group and a carbon atom, not further substituted by oxygen atoms, i.e. esters of peroxy acids [5]
C=O group and a carbon atom, not further substituted by oxygen atoms, i.e. esters of peroxy acids [5]
 C=O group and a carbon atom, not further substituted by oxygen atoms, i.e. esters of peroxy acids [5]
C=O group and a carbon atom, not further substituted by oxygen atoms, i.e. esters of peroxy acids [5]•
containing nitrogen atoms [5]
•
containing sulfur atoms [5]
•
•
with sulfur atoms directly bound to the —O—O— groups, e.g. persulfonic acids [5]
